Abstract
This paper addresses the joint entropy maximization algorithm constrained by the variable leaky factor (JEM-VL) aiming at mitigating the feedback filter (FBF) mismatch effects characterizing the operation of the decision feedback equalizer which, at the start of adaptation, swaps positions of feedforward and feedback filters so that the latter acts as a linear all-pole whitener of the received signal. The FBF mismatch is a result of disparity between the FBF setup achieved in the blind mode by observing channel outputs and an excepted FBF setup in the tracking mode which is driven by detected data symbols. Depending on the given signal complexity and inter-symbol interference severity, the FBF filter mismatch is typically manifested by the equalizer convergence instability or even the catastrophic error propagation effects arising at the time of the equalizer structure-criterion switching from the blind to the tracking operation mode. The constraint of superfluous coefficients of the FBF filter by means of the JEM-VL algorithm eliminates the equalizer convergence instability at the time of its switching and, consequently, increases equalization successfulness. The efficiency of the JEM-VL algorithm is verified by simulations using the 64-QAM signal.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The hypothesis of correctness of previous detected symbols is commonly use in the DFE analysis.
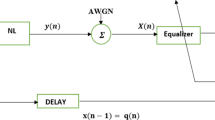
Although the outputs z n are not noise free, the noiseless system model is assumed in order to simplify the derivation of the JEM algorithm. In simulations presented in the paper we have used more realistic noisy channels.
References
Treichler, J. R., Larimore, M. G., & Harp, J. C. (1998). Practical blind demodulators for high-order QAM signals. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(10), 1907–1926.
Ghosh, M. (1998). Blind decision feedback equalization for terrestrial television receivers. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(10), 1907–1926.
Savaux, V., Bader, F., & Palicot, J. (2016). OFDM/OQAM blind equalization using CNA approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 64(9), 2324–2333. doi:10.1109/TSP.2016.2519000.
Proakis, J. G. (1995). Digital communications (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Papadias, C.B., & Paulraj, A. (1995). Decision-feedback equalization and identification of linear channels using blind algorithms of the bussgang type. In Proceedings of Twenty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (pp. 335–340). Pacific Grove, CA.
Rocha, C.A.F., Macchi, O., & Romano, J.M. (1994). An adaptive nonlinear IIR filter foe self-learning equalization. In Proceedings of International Telecommunications Symposium—IT94 (pp. 184–190). Rio de Janeiro.
Labat, J., Macchi, O., & Laot, C. (1998). Adaptive decision feedback equalization: Can you skip the training period? IEEE Transactions on Communications, 46(7), 921–930.
Krstić, V. R., & Dukić, M. L. (2009). Blind DFE with maximum-entropy feedback. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 16(1), 26–29.
Goupil, A., & Palicot, J. (2010). An efficient blind decision feedback equalizer. IEEE Communications Letters, 14(5), 462–464.
Szczecinski, L. L., & Gei, A. (2002). Blind decision feedback equalisers, how to avoid degenerative solutions. Signal Processing, 82(11), 1675–1693.
Filha, J. M., Mirinda, M. D., & Silva, T. M. (2011). An efficient algorithm for decision feedback blind equalization. Revista Telecomunicacoes, 13(02), 79–86.
Cioffi, J. M., Dudevior, G. P., Eyuboglu, M. V., & Forney, G. D. (1995). MMSE decision-feedback equalizers and coding-Part I: Equalization results. IEEE Transactions on. Communication, 43(10), 2582–2594.
Al-Dhahir, N., & Cioffi, J. C. (1995). MMSE decision-feedback equalizers: Finite-length results. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 42(4), 961–975.
Casas, R.A., Johnson, Jr., C.R., Harp, J., & Caffee, S. (1999). On initialization strategies for blind adaptive DFEs. In Proceedings of 1st IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (pp. 792–796). New Orleans, LA.
Chang W.C., & Chuang, S.H. (2014). A zero-pole whitening filter in adaptive blind decision feedback equalizers. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, Cybernetics, Oct 5–8, 2014 (pp. 3259–3264), San Diego, CA.
Belfiore, C. A., & Park, J. H. (1979). Decision feedback equalization. Proceedings of the IEEE, 67(8), 1143–1156.
Krstić, V. R., & Dukić, M. L. (2014). Decision feedback blind equalizer with tap-leaky whitening for stable structure-criterion switching. International Journal of Digital Multimedia Broadcasting. doi:10.1155/2014/987039.
Krstić, V. R. (2016). Entropy-based stochastic gradient algorithm with adaptive neuron slope for all-pole filtering. Electronic Letters, the Institute of Engineering and Technologies, 52(5), 397–399. doi:10.1049/el.2015.3052.
Rey, G. J., Bitmead, R. R., & Johnson, C. R., Jr. (1991). The dynamics of bursting in simple adaptive feedback systems with leakage. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 38(5), 476–488.
Ljung, L., & Sjoberg, J.A. (1992). Comment on “leakage” in adaptive algorithms. Department of Electrical Engineering. Linkoping University. http://www.diva-portal.org.
Kamenetsky, M., & Widrow, B. (2004). A variable leaky LMS adaptive algorithm. Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Asilomar Conference on Signal, Systems and Computers, 1, 125–126.
Godard, D. N. (1980). Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 18(11), 1867–1875.
Bell, A. J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 7(6), 1129–1159.
Kim, Y. H., & Shamsunder, H. S. (1998). Adaptive algorithms for channel equalization with soft decision feedback. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 16(9), 1660–1669.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia; the project of technological development TR 32037, 2011–2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krstić, V.R., Stevanović, A.M. & Odadžić, B.L. A Variable Leaky Entropy-Based Whitening Algorithm for Blind Decision Feedback Equalization. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 931–946 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3806-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3806-7