Abstract
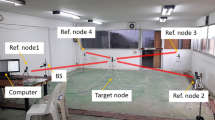
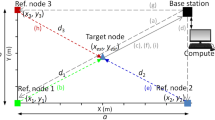
Nowadays location estimation using WiFi networks in indoor environments has become a hot research topic. Challenging methods without calibration or hardware integration are essentially required for cost-effective and practical solutions. The Received Signal Strength Indicator-based localization methods offer low cost solutions. However, their propagation models are difficult to characterize due to environmental factors in indoor and multiple parameters. There are a number of works over estimation of location and pathloss exponent presented in the literature. This paper introduces a new method shortly named as ERLAK in order to estimate the K constant term using log normal channel model in addition to the location of mobile station in indoor environment. The ERLAK method has been consistently compared to the well-known Least Square and Weighted Least Square methods. It achieves the least errors in distance estimations compared to the classical methods on especially critical measurement points. It remarkably accomplishes less than 5 m mean errors for distance estimation results particularly when signal is received from all of the access points.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, N., Rashidzadeh, R., & Ahmadi, M. (2010). Robust indoor positioning using differential Wi-Fi access points. IEEE Transactions on Comsumer Electronics, 56(3), 1860–1867.
Tarrio, P., Bernardos, A. M., & Casar, J. R. (2011). Weighed least squares techniques for improved received signal strength based localization. Sensors, 11(9), 8569–8592.
Cheng, Y. C., Chawathe, Y., LaMarca A., Krumm, J. (2005). “Accuracy characterization for metropolitan-scale Wi-Fi localization,” In Proceedings The Third International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (pp. 233–245). Seattle, Washington, USA.
Mazuelas, S., et al. (2009). Robust indoor positioning provided by real-time RSSI values in unmodified WLAN networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 3(5), 821–831.
Tarrio, P., Bernardos, A. M., Besada, J. A., Casar, J. R. (2008). “A new positioning technique for RSS-based localization based on a weighted least squares estimator,” In Proceedings IEEE International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems( pp. 633–637).
Guvenc, I., & Chong, C. C. (2009). A survey on TOA based wireless localization and NLOS mitigation techniques. IEEE Communication Surveys and Tutorials, 11(3), 107–124.
Dawes, B., & Chin, K. W. (2011). A comparison of deterministic and probabilistic methods for indoor localization. The Journal of Systems and Software, 84(3), 442–451.
Koo, J., & Cha, H. (2011). Localizing WiFi access points using signal strength. IEEE Communications Letters, 15(2), 187–189.
Cheng, Y. Y., & Lin, Y. Y. (2009). A new received signal strength based location estimation scheme for wireless sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 55(3), 1295–1299.
Bandirmali, N. & Torlak, M. (2015). “BLUE-based real-time location estimation using indoor RSSI measurements,” 23th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference. (pp. 1757–1760).
Kay, S. M. (1998). Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandirmali, N., Torlak, M. ERLAK: On the Cooperative Estimation of the Real-Time RSSI Based Location and K Constant Term. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 3923–3932 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4032-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4032-7