Abstract
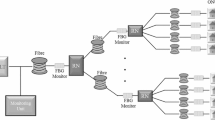
At present Optical fibre cable is used as media to design long/short network and it supports high bandwidth in Gigabits per second speed. Earlier OFC is used to connect the long distance places and called Optical transport network and presently used even in local/Access network called Optical Access network. In present environment data to be transmitted is so high due to growth in internet. Successful transmission of such a huge bandwidth is big challenging job for long distance network designer. This paper aims to explain the design and planning of a Passive Optical Network (PON) based wireless fibre to the Home architecture. The purpose is to show the behaviour of links of optical fibre when the signal goes through all the elements such as optical fibre, splitters, multiplexers and the goal is to find a good quality of signal in all receivers. The final goal pursued with this paper is to evaluate the performance of the whole system. The steady increase in the demand for broadband services and the consequent increase in the volume of generated traffic in our communication networks have motivated the need to implement next generation access networks in our territories. To develop multimedia telecommunication networks as an infrastructure, it is necessary to install highly reliable optical fibre cable network architecture like PON based fibre to the Home Network. In a point-to-multipoint architecture, PON is an appropriate architecture to provide high bandwidth for many customers. For any Internet Service Providers, the biggest challenge is to design an efficient access network like PON to ensure the QoS and maintenance of that network that includes Identification and Rectification of cable faults in that access network within short time thus enabling efficiency and reputation of ISPs. So this work deals with design and analysis of access network like PON and also the maintenance of the access network which includes Identification and Rectification of optical fibre cable faults in PON based fibre to the Home Network. The quality of this fibre infrastructure/network is monitored by Optical Time Domain Reflectometer for observing losses and fibre breaks and its efficiency is improved by Centralized Fault Detection System. The hardware implementation of the access network like PON based wireless fibre to the Home Network and the testing instruments are also considered for fault identification.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksic, S., & Lovric, A. (2010). Power efficiency of extended reach 10G-EPON and TDM/WDM PON, Optical Fiber Communication (OFC),pp. 1, 21–25, San Diego.
Malik, D., Dung, S., & Walia, R. (2012). Quality of service in two-stages EPON for fiber-to- the-home. International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE), 2(2), 95–102.
Effenberger, F. (2006). Next-generation PON-part III: System specifications for XP-PON. IEEE Communication Magazine, 47(11), 58–64.
Lee, C. H., Sorin, W. V., & Kim, B. Y. (2006). Fiber to the home using a PON infrastructure. IEEE Journal of Light wave Technology, 24(12), 4568–4583.
ShamimAhsan, Md, Man SeopLeeShahNewaz, S. H., & Syed Asif, Md. (2011). Migration to the next generation optical access networks using hybrid WDM/TDM-PON. Journal Of Networks, 6(1), 75–85.
Sitaram, A. M., Swamy, K. M., & Ramakrishna, A. (2012). Gigabit passive optical networks (GPON) the ultimate solution for large bandwidth. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE), 1(6), 55–65.
Ehrhardt, A., Escher, F., Schürer, L., Foisel, H. M., Templin, A., Adamy, M., et al. (2011). PON measurements and monitoring solutions for FTTH networks during deployment and operation. IEEE Transactions on optical communication, 5, 103–116.
Larrabeiti, D. (2011). Towards an energy efficient 10 Gb/s optical ethernet: Performance analysis and viability. Journal of Optical Switching and Networking, 8(3), 131–138.
Yadav, Rajesh. (2012). Passive-optical-network-(PON-) based converged access network. Journal of Optical Communication Network, 4(8), 25–35. B124.
Reyes, R. R., Zhao, R., & Machuca, C. M. (2010). Dynamic migration planning towards FTTH, 14th Int’l. In Telecommunication Network Strategy and Planning Symposium, (Vol. 3).
Rad, M. M., Fathallah, H. A., Rusch, L. A., & Maier, M. (2011). Passive optical network monitoring: Challenges and requirements. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2, 102–108.
Moran, J. (2003). Moving beyond the standard: Creating additional bandwidth through extending DOCSIS 2.0. Motorola Broadband Communication Sector, White paper.
Yan, Y., & Wong, S.W. (2010). Energy management mechanism for ethernet passive optical networks (EPONs). In IEEE International Conference on Communication (ICC), (Vol. 1, pp. 23–27).
Wuilpart, M., Yuksel, K., & Megret, P. (2007). Optical frequency domain reflectometry: roadmap for high-resolution distributed measurements. IEEE Transaction on Neural Networks, 8(19), 322–325.
Singh, Sandeep, Jaiswal, Arvind Kumar, & Kumar, Mukesh. (2012). Transmission of voice, video and data in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks using OFDM. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 2(5), 55–60.
Mary Praveena, S., & Vennila, I. L. A. (2016). An effective security based fusion using principal component analysis. Wireless Personal Communication, 86(2), 887–899. doi:10.1007/s11277-015-2960-7.
Effenberger, Frank, et al. (2007). An introduction to PON technologies. IEEE Communications Magazine, 5, 517–525.
Ab-Rahman, M. S., et al. (2012). New optical splitter design for application in fibre-to-the home passive optical network using virtual lab platform. Journal of Computer Science: Science Publications, 12, 846–871.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. A. Vetrivel, Senior Manager, BSNL, Chennai for his constant guiding and support. This work was carried out at BSNL Telecommunication Research Centre Laboratory, Chennai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mary Praveena, S., Vennila, I. & Vaishnavi, R. Investigation of Passive Optical Network Based on QoS Issues in Wireless Fibre to the Home Architecture for Fault Identification and Detection. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 961–976 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4213-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4213-4