Abstract
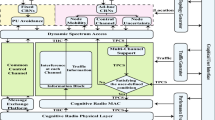
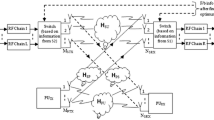
A flexible transmit power selection concept for underlay cognitive users is proposed in this paper. We have employed an opportunistic, sensing based spectrum sharing method. Besides the power constraint to avoid interference at PU, the transmit power constraints of secondary user is also considered. Received Signal Strength Indicator based carrier selection method has been adopted. To resolve hidden terminal problem, twin scan concept is used at both ends (secondary transmitter and receiver) with same carrier frequency. Secondary transmitter selects suitable carrier frequency to initiate communication with the minimum power level as defined by the proposed algorithm. If received signal strength at the corresponding secondary receiver is below the predefined required receiver threshold, then power level is stepped up automatically. To maximize secondary user channel capacity, we have considered flexible power selection strategy as per channel state information. If the cognitive receiver is unable to recover the received information, even with the peak transmit power, it will again perform the frequency scanning operation. This is repeated till the best result is achieved. A power control circuit is designed to check the power selection concept.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitola, J. (2000). Cognitive radio—an integrated agent architecture for software defined radio. PhD Dissertation, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden.
Zhao, Q., & Sadler, B. M. (2007). A survey of dynamic spectrum access. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 24(3), 79–89.
Le, L. B., & Hossain, E. (2008). Resource allocation for spectrum underlay in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(12), 5306–5315.
Kang, X., Liang, Y. C., Garg, H. K., & Zhang, L. (2009). Sensing-based spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(8), 4649–4654.
Badawy, A., & Khattab, T. (2013, October). A hybrid spectrum sensing technique with multiple antenna based on GLRT. In Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), 2013 IEEE 9th International Conference on (pp. 736–742). Lyon, France: IEEE. doi:10.1109/WiMOB.2013.6673438.
Yongjun, X., & Xiaohui, Z. (2013). Optimal power allocation for multiuser underlay cognitive radio networks under QoS and interference temperature constraints. China Communications, 10(10), 91–100.
Liu, Z., Wang, P., Xia, Y., Yang, H., & Guan, X. (2016). Chance-constraint optimization of power control in cognitive radio networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 9(1), 245–253.
Yao, H., Zhou, Z., Liu, H., & Zhang, L. (2009, June). Optimal power allocation in joint spectrum underlay and overlay cognitive radio networks. In Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Communications, 2009 (CROWNCOM’09) 4th International Conference on (pp. 1–5) Germany: IEEE, Courtyard Hannover Maschsee. doi:10.1109/CROWNCOM.2009.5189342.
Wang, Y., Ren, P., Du, Q., & Sun, L. (2015). Optimal power allocation for underlay-based cognitive radio networks with primary user’s statistical delay QoS provisioning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(12), 6896–6910.
Gu, J., & Jeon, W. S. (2013). Optimal power allocation in an “off” spectrum sensing interval for cognitive radio. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(10), 1908–1911.
Benaya, A. M., Shokair, M., El-Rabaie, E. S., & Elkordy, M. F. (2015). Optimal power allocation for sensing-based spectrum sharing in MIMO cognitive relay networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(4), 2695–2707.
Chen, Y., Lei, Q., & Yuan, X. (2014). Resource allocation based on dynamic hybrid overlay/underlay for heterogeneous services of cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 79(3), 1647–1664.
Oh, J., & Choi, W. (2010, September). A hybrid cognitive radio system: A combination of underlay and overlay approaches. In Vehicular Technology Conference Fall (VTC 2010-Fall), 2010 IEEE 72nd (pp. 1–5). Ottawa, Ontario, Canada: IEEE. doi: 10.1109/VETECF.2010.5594302.
Qiu, T., Xu, W., Song, T., He, Z., & Tian, B. (2011, May). Energy-efficient transmission for hybrid spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks. In Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), 2011 IEEE 73rd (pp. 1–5). Budapest, Hungary: IEEE. doi: 10.1109/VETECS.2011.5956224.
Lan, P., Sun, F., Chen, L., Xue, P., & Hou, J. (2013). Power allocation and relay selection for cognitive relay networks with primary QoS constraint. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2(6), 583–586.
Lee, C. H., & Haenggi, M. (2012). Interference and outage in Poisson cognitive networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(4), 1392–1401.
Xing, Y., Mathur, C. N., Haleem, M. A., Chandramouli, R., & Subbalakshmi, K. P. (2007). Dynamic spectrum access with QoS and interference temperature constraints. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(4), 423–433.
Kang, X., Zhang, R., Liang, Y. C., & Garg, H. K. (2011). Optimal power allocation strategies for fading cognitive radio channels with primary user outage constraint. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 29(2), 374–383.
Bepari, D., & Mitra, D. (2014, February). GA based optimal power allocation for underlay cognitive radio networks. In Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), 2014 International Conference on (pp. 1–6). Coimbatore, India: IEEE. doi:10.1109/ECS.2014.6892554.
Rosas, A. A., Shokair, M., & El_dolil, S. A. (2015). Proposed optimization technique for maximization of throughput under using different multicarrier systems in cognitive radio networks. In The Proceedings of Second International Conference on Electronics Engineering, Clean Energy and Green Computing (EEECEGC) (pp. 25–33). Konya, Turkey: Mevlana University, ISBN: 978-1-941968-12-3©2015 SDIWC.
Hou, L., Yeung, K. H., & Wong, K. Y. (2015). SEER: Spectrum-and energy-efficient routing protocol for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. Wireless Networks, 21(7), 2357–2368.
Lan, P., Chen, L., Zhang, G., & Sun, F. (2015). Optimal resource allocation for cognitive radio networks with primary user outage constraint. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015(1), 239.
Kang, X., Liang, Y. C., Nallanathan, A., Garg, H. K., & Zhang, R. (2009). Optimal power allocation for fading channels in cognitive radio networks: Ergodic capacity and outage capacity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(2), 940–950.
Bala, I., Bhamrah, M. S., & Singh, G. (2015). Capacity in fading environment based on soft sensing information under spectrum sharing constraints. Wireless Networks, 23(2), 1–13.
Ozcan, G., & Gursoy, M. C. (2015). Optimal power control for underlay cognitive radio systems with arbitrary input distributions. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(8), 4219–4233.
Quan, Z., Cui, S., & Sayed, A. H. (2008). Optimal linear cooperation for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2(1), 28–40.
Liu, X., Jia, M., & Tan, X. (2013). Threshold optimization of cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. Radio Science, 48(1), 23–32.
Zhao, Y., Li, S., Zhao, N., & Wu, Z. (2010). A novel energy detection algorithm for spectrum sensing in cognitive radio. Information Technology Journal, 9(8), 1659–1664.
Atapattu, S., Tellambura, C., & Jiang, H. (2011, June). Spectrum sensing via energy detector in low SNR. In Communications (ICC), 2011 IEEE International Conference on (pp. 1–5). Japan: IEEE, Kyoto International Conference Centre. doi: 10.1109/icc.2011.5963316.
Zhang, W., Mallik, R. K., & Letaief, K. B. (2009). Optimization of cooperative spectrum sensing with energy detection in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(12), 5761–5766.
Lee, W. C. (2010). Mobile communications design fundamentals (Vol. 25). Hoboken: Wiley.
Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC. (2003). 3.3V/5V Programmable PLL Synthesized Clock Generator, NBC12429 (2003–Rev. 2) NBC12429/D, 1–2.
Philips Semiconductors, SA636. (1997). Low voltage high performance mixer FM IF system with high speed RSSI, IC17 Data Handbook, Nov 07.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatterjee, S., Banerjee, P. & Nasipuri, M. Optimized Flexible Power Selection for Opportunistic Underlay Cognitive Radio Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 1193–1213 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4231-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4231-2