Abstract
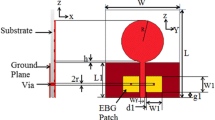
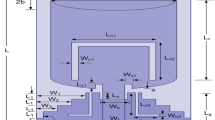
Band notched circular monopole antennas for ultra-wide band applications are proposed in this paper. The proposed antennas in this paper can reject worldwide interoperability for microwave access WiMAX band (3.3–3.8 GHz) and wireless local area network WLAN band (5–6 GHz). Antennas utilises mushroom-type electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structures and I-slot embedded edge located via (ELV) EBG structures to achieve band-notched designs. The advantages of band notched designs using EBG structures like notch-frequency tuning, dual-notch antenna designs and stable radiation pattern are also verified. Various antenna designs with slot in EBG structures, variations in placement of EBG structures, number of EBG structures and ELV type EBG structures are simulated. About 30% reduction in size of EBG structures is obtained if conventional mushroom type EBG is replaced by proposed I-slot embedded ELV-EBG structure. Fabricated and measured results are in good agreement with simulated ones.











































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balanis, C. A. (2012). Antenna theory analysis and design. New York: Wiley.
Lee, K. F., & Luk, K. M. (2011). Microstrip patch antennas. London: Imperial College Press.
Ghavami, M., Michael, L. B., & Kohno, R. (2007). Ultra-wideband signals and systems in communication engineering. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Cho, Y. J., Kim, K. H., Choi, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Park, S. O. (2006). A miniature UWB planar monopole antenna with 5-GHz band-rejection filter and the time-domain characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54, 1453–1460.
Chu, Q. X., & Yang, Y. Y. (2008). A compact ultra-wideband antenna with 3.4/5.5 GHz dual band-notched characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56, 3637–3644.
Dong, Y. D., Hong, W., Kuai, Z. Q., & Chen, J. X. (2009). Analysis of planar ultra-wideband antennas with on-ground slot band-notched structures. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57, 1886–1893.
Ryu, K. S., & Kishk, A. A. (2009). UWB antenna with single or dual band notches for lower WLAN band and upper WLAN band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57, 3942–3950.
Abbosh, A. M., & Bialkowski, M. E. (2009). Design of UWB planar band-notched antenna using parasitic elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57, 796–799.
Kim, K. H., & Park, S. O. (2006). Analysis of the small band-rejected antenna with the parasitic strip for UWB. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54, 1688–1692.
Lui, W. J., Cheng, C. H., Cheng, Y., & Zhu, H. (2005). Frequency notched ultra-wideband microstrip slot antenna with fractal tuning stub. Electronics Letters, 41, 294–296.
Qu, S. W., Li, J. L., & Xue, Q. (2006). A band-notched ultra-wideband printed monopole antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 5, 495–498.
Pancera, E., Modotto, D., Locatelli, A., Pigozzo, F. M., & Angelis, C. D. (2007). Novel design of UWB antenna with band-notch capability. In Proc. Eur. Conf. Wireless Technology (pp. 48–50).
Kamgaing, T. (2003). High-impedance electromagnetic surfaces for mitigation of switching noise in high speed circuits. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Maryland, USA.
Sivenpiper, D. (1999). High-impedance electromagnetic surface. Ph.D Thesis. Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, CA.
Yang, F., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2003). Reflection phase characterizations of the EBG ground plane for low profile wire antenna applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 51, 2691–2703.
Yazdi, M., & Komjani, N. (2011). Design of a band-notched UWB monopole antenna by means of an EBG structure. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 10, 170–173.
Peng, L., & Ruan, C. (2011). UWB band-notched monopole antenna design using electromagnetic-bandgap structures. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59, 1074–1081.
Liu, L., Cheung, S. W., & Yuk, T. I. (2015). Compact MIMO antenna for portable UWB applications with band-notched characteristic. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 63, 1917–1924.
Li, Q., & Feresidis, A.-P. (2015). Miniaturized double-layer EBG structures for broadband mutual coupling reduction between UWB monopoles. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 63, 1168–1171.
Majid, H. A., Rahim, M. K. A., Hamid, M. R., Yusoff, M. F. M., Murad, N. A., Samsuri, N. A., et al. (2015). Wideband antenna with reconfigurable band notched using EBG structure. Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, 54, 7–13.
Barth, S., & Iyer, A. K. (2016). A miniaturized uniplanar metamaterial-based EBG for parallel-plate mode suppression. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 64, 1176–1185.
Sarkar, D., Sarkar, K., & Saurav, K. (2014). A compact microstrip-fed triple band-notched UWB monopole antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 396–399.
Zhu, F., Gao, S., Ho, A. T. S., Al Hameed, A., See, C. H., Brown, T. W. C., et al. (2013). Multiple band-notched UWB antenna with band-rejected elements integrated in the feed line. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 61, 3952–3960.
Foudazi, A., Hassani, H. R., & Ali Nezhad, S. M. (2012). Small UWB planar monopole antenna with added GPS/GSM/WLAN bands. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60, 2987–2992.
Liang, J., Chiau, C. C., Chen, X., & Parini, C. G. (2004). Printed circular disc monopole antenna for ultra-wideband applications. Electronics Letters, 40, 1246–1248.
Zheng, Q. R., Fu, Y., & Yuan, N. C. (2008). A novel compact spiral electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) structure. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56, 1656–1660.
Boutayeb, H., & Denidni, T. A. (2007). Gain enhancement of a microstrip patch antenna using a cylindrical electromagnetic crystal substrate. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 55, 3140–3145.
Yang, X., Sun, Q., Jing, Y., Cheng, Q., Zhon, X., Kong, H., et al. (2011). Increasing the bandwidth of microstrip patch antenna by loading compact artificial magneto dielectrics. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 59, 373–378.
Luukkonen, O., Simovski, C., Granet, G., Goussetis, G., Lioubtchenko, D., Rai, A., et al. (2008). Simple and accurate analytical model of planar grids and high impedance surface comprising metal strips or patches. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56, 1624–1632.
Jaglan, N., & Gupta, S. D. (2015). Design and analysis of performance enhanced microstrip patch antenna with EBG substrate. International Journal of Microwave and Optical Technology, 10, 79–88.
Yang, F., & Rahmat, Y. (2009). Electromagnetic band gap structures in antenna engineering. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ansoft’sHFSS [Online]. http://www.ansoft.com.
Rajo-Iglesias, E., Inclan-Sanchez, L., Vazquez-Roy, J. L., & Garcia-Muoz, E. (2007). Size reduction of mushroom-type EBG surfaces by using edge-located vias. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 17, 670–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaglan, N., Kanaujia, B.K., Gupta, S.D. et al. Design and Development of an Efficient EBG Structures Based Band Notched UWB Circular Monopole Antenna. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 5757–5783 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4446-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4446-2