Abstract
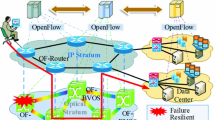
The Internet generation infrastructure is growing and moving towards a consistency model of high-speed nodes interconnected by optical core networks. Therefore, the interaction between IP and optical network layers, specifically, the routing and signalling aspects, are maturing and they can lead to enhance the services and network performance. At the same time, a consensus has emerged in the industry on utilizing IP-based protocols for the optical control plane. This paper defines a new technique for IP over Optical networks (interacting between bottom layers), considering both the IP-based control plane for optical networks as well as IP-optical network interactions (together referred to as “IP over optical networks”). In this paper, a new technique is proposed that reduces recovery time by making an interoperation between the data link layer (layer 2) with the network layer (layer 3). The proposed technique enables layer 2 with layer 3 to make a hybrid mechanism that improves the recovery time in the network through two cases (1st-Detection and 2nd-Rerouting). The technique involves detecting failure in less time through layer 2 and rerouting traffic through an alternative path between source and destination by using a new algorithm in layer 3 to deliver data packets without the need to wait for the routing protocol to update the network topology and compute the routing table. In case of the network recovery, layer 2 has demonstrated its capability to detect failure extremely quickly shown through the immediate detection of the loss of signals for the link or node. The recovery mechanism, i.e., the rerouting mechanism, which leads the node, switches the data packets through an adjacent node to its destination via the life node. The latter is created by the proposed mechanism before the occurrence of the failure. The aim of this mechanism is to avoid loss of packets, improve QoS and improve recovery time as we have shown in the results shown below.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Request for Comments (Informational) RFC 1631, Internet Engineering Task Force, May 1994.
RFC 1812, IETF, June 1995.
RFC 2461, December 2006.
Goldberg, A., & Radzik, T. (1993). A heuristic improvement of the Bellman–Ford algorithm. Applied Mathematics Letters, 6(3), 3–6.
Hawkinson, J., & Bates, T. (1996). RFC 1930: Guidelines for creation, selection, and registration of an autonomous system (AS). http://ftp.apnic.net/ietf/rfc/rfc1000/rfc1930.txt.
Cormen, T. H. (2001). Introduction to algorithms. Cambridge: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Black, U. (2000). IP routing protocols: RIP, OSPF, BGP, PNNI and cisco routing protocols. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall PTR.
Zeng, X., Bagrodia, R., & Gerla, M. (1998). Glomosim: A library for parallel simulation of large-scale wireless networks. In Proceedings of twelfth workshop on parallel and distributed simulation, 1998. PADS 98. (pp 154–161). IEEE.
Dube, R., Rais, C., Wang, K., & Tripathi, S. (1997). Signal stability-based adaptive routing (ssa) for ad hoc mobile networks. In Personal communications, IEEE (Vol 4, pp. 36–45). IEEE.
Toh, C. (1996). A novel distributed routing protocol to support ad-hoc mobile computing. In Conference on computers and communications, 1996., Conference Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE Fifteenth Annual International Phoenix (pp. 480–486). IEEE.
Lee, S., & Gerla, M. (2000). Aodv-br: Backup routing in ad hoc networks. In Wireless communications and networking conference, IEEE (Vol. 3, pp. 1311–1316).
Abramovich, Y. A., Aliprantis, C. D., & Burkinshaw, O. (1995). Another characterization of the invariant subspace problem. In Operator theory in function spaces and banach lattices. The A.C. Zaanen Anniversary Volume, operator theory: advances and applications (Vol. 75, pp. 15–31). Birkhäuser Verlag.
Shahbaz, S., Gholamreza, G., Rabiee, H., & Ghanbari, M. (2006). A distributed intelligent ad-hoc network. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (pp. 4308–2006).
Mérindol, P., Pansiot, J.J., & Cateloin, S. (2008). Improving load balancing with multipath routing (pp. 1–8).
Aupetit, B. (1991). A primer on spectral theory. New York: Springer.
Pannell, D., & Chou, H. Y. (2016). Wake-on-frame for frame processing devices, January 5. US Patent 9,229,518.
Perlman, R. (1991). A Comparison between two routing protocols: OSPF and IS-IS. Network Communication, 5(5), 18–24.
Song, Xiaoheng., & Qin, Xia. (2016). Ethernet virtualisation interconnection networks having a hub-spoke structure, January 7. US Patent 20,160,006,657.
Saste, P., & Martis, J. (2016). Converged OAM. In Proceedings of the second international conference on computer and communication technologies (pp. 437–444). Springer.
Sterle, J., Sedlar, U., Rugelj, M., Kos, A., & Volk, M. (2016). Application-driven OAM framework for heterogeneous IOT environments. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 12, 5649291.
Broch, J., Maltz, D., Johnson, D., Hu, Y., & Jetcheva, J. (1998). A performance comparison of multihop wireless ad hoc network routing protocols. In Proceeding of international conference mobile computing and networking (MobiCom) ACM (pp. 85–97).
Simonič, A. (1990) Grupe operatorjev s pozitivnim spektrom. Master’s thesis, Univerza v Ljubljani, FNT, Oddelek za Matematiko.
Bryant, S., Filsfils, C., Previdi, S., & Shand, M. (2005). Ip fast reroute using tunnels. Work in Progress in IETF.
Baccelli, E., Jacquet, P., Nguyen, D., & Clausen, T. (2009). OSPF multipoint relay (MPR) extension for ad hoc networks. Internet Engineering Task Force, Request For Comments (Experimental) RFC 5449.
Ljubič, J. I., & Macaev, V. I. (1965). On operators with a separable spectrum. American Mathematical Society Translations, 47(2), 89–129.
Eriksson, J., Faloutsos, M., & Krishnamurthy, S. V. (2007). Dart: Dynamic address routing for scalable ad hoc and mesh networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 15(1), 119–132.
Rudin, W. (1973). Functional Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Conway, J. B. (1990). A course in functional analysis (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) A. Malis, Ed. Request for Comments: 7771 L. Andersson Updates: 6870 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Category: Standards Track H. van Helvoort, January 2016.
Law, D., Dove, D., D’Ambrosia, J., Hajduczenia, M., Laubach, M., & Carlson, S. (2013). Evolution of ethernet standards in the ieee 802.3 working group. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(8), 88–96.
Cavendish, D., Murakami, K., Yun, S.-H., Matsuda, O., & Nishihara, M. (2002). New transport services for next-generation SONET/SDH systems. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(5), 80–87.
Kramer, G., & Pesavento, G. (2002). Ethernet passive optical network (epon): Building a next-generation optical access network. IEEE Communications magazine, 40(2), 66–73.
Wiley, W. L., & Bugenhagen, M. K. (2016). System and method for restricting access to network performance information. January 19, US Patent 9,241,271.
Meilik, I., & Stern, Y. (2015). Ethernet operation and maintenance (OAM) with flexible forwarding. March 17, US Patent 8,982,710.
Moy, J. (1998). OSPF: Anatomy of an Internet routing protocol. Boston: Addison-Wesley Professional.
Brandes, U. (2001). A faster algorithm for betweenness centrality. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 25(2), 163–177.
Owada, Y., Maeno, T., Imai, H., & Mase, K. (2007). Olsrv2 implementation and performance evaluation with link layer feedback. In Proceedings of the 2007 international conference on Wireless communications and mobile computing (pp. 67–72). ACM.
Rabbat, R., & Siu, K.-Y. (2001). Restoration methods for traffic engineered networks for loop-free routing guarantees. In Proceeding of IEEE International Conference Communications (ICC’01) (Vol. 5, pp. 1566–1570). Helsinki.
Knuth, D. E. (1984). The TeXbook. Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Moy, J. (1995). Link-state routing. In M. E. Steenstrup (Ed.), Routing in communications networks (Chapt. 5, pp. 135–157). Prentice Hall.
Malkin, G. (1998). RIP Version 2 - Carrying Additional Information. Internet Draft, draft-ietf-ripv2-protocol-v2- 05.txt, (work in progress).
Atlas, A., & Zinin, A. (2008). Basic specification for ip fast-reroute: Loop-free alternates. Internet Engineering Task Force, Work in Progress, draft-ietf-rtgwg-ipfrr-spec-base-03.txt.
Han, W., Tellez, L. A., Niu, J., Medina, S., Ferreira, T. L., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Striatal dopamine links gastrointestinal rerouting to altered sweet appetite. Cell Metabolism, 23(1), 103–112.
Sueviriyapan, N., Suriyapraphadilok, U., Siemanond, K., Quaglia, A., & Gani, R. (2016). Industrial wastewater treatment network based on recycling and rerouting strategies for retrofit design schemes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 111, 231–252.
Zeng, K., Ren, K., & Lou, W. (2005). Geographic on-demand disjoint multipath routing in wireless ad hoc networks. In Military Communications Conference, MILCOM (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Abujassar, R. S. (2016). Mitigation fault of node mobility for the manet networks by constructing a backup path with loop free: enhance the recovery mechanism for pro-active manet protocol. Wireless Networks, 22(1), 119–133.
Iannaccone, G., Chuah, C. N., Bhattacharyya, S., & Diot, C. (2004). Feasibility of IP restoration in a tier-1 backbone. IEEE Network 18.
Zhong, Z., Nelakuditi, Z., Yu, Y., Lee, S., Wang, J., & Chuah, C. N. (2005). Failure inferencing based fast rerouting for handling transient link and node failures. In INFOCOM 2005. 24th annual joint conference of the ieee computer and communications societies. Proceedings IEEE (Vol. 4, pp. 2859–2863). IEEE.
Yi, J., Adnane, A., David, S., & Parrein, B. (2011). Multipath optimized link state routing for mobile ad hoc networks. Mobile Ad Hoc Networks, 9(1), 28–47.
Xu, P., Yang, C., Song, S., & Bi, G. (2005). Novel multi-path routing scheme for UWB ad hoc network. China Institute of Communications, 10, 17.
Francois, P., Filsfils, C., Evans, J., & Bonaventure, O. (2005). Achieving sub-second igp convergence in large ip networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 35(3), 35–44.
Markopoulou, A., Iannaccone, G., Bhattacharyya, S., Chuah, C., & Ganjali, C. (2008). Characterization of failures in an operational ip backbone network. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (TON), 16(4), 749–762.
Markopoulou, A., Iannaccone, G., Bhattacharyya, S., Chuah, C. N., & Diot, C. (2004). Characterization of failures in an IP backbone. In INFOCOM 2004. Twenty-third annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (Vol. 4, pp. 2307–2317). IEEE.
Iannaccone, G., Chuah, C., Mortier, R., Bhattacharyya, S., & Diot, C. (2002). Analysis of link failures in an IP backbone. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGCOMM workshop on internet measurment (pp. 237–242). ACM.
Iannaccone, G., Chuah, C. N., Bhattacharyya, S., & Diot, C. (2004). Feasibility of IP restoration in a tier 1 backbone. IEEE Network, 18(2), 13–19.
Labovitz, C., Ahuja, A., Bose, A., & Jahanian, F. (2000). Delayed internet routing convergence. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 30(4), 175–187.
Labovitz, C., Ahuja, A., & Jahanian, F. (1999). Experimental study of internet stability and backbone failures. In Twenty-ninth annual international symposium on fault-tolerant computing, digest of papers (pp. 278–285). IEEE.
Goyal, M., Ramakrishnan, K. K., & Feng, W. (2003). Achieving faster failure detection in ospf networks. In IEEE international conference on computer communications, 2003. ICC’03 (Vol. 1, pp. 296–300). IEEE.
Gill, P., Jain, N., & Nagappan, N. (2011). Understanding network failures in data centers: measurement, analysis, and implications. In Proceedings of SIGCOMM.
Gjoka, M., Ram, V., & Yang, X. (2007). Evaluation of ip fast reroute proposals. In 2nd international conference on communication systems software and middleware, COMSWARE (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Lakshminarayanan, K., Caesar, M., Rangan, M., Anderson, T., Shenker, S., & Stoica, I. (2007). Achieving convergence-free routing using failure-carrying packets. In ACM SIGCOMM computer communication review (Vol. 37, pp. 241–252). ACM.
Menth, M., Hartmann, M., Martin, R., Cicic, T., & Kvalbein, A. (2010). Loop-free alternates and not-via addresses: A proper combination for IP fast reroute? Computer Networks, 54(8), 1300–1315.
Francois, P., & Bonaventure, O. (2005). Avoiding transient loops during IGP convergence in IP networks. In Proceedings 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies. IEEE INFOCOM (Vol. 1, pp. 237–247). IEEE.
Bryant, S., Shand, M., & Previdi, S. (2006) IP fast reroute using not-via addresses. draft-bryant-shand-ipfrr-notvia-addresses-03. txt.
Hansen, A. F., Cicic, T., & Gjessing, S. (2006). Alternative schemes for proactive IP recovery. In 2006 2nd conference on next generation internet design and engineering, 2006. NGI’06 (p. 8). IEEE.
Nelakuditi, S., Lee, S., Yu, Y., Zhang, Z. L., & Chuah, C. N. (2007). Fast local rerouting for handling transient link failures. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 15(2), 359–372.
Nelakuditi, S., Lee, S., Yu, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2003). Failure insensitive routing for ensuring service availability. In International workshop of quality of service 2003. IWQoS’03.
Liu, Y., & Reddy, N. (2004). A fast rerouting scheme for OSPF/IS-IS networks (pp. 47–52).
Shand, M., & Bryant, S. (2010). IP fast reroute framework. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) M. Shand Request for Comments: 5714 S. Bryant Category: Informational Cisco Systems.
Hawkings, J., Wadham, J., Tranter, M., Telling, J., Bagshaw, E., Beaton, A., et al. (2016). The greenland ice sheet as a hotspot of phosphorus weathering and export in the arctic. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 30, 191–210.
Ulrich, A. E., Malley, D. F., & Watts, P. D. (2016). Lake winnipeg basin: Advocacy, challenges and progress for sustainable phosphorus and eutrophication control. Science of The Total Environment, 542, 1030–1039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abujassar, R.S. Restoration of IP Networks by Using a Hybrid Interacting Mechanism Between Layer 2 & 3 in the Networks Over OA&M. Wireless Pers Commun 100, 819–849 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5351-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5351-z