Abstract
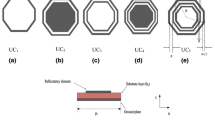
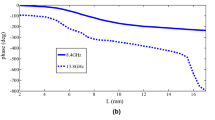
For decades, the design of reflectarray antennas followed a unified strategy of selecting a certain unit cell for the whole design. After that, the dimensions or orientations of this unit cell are changed to achieve the required phase shift at each position on the reflectarray surface. This strategy requires a 360° span of the phase characteristics of the selected unit cell versus a control parameter. In addition, it requires maximal linearity of the phase characteristics of the unit cell. This paper considers a different and more flexible strategy for the design of reflectarrays. This strategy is based on switching between unit cells to make use of the regions of the characteristic phase curves of best linearity for each unit cell. With this strategy, we can use unit cells with similar polarization, and unit cells that do not span 360° in phase characteristics in the design process of the same reflectarray. The single criterion for switching between unit cells is the maximal linearity of the phase characteristics of the unit cell at the required phase. This strategy guarantees maximization of the gain, and minimization of the side-lobe level (SLL) at the design frequency. The proposed strategy is validated for the design of a reflectarray antenna to work at 28 GHz using five different unit cells for possible 5G applications. The simulation results reveal the feasibility of the proposed strategy for achieving high gain and low SLL at 28 GHz.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, D. G., et al. (1963). The reflectarray antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 11, 645–651.
Huang, J., & Encinar, J. A. (2008). Reflectarray antennas. New York: IEEE Press.
Chang, D., & Huang, M. (1995). Multiple-polarization microstrip reflectarray antenna with high efficiency and low cross-polarization. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 43(8), 829–834.
Huang, J., et al. (1998). A Ka-band microstrip reflectarray with elements having variable rotation angles. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 46(5), 650–656.
Chaharmir, M. R., et al. (2006). Broadband reflectarray antenna with double cross loops. Electronics Letters, 42(2), 65–66.
Chaharmir, M. R., & Shaker, J. (2008). Broadband reflectarray antenna with combination of cross and rectangle loop elements. Electronic Letters, 44(11), 658–659.
Chaharmir, M. R., et al. (2009). Broadband design of a single layer large reflectarray using multi cross loop elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57(10), 3363–3366.
Mohammadirad, M., Komjani, N., Chaharmir, M. R., Shaker, J., & Sebak, A. R. (2012). Impact of feed position on the operating band of broadband reflectarray antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 11, 1104–1107.
Vosoogh, A., et al. (2014). A high-efficiency Ku-band reflectarray antenna using single-layer multiresonance elements. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 891–894.
An, W., Xu, S., & Yang, F. (2014). A metal-only reflectarray antenna using slot-type elements. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagations Letters, 13, 1553.
Zebrowski, M. (2012). Illumination and spillover efficiency calculations for rectangular reflectarray antennas. High Frequency Design, 1, 28–38.
Chaharmir, M. R., Shaker, J., Cuhaci, M., & Sebak, A. (2003). Reflectarray with variable slots on ground plane. IEE Proceedings on Microwaves, Antennas and Propagations, 150(6), 436–439.
Derafshi, I., Komjani, N., & Mohammadirad, M. (2015). A single-layer broadband reflectarray antenna by using quasi-spiral phase delay line. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagations Letters, 14, 84–87.
Encinar, J. A. (2001). Design of two-layer printed reflectarrays using patches of variable size. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 49(10), 1403–1410.
Yu, A., Yang, F., Elsherbeni, A. Z., Huang, J., & Kim, Y. (2012). An offset-fed X-band reflectarray antenna using a modified element rotation technique. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60(3), 1619–1624.
Rajagopalan, H., Xu, S., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2012). On understand in the radiation mechanism of reflectarray antennas: An insightful and illustrative approach. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 54(5), 14–38.
Ramli, M., Misran, N., Mansor, M. F., Islam, M. T. (2014). Analysis of reflectarray unit cell with capacitive effect. In 2nd international conference on information and communication technology (ICOICT) (pp. 95–99).
Balanis, C. A. (2005). Antenna theory analysis and design. Hoboken: Wiley.
CST-Computer Simulation Technology, Documentation. Available online: www.cst.com.
Carrasco, E., Barba, M., & Encinar, J. A. (2007). Reflectarray element based on aperture—coupled patches with slots and lines of variable length. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 55(3), 820–825.
Carrasco, E., Barba, M., & Encinar, J. A. (2006). Aperture-coupled reflectarray element with wide range of phase delay. Electronics Letters, 42(12), 667–668.
Hasani, H., Kamyab, M., & Mirkamali, A. (2010). Broadband reflectarray antenna incorporating disk elements with attached phase-delay lines. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 9, 156–158.
Carrasco, E., Encinar, J. A., & Barba, M. (2008). Bandwidth improvement in large reflectarrays by using true-time delay. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56(8), 2496–2503.
Han, C., Rodenbeck, C., Huang, J., & Chang, K. (2004). A C/Ka dual frequency dual layer circularly polarized reflectarray with microstrip ring elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 52(11), 2871–2876.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsharkawy, R., Hindy, M., Sebak, AR. et al. Switching Between Unit Cells: A Tool to Break the Limits on the Performance of Reflectarray Antennas. Wireless Pers Commun 101, 1429–1443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5770-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5770-x