Abstract
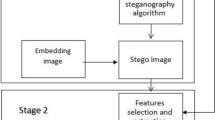
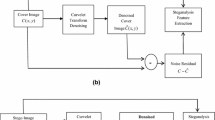
Blind universal steganalysis has been the choice of Steganalysers owing to it’s capability to detect stego images without any prior information about the embedding method. Universal steganalysis is a two class optimization problem and the detecting efficiency depends on the feature set chosen from the stego and clean images. Though extracting all possible features of an image may lead to more efficiency the classification suffers due to large dimension of feature set. To overcome the problem of dimensionality appropriate feature reduction techniques need to be employed. This paper presents a blind universal image steganalysis technique that extracts the noise models of adjacent pixels of an image. The exact model construction involves the formation of four dimensional co-occurrence matrices of the quantised and truncated noise residues. From the 106 sub models 34,671 features have been extracted and further reduced by a novel unsupervised optimization technique to identify the most appropriate features for classification. The classifiers implemented include Support Vector Machines (SVM), Multi Layer Perceptron (MLP) and three fusion classifiers based on Bayes, Decision Template and Dempster Schafer fusion schemes. It has been identified that MLP performs better than SVM but is not superior to fusion classifiers. Comparing all the classifiers, Decision Template based fusion method gives the best classification accuracy (99.25%). Thus the proposed unsupervised optimization method combined with Decision Template fusion classification scheme provides the best classification of stego and clear images as compared to the existing research work.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cachin, C. (2004). An information-theoretic model for steganography. Information and Computation Elsevier, 192(1), 41–56.
Pevny, T., Bas, P., & Fridrich, J. (2010). Steganalysis by subtractive pixel adjacency matrix. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 5(2), 215–224.
Pevny, T., Filler, T., & Bas, P. (2010). Using high-dimensional image models to perform Highly undetectable steganography. International Workshop on Information Hiding, 6387, 161–177.
Holub, V., Fridrich, J., & Denemark, T. (2014). Universal distortion function for steganography in an arbitrary domain. EURASIP Journal on Information Security. http://jis.eurasipjournals.com/content/2014/1/1. Accessed December 25, 2016.
Holub, V., & Fridrich, J. (2012). Designing steganographic distortion using directional filters. In Fourth IEEE international workshop on information forensics and security (pp. 234–239).
Fridrich, J., & Kodovsky, J. (2011). Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7(30), 868–882.
Filler, T., Judas, J., & Fridrich, J. (2011). Minimizing additive distortion in steganography using syndrome-trellis codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 6(3), 920–935.
Goljan, M., Fridrich, J., Holotyak, Y. (2006). New blind steganalysis and its implications. In Electronic imaging (p. 607201-13).
Zou, D., Shi, Y. Q., & Xuan, W. S. G. (2006). Steganalysis based on Markov model of thresholded prediction-error image. In Proceedings IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 1365–1368).
Ker, A. D., & Bohme, R. (2012). Revisiting weighted stego-image steganalysis. In Electronic imaging (p. 681905-17).
Kodovsky, J., Fridrich, J., & Holub, V. (2012). Ensemble classifiers for steganalysis of digital media. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7(2), 432–444. https://doi.org/10.1109/tifs.2011.2175919.
Holub, V., Fridrich, J., & Denemark, T. (2013). Random projections of residuals as an alternative to co-occurrences in steganalysis. IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.1000330.
Du, K. L. (2010). Clustering—A neural network approach. Journal Neural Networks, 23(1), 89–107.
Shi, Y. Q., Chen, C., & Chen, W. (2006). A Markov process based approach to effective attacking JPEG steganography. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop information hiding (pp. 249–264). Springer, Berlin.
Lyu, S., & Farid, H. (2004). Steganalysis using color wavelet statistics and one-class vector support machines. Proceedings of SPIE Security Steganography Watermarking of Multimedia Contents, 5301, 35–45.
Yu, H. F., Hsieh, C. J., Chang, K. W., & Lin, C. J. (2012). Large linear classification when data cannot fit in memory. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery From Data, 5(4), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1145/2086737.2086743.
Sri Lalitha, Y., & Govardhan, A. (2015). Improved Text Clustering with Neighbours. International Journal of Data Mining & Knowledge Management Process (IJDKP), 5(2), 23–37. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijdkp.2015.5203.
Sheikhan, M., Moin, M. S., & Pezhmanpour, M. (2010). Blind image steganalysis via joint co-occurrence matrix and statistical moments of contourlet transform. In Intelligent systems design and applications (ISDA) (pp. 368–372).
Avcibas, I., Kharrazib, M., Memon, N., & Sankurd, B. (2005). Image steganalysis with binary similarity measures. EURASIP JASP, 17, 2749–2757.
Pevny, T., & Fridrich, J. (2007). Merging Markov and DCT features for multi-class jpeg steganalysis. In IS and T/SPIE EI (Vol. 6505).
Windeatt, T. (2006). Accuracy/diversity and ensemble MLP classifier design. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 17(5), 1194–1211.
Gader, P. D., Mohamed, M. A., & Keller, M. (1996). Fusion of handwritten word classifiers. Pattern Recognition Letters—Special Issue on Fuzzy Set Technology in Pattern Recognition, 17(6), 577–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8655(96)00021-9.
Kuncheva, L. I., Bezdek, J. C., & Duin, R. P. W. (2001). Decision templates for multiple classifier fusion: An experimental comparison. Pattern Recognition, 34(2), 299–314.
Bas, P., Filler, T., & Pevny, T. (2011). Break our steganographic system—The ins and outs of organizing BOSS. In Proceedings of information hiding conference (Vol. 6958, pp. 59–70).
Kantarcioglu, M., Xi, B., & Clifton, C. (2011). Classifier evaluation and attribute selection against active adversaries. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery—DATAMINE, 22(1–2), 291–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-010-0197-3.
Fridrich, J., Kodovský, J., Goljan, M., & Holub, V. (2011). Steganalysis of content-adaptive steganography in spatial domain. In T. Filler, T. Pevný, A. Ker, & S. Craver (Eds.), Information Hiding, 13th International Workshop, volume 6958 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science (pp. 102–117). Prague, Czech Republic, May 18–20, 2011.
Chonev, V. K., & Ker, A. D. (2011). Feature restoration and distortion metrics. In Multimedia Watermarking, Security and Forensics XIII, volume 7880 of Proc. SPIE, 2011 (pp. 0G01–0G14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnvictor, A.C., Rangaswamy, R., Chidambaram, G. et al. Unsupervised Optimization for Universal Spatial Image Steganalysis. Wireless Pers Commun 102, 1–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5790-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5790-6