Abstract
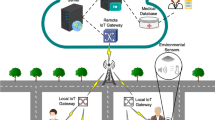
In this paper we present a case study of IoT cloud participatory sensing where a user sends a query to the cloud about the air quality of a location at a particular time to decide if it should enter the location based on its susceptibility to the air quality detected. All IoT devices (e.g., smart phones carried by humans or smart cars driven by humans) capable of detecting air quality can act as participants and submit sensing reports to the cloud for sensing result aggregation. The major challenge is the selection of trustworthy participants because not all IoT devices will be trustworthy. We leverage a “Trust as a Service” (TaaS) cloud utility to address the issue of selecting trustworthy participants. Using real traces of ozone (O3) levels and mobility traces of users in the O3 community of interest (O3COI) group in the city of Houston, we demonstrate that TaaS outperforms contemporary IoT trust protocols in selecting trustworthy participants. We compare the performance of the TaaS cloud utility with two contemporary IoT trust protocols for supporting trust-based IoT participatory sensing applications. With the help of the TaaS cloud utility, a user in this O3COI group is able to obtain O3 readings very close to the ground truth O3 level despite 30% participants are untrustworthy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan, W. Z., Xiang, Y., Aalsalem, M. Y., & Arshad, Q. (2013). Mobile phone sensing systems: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 15(1), 402–427.
Mousa, H., et al. (2015). Trust management and reputations systems in mobile participatory sensing applications: A survey. Computer Networks, 90, 49–73.
Amintoosi, H., Kanhere, S. S., & Allahbakhsh, M. (2015). Trust-based privacy-aware participant selection in social participatory sensing. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 20, 11–25.
Al-Hamadi, H., & Chen, I. R. (2017). Trust-based decision making for health IoT systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1408–1419.
Chen, I. R., Guo, J., Wang, D. C., Tsai, J. J. P., Al-Hamadi, H., & You, I. (2018). Trust as a service for IoT service management in smart cities. The 16th IEEE International Conference on Smart City, Exeter, UK, June 2018.
Chen, I. R., Guo, J., & Bao, F. (2016). Trust management for SOA-based IoT and its application to service composition. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 9(3), 482–495.
Nitti, M., Girau, R., & Atzori, L. (2014). Trustworthiness management in the social internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Management, 26(5), 1253–1266.
Pires B. et al. (2015). Towards an in silico experimental platform for air quality: Houston, TX as a case study. In Computational social science society of America conference, Santa Fe, NM, USA.
Jøsang, A., & Ismail, R. (2002). The beta reputation system. Bled electronic commerce conference, Bled, Slovenia, pp. 1–14.
Guo, J., Chen, I. R., & Tsai. J. J. P. (2017). A mobile cloud hierarchical trust management protocol for IoT systems, In 5th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Cloud Computing, Services, and Engineering, San Francisco, April 2017.
Chen, I. R., Gu, B., George, S. E., & Cheng, S. T. (2005). On failure recoverability of client-server applications in mobile wireless environments. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 54(1), 115–122.
Gu, B., & Chen, I. R. (2005). Performance analysis of location-aware mobile service proxies for reducing network cost in personal communication systems. Mobile Networks and Applications, 10(4), 453–463.
Cheng, S. T., Chen, C. M., & Chen, I. R. (2000). Dynamic quota-based admission control with sub-rating in multimedia servers. Multimedia Systems, 8(2), 83–91.
Cheng, S. T., Chen, C. M., & Chen, I. R. (2003). Performance evaluation of an admission control algorithm: Dynamic threshold with negotiations. Performance Evaluation, 52(1), 1–13.
Yilmaz, O., & Chen, I. R. (2009). Utilizing call admission control for pricing optimization of multiple service classes in wireless cellular networks. Computer Communications, 32(2), 317–323.
Chen, I. R., Chen, T. M., & Lee, C. (2001). Agent-based forwarding strategies for reducing location management cost in mobile networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 6(2), 105–115.
Chen, I. R., & Wang, D. C. (1996). Analysis of replicated data with repair dependency. The Computer Journal, 39(9), 767–779.
Chen, I. R., Yilmaz, O., & Yen, I. L. (2006). Admission control algorithms for revenue optimization with QoS guarantees in mobile wireless networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 38(3), 357–376.
Chen, I. R., & Bastani, F. B. (1991). Effect of artificial-intelligence planning procedures on system reliability. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 40(3), 364–369.
Chen, I. R., Guo, J., Bao, F., & Cho, J. H. (2014). Trust management in mobile Ad Hoc networks for bias minimization and application performance maximization. Ad Hoc Networks, 19, 59–74.
Guo, J., Chen, I. R., & Tsai, J. J. P. (2017). A survey of trust computation models for service management in internet of things systems. Computer Communications, 97, 1–14.
Saied, Y. B., Olivereau, A., Zeghlache, D., & Laurent, M. (2013). Trust management system design for the internet of things: A context-aware and multi-service approach. Computers and Security, 39, 351–365.
Chen, I. R., Bao, F., & Guo, J. (2016). Trust-based service management for social internet of things systems. In IEEE transactions on dependable and secure computing, vol. 13, no. 6, Nov–Dec 2016, (pp. 684–696).
Nitti, M., Atzori, L., & Cvijikj, I. P. (2015). Friendship selection in the social internet of things: Challenges and possible strategies. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2(3), 240–247.
Kamvar, S. D., Schlosser,M. T., & Garcia-Molina, H. The EigenTrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P networks. In 12th International conference on world wide web, Budapest, Hungary, 2003.
Xiong, L., & Liu, L. (2004). PeerTrust: Supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities. In IEEE transaction on knowledge and data engineering 16, (pp. 843–857).
Su, Z., Liu, L., Li, M., Fan, X., Zhou, Y. ServiceTrust: Trust management in service provision networks. In IEEE international conference on services computing, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2013, pp. 272-279
Wang, Y., Chen, I. R., & Wang, D. C. (2015). A survey of mobile cloud computing applications: Perspectives and challenges. Wireless Personal Communications, 80, 1607–1623.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the U.S. AFOSR under grant number FA2386-17-1-4076.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Chen, IR., Wang, DC. et al. Trust-Based IoT Cloud Participatory Sensing of Air Quality. Wireless Pers Commun 105, 1461–1474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06154-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06154-y