Abstract
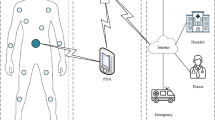
Wireless body area networks (WBANs) consist of tiny sensors that placed around or implant in the human body. These nodes can permanently monitor the health of patients. WBANs require medical applications for remote monitoring and health care. In WBANs, the main challenge is delay and limitations of energy consumption to prolong the network lifetime. In this context, a MAC protocol has been provided to guarantee energy consumption and delay reduction based on priority of data traffic. The design of this protocol consisted of four sections: First, the patient data traffic is prioritized and classified, which included normal data, periodic data, and emergency data. Second, the superframe structure is improved according to IEEE 802.15.4 and the priorities for the data are optimized. Third, the energy consumption and delay have been reduced by using the radio wake-up mechanism and through controlling the node modes. Four, for checking the node modes, the state diagram and the asymmetric hidden Markov method have been exploited to model the limited capacity of the buffers. This protocol has been simulated using NS-3, and simulation and evaluation results indicated that lower energy consumption and delay as well as improved network lifetimes compared to the previous methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gravina, R., Alinia, P., Ghasemzadeh, H., & Fortino, G. (2016). Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Information Fusion, 35, 68–80.
Fortino, G., Giannantonio, R., Gravina, R., & Kuryloski, P. (2013). Enabling effective programming and flexible management of efficient body sensor network applications. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 43, 115–133.
Fallahzadeh, R., Ma, Y., & Ghasemzadeh, H. (2016). Context-aware system design for remote health monitoring: An application to continuous edema assessment. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 16(8), 2159–2173.
Hu, Y., Dong, M., Ota, K., & Liu, A. (2016). Mobile target detection in wireless sensor networks with adjustable sensing frequency. IEEE Systems Journal, 10, 1160–1171.
Roy, S. V., Quitin, F., Liu, L., & Oestges, C. (2013). Dynamic channel modeling for multi-sensor body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 61, 2200–2208.
Ayatollahitafti, V., Ngadi, M. A., Sharif, J. M., & Abdullahi, M. (2016). An efficient next hop selection algorithm for multi-hop body area networks. PLoS ONE, 11, e0146464.
Yigitel, M. A., Incel, O. D., & Ersoy, C. (2011). Design and implementation of a Qos-aware MAC protocol for wireless multimedia sensor networks. Computer Communication, 34(16), 1991–2001.
El-Hoiydi, A., & Decotignie, J.-D. (2004).WiseMAC: An ultra-low power MAC protocol for the downlink of infrastructure wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE symposium on computers and communication (ISCC 2004), Alexandria, Egypt (pp. 244–251).
Xia, F., Wang, L., Zhang, D., He, D., & Kong, X. (2015). An adaptive MAC protocol for real-time and reliable communications in medical cyber-physical systems. Telecommunication Systems, 58(2), 125–138.
Okdem, S. (2017). A real-time noise resilient data link layer mechanism for unslotted IEEE 802.15.4 networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 30, e2955.
IEEE 802.15.4. (2006). IEEE Standard for Information Technology 802.15.4, Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs). New York, NY: The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
Zhou, J., Guo, A., Xu, J., & Su, S. (2014). An optimal fuzzy control medium access in wireless body area networks. Neurocomputing, 142, 107–114.
Yoon, J. S., Ahn, G.-S., Joo, S.-S., & Lee, M. J. (2010). PNP-MAC: Preemptive slot allocation and non-preemptive transmission for providing QoS in body area networks. In 2010 7th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference (pp. 1–5).
Liu, B., Yan, Z. S., & Chen, C. W. (2013). MAC protocol in wireless body area networks for E-health: Challenges and a context-aware design. IEEE Wireless Communication, 20, 64–72.
Antoni, M., Alejandro, C., Marc, B., & Lopez, V. (2016). Data aggregation and principal component analysis in WSNs. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communication, 15, 3908–3919.
Asemani, M., & Esnaashari, M. (2015). Learning automata based energy efficient data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Network, 21, 2035–2053.
Mouzehkesh, N., Zia, T., Shafigh, S., & Zheng, L. H. (2015). Dynamic backoff scheduling of low data rate applications in wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks, 21, 2571–2592.
Latre, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., & Demeester, P. (2011). A survey on wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks, 17(1), 1–18.
Laufer, R., & Kleinrock, L. (2016). The capacity of wireless CSMA/CA networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networks, 24, 1518–1532.
Sasaki, M., Furuta, T., Ukai, T., & Ishizaki, F. (2016). TDMA scheduling problem avoiding interference in multi-hop wireless sensor networks. Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.1299/jamdsm.2016jamdsm0047.
Feng, L., Yu, J. G., Cheng, X. Z., & Wang, S. L. (2016). Analysis and optimization of delayed channel access for wireless cyber-physical systems. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communication and Network, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-016-0557-9.
Yu, J. G., Huang, B. G., Cheng, X. Z., & Atiquzzaman, M. (2017). Shortest link scheduling algorithms in wireless networks under the SINR model. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66, 2643–2657.
Akbar, M. S., Yu, H. N., & Cang, S. (2016). Delay, reliability, and throughput based QoS profile: A MAC layer performance optimization mechanism for biomedical applications in wireless body area sensor networks. Journal of Sensors. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7170943.
Gama, O., & Simoes, R. (2014). A hybrid MAC scheme to improve the transmission performance in body sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communication, 80, 1263–1279.
Ullah, S., Imran, M., & Alnuem, M. (2014). A hybrid and secure priority-guaranteed MAC protocol for wireless body area network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/481761.
Sarkar, S., Misra, S., Bandyopadhyay, B., Chakraborty, C., & Obaidat, M. S. (2015). Performance analysis of IEEE 802.15.6 MAC protocol under non-ideal channel conditions and saturated traffic regime. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 64, 2912–2925.
Ali, K., Sarker, J., & Mouftah, H. (2010). Urgency-based MAC protocol for wireless sensor body area networks. In Communications workshops.
Yoon, J. S., Ahn, G.-S., Joo, S.-S., & Lee, M. J. (2010). PNP-MAC: Preemptive slot allocation and non-preemptive transmission for providing QoS in body area networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA (pp. 1–5).
Monowar, M. M., Hassan, M. M., Bajaber, F., Al-Hussein, M., & Alamri, A. (2012). McMAC: Towards a MAC protocol with multi-constrained Qos providing for diverse traffic in wireless body area networks. Sensors, 12, 15599–15627.
Anjum, I., Alam, N., Razzaque, M. A., Mehedi Hassan, M., & Alamri, A. (2013). Traffic priority and load adaptive MAC protocol for QoS provisioning in body sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 9(3), 1–9.
Hossain, M. U., Dilruba, M. K., Rana, M. R., & Rahman, M. O. (2014). Multi-dimensional traffic adaptive energy-efficient MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Forum on Strategic Technology (IFOST’14) (pp. 161–165). Chittagong: IEEE.
Bhandari, S., & Moh, S. (2016). A priority-based adaptive MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. Sensors, 16, 401.
Kim, B., & Cho, J. (2012). A novel priority-based channel access algorithm for contention-based MAC protocol in WBANs. In Proceedings of the 6th international conference on ubiquitous information management and communication (ICUIMC 2012), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (pp. 1–5).
Alam, M. M., Berder, O., Menard, D., & Sentieys, O. (2012). TAD-MAC: Traffic-aware dynamic MAC protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2, 2156–3357. https://doi.org/10.1109/JETCAS.2012.2187243.
Lin, L., Yang, C., Wong, K. J. U., Yan, H., Shen, J., & Phee, S. J. A. (2014). An energy efficient MAC protocol for multi-hop swallowable body sensor networks. Sensors, 14(10), 19457–19476.
Ullah, S., & Kwak, K. S. (2012). An ultra-low-power and traffic adaptive medium access control protocol for wireless body area network. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(3), 1021–1030.
Zhang, C. Q., Wang, Y. L., Liang, Y. Q., Shu, M., & Chen, C. F. (2016). An energy-efficient MAC protocol for medical emergency monitoring body sensor networks. Sensors, 16, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030385.
Yan, Z., & Liu, B. (2011). A context aware MAC protocol for medical wireless body area network. In Proceedings of the 7th international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC 2011), Istanbul, Turkey (pp. 2133–2138).
Hayes, J. F., & Babu, T. V. J. G. (2004). Modeling and analysis of telecommunications networks. New York: Wiley.
Bueno, M. L. P., Hommersom, A., Lucas, P. J. F., & Linard, A. (2017). Asymmetric hidden Markov models. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 88, 169–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2017.05.011.
Rasheed, M. B., Javaid, N., Imran, M., Khan, Z. A., Qasim, U., Vasilakos, A. (2017). Delay and energy consumption analysis of priority guaranteed MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. Wireless Network, 23, 1249–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1199-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rismanian Yazdi, F., Hosseinzadeh, M. & Jabbehdari, S. A Priority-Based MAC Protocol for Energy Consumption and Delay Guaranteed in Wireless Body Area Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 108, 1677–1696 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06490-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06490-z