Abstract
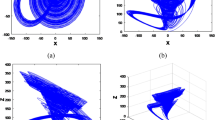
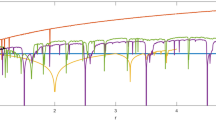
In this article, enhanced chaotic range map is used for data hiding and multimedia security. By using complex properties of improved chaotic logistic map that include non-periodical motion and non-convergence, a new watermarking algorithm and image encryption scheme is proposed. For image encryption, the process of grayscale substitution in the form of encryption matrix randomly changes all pixel values of an image. In watermarking, the chaotic improved logistic system is used for identifying the embedding locations of the watermark. The Simulation results and statistical analyses specify that our techniques are comparatively secure and effective from existing ones, and are more practicable.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hussain, I., Shah, T., & Gondal, M. A. (2012). An efficient image encryption algorithm based on S8 S-box transformation and NCA map. Optics Communications,285, 4887–4890.
Guan, Z. H., Huang, F. J., & Guan, W. J. (2005). Chaos-based image encryption algorithm. Physics Letters A,34, 153–157.
Cox, I. J., Doerr, G., & Furon, T. (2006). Digital watermarking (pp. 1–15). Berlin: Springer.
Alexopoulos, C., Bourbakis, N. G., & Ioannou, N. (1995). Image encryption method using a class of fractals. Journal of Electronic Imaging,4, 251–259.
Zhou, Y., Panetta, K., Agaian, S., & Chen, C. L. P. (2012). Image encryption using P-Fibonacci transform and decomposition. Optics Communication,285(5), 594–608.
Zhou, Y., Panetta, K., Agaian, S., & Chen, C. L. P. (2013). (n, k, p)-gray code for image systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics,43(2), 515–529.
Chen, T. H., & Wu, C. S. (2010). Compression-unimpaired batch-image encryption combining vector quantization and index compression. Information Sciences,180(9), 1690–1701.
Jamal, S. S., Shah, T., & Hussain, I. (2013). An efficient scheme for digital watermarking using chaotic map. Nonlinear Dynamics,73, 1469–1474.
Attaullah, Jamal, S. S., & Shah, T. (2017). A novel scheme for image encryption using substitution box and chaotic system. Nonlinear Dynamics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3874-6.
Zhang, Y. (2018). The unified image encryption algorithm based on chaos and cubic S-Box. Information Sciences,450, 361–377.
Wu, J., Liao, X., & Yang, B. (2018). Image encryption using 2D Henan-Sine map and DNA approach. Signal Processing,153, 11–23.
Hussain, I., Shah, T., Gondal, M. A., & Mahmood, H. (2013). A novel image encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps and GF(28) exponent transformation. Nonlinear Dynamics,72, 399–406.
Khan, M., & Shah, T. (2015). An efficient construction of substitution box with fractional chaotic system. Signal, Image and Video Processing,9(6), 1335–1338.
Liu, D., Zhang, W., Yu, H., & Zhu, Z. (2018). An image encryption scheme using self-adaptive selective permutation and inter-intra-block feedback diffusion. Signal Processing,151, 130–143.
Ping, P., Wu, H., Mao, Y., Xu, F., & Fan, J. (2018). Design of image cipher using life-like cellular automata and chaotic map. Signal Processing,150, 233–247.
Zhou, Y., Bao, L., & Chen, C. L. P. (2014). A new 1D chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Processing,97, 172–182.
Khan, M., Shah, T., Mahmood, H., & Gondal, M. A. (2013). An efficient method for the construction of block cipher with multi-chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dynamics,71(3), 489–492.
Wu, Y., Yang, G., Jin, H., & Noonan, J. P. (2012). Image encryption using the two-dimensional Logistic chaotic map. Journal of Electronic Imaging,21(1), 013014-1.
Wang, X., Liu, L., & Zhang, Y. (2015). A novel chaotic block image encryption algorithm based on dynamic random growth technique. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,66, 10–18.
Belazi, A., Khan, M., El-Latif, A. A. A., & Belghith, S. (2017). Efficient cryptosystem approaches: S-boxes and permutation–substitution-based encryption. Nonlinear Dynamics,88, 337–362.
Hernandez, L. R., & Amado, M. (2000). DCT-domain watermarking techniques for still images: Detector performance analysis and a new structure. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,9(1), 55–68.
Furon, T., & Duhamel, P. (2003). An asymmetric watermarking method. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,51(4), 981–995.
Cox, U., Kilian, L., Leighton, F., & Shamoon, T. (1997). Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,6, l673–l1687.
Cox, U., Miller, M. L., & Bloom, J. (2002). Digital watermarking. San Mateo: Morgan Kaufmann.
Nikolaidis, A., & Pitas, L. (2000). Comparison of different chaotic maps with application to image watermarking. In Proceedings IEEE symposium circuits and system, Geneva (Vol. 5, pp. 509–512).
Giovanardi, A., & Mazzini, G. (2001). Frequency domain chaotic watermarking. In Proceedings IEEE symposium circuits and system, Sydney (Vol. 2, pp. 521–524).
Wu, X., & Guan, Z. H. (2007). A novel digital watermark algorithm based on chaotic maps. Physics Letters A,365, 403–406.
Xiang, T., Wong, K. W., & Liao, X. (2007). Selective image encryption using a spatiotemporal chaotic system. Chaos,17, 023115.
Wang, X. Y. (2003). Chaos in the complex nonlinearity System. Beijing: Electronics Industry Press.
Attaullah, Jamal, S. S., & Shah, T. (2017). A novel construction of substitution box using a combination of chaotic maps with improved chaotic range. Nonlinear Dynamics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3409-1.
Acknowledgement
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University fo r funding this work through research groups program under grant number R.G.P. 2/58/40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attaullah, Shah, T. & Jamal, S.S. An Improved Chaotic Cryptosystem for Image Encryption and Digital Watermarking. Wireless Pers Commun 110, 1429–1442 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06793-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06793-1