Abstract
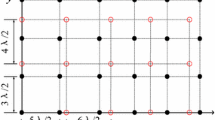
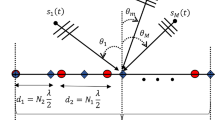
In this paper, we extend the coprime planar array to coprime cubic array and propose a three dimensional coprime array (TDCA) for two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) estimation, which possesses larger inter-element spacing so that the mutual coupling effects can be effectively relieved. Moreover, due to the larger array aperture, better DOA estimation performance can be achieved. To obtain more degrees of freedom (DOFs), a generalized TDCA (G-TDCA) configuration is proposed, which has a flexible array geometry and can extend the array aperture to obtain performance improvement. The principle for optimal array design of G-TDCA is derived to achieve the maximum DOF. And the Cramer–Rao Bounds which denotes as a theoretical benchmark for the lower bound of unbiased estimate are derived. Then we propose Khatri–Rao estimation signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques (KR-ESPRIT) algorithm and obtain the close-form expression. The algorithm can achieve angles with automatic pairing and doesn’t need spectrum peak searching. In order to decrease the computational complexity, we propose KR-Unitary ESPRIT algorithm, which can achieve approximate DOA estimation performance of the KR-ESPRIT algorithm with the lower computational complexity. Numerical simulation results verify the superiority of G-TDCA with proposed algorithms.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krim, H., & Viberg, M. (1996). Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,13(4), 67–94.
Zhang, X., Xu, L., et al. (2010). Direction of departure (DOD) and direction of arrival (DOA) estimation in MIMO radar with reduced-dimension MUSIC. IEEE Communications Letters,14(12), 1161–1163.
Cong, L., & Zhuang, W. (2002). Hybrid TDOA/AOA mobile user location for wideband CDMA cellular systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications,1(3), 439–447.
Liu, J., Zhou, W., Juwono, F. H., et al. (2017). Reweighted smoothed l0-norm based DOA estimation for MIMO radar. Signal Processing,137(C), 44–51.
Capon, J. (2005). High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proceedings of the IEEE,57(8), 1408–1418.
Schmidt, R. O. (1986). Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,34(3), 276–280.
Roy, R., & Kailath, T. (2002). ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,37(7), 984–995.
Marcos, S., Marsal, A., & Benidir, M. (1995). The propagator method for source bearing estimation. Signal Processing,42(2), 121–138.
Zheng, W., Zhang, X., Sun, H., et al. (2017). Non-circular generalized-ESPRIT algorithm for direction of arrival estimation. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation,11(5), 736–744.
Chen, H., Hou, C., Wang, Q., et al. (2015). Improved azimuth/elevation angle estimation algorithm for three-parallel uniform linear arrays. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters,14, 329–332.
Xia, T., Zheng, Y., Wan, Q., et al. (2007). Decoupled estimation of 2-D angles of arrival using two parallel uniform linear arrays. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,55(9), 2627–2632.
Cai, J. J., Qin, G. D., Peng, L. I., et al. (2014). Two-dimensional DOA estimation with reduced-dimensional MUSIC algorithm using the modulus constraint. Systems Engineering and Electronics,36(9), 1681–1686.
Zhang, Z., Wang, W., Huang, Y., et al. (2017). Decoupled 2-D direction of arrival estimation in L-shaped array. IEEE Communications Letters,21, 1989–1992.
Mathews, C. P., & Zoltowski, M. D. (1994). Eigenstructure techniques for 2-D angle estimation with uniform circular array. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,42(9), 2395–2407.
Ye, Z., & Liu, C. (2008). 2-D DOA estimation in the presence of mutual coupling. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,56(10), 3150–3158.
Steinberg, B. D. (1976). Principles of aperture and array system design. New York: Wiley.
Pal, P., & Vaidyanathan, P. P. (2011). Sparse sensing with coprime samplers and arrays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,59(2), 573–586.
Qin, S., Zhang, Y. D., & Amin, M. G. (2015). Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,63(6), 1377–1390.
Pal, P., & Vaidyanathan, P. P. (2011). Coprime sampling and the music algorithm. In Digital signal processing workshop and IEEE signal processing education Workshop (pp. 289–294).
Zhou, C., Shi, Z., Gu, Y., & Shen, X. (2013). DECOM: DOA estimation with combined MUSIC for coprime array. In International conference on wireless communications and signal processing (pp. 1–5).
Zheng, W., Zhang, X. F., Gong, P., et al. (2017). DOA estimation for coprime linear arrays: An ambiguity-free algorithm involving full DOFs. IEEE Communications Letters,22(3), 562–565.
Wu, Q., Sun, F., Lan, P., Ding, G., & Zhang, X. (2016). Two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation for co-prime planar arrays: A partial spectral search approach. IEEE Sensors Journal,16(14), 5660–5670.
Zheng, W., Zhang, X. F., & Shi, Z. (2017). Two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation for coprime planar arrays via a computationally efficient one-dimensional partial spectral search approach. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation,11(10), 1581–1588.
Zheng, W., Zhang, X. F., & Zhai, H. (2017). Generalized coprime planar array geometry for 2-D DOA estimation. IEEE Communications Letters,21(5), 1075–1078.
Vu, D. T., Renaux, A., Boyer, R., & Marcos, S. (2011). A Cramér Rao bounds based analysis of 3D antenna array geometries made from ULA branches. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing,24(1), 121–155.
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1989). MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer–Rao bound. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,37(5), 720–741.
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1990). MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer–Rao bound: Further results and comparisons. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,38(12), 2140–2150.
Stoica, P., & Nehorai, A. (1990). Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,38(10), 1783–1795.
Roy, R., & Kailath, T. (1989). ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,37(7), 984–995.
Jinli, C., Hong, G., & Weimin, S. (2008). Angle estimation using ESPRIT without pairing in MIMO radar. Electronics Letters,44(24), 1422–1423.
Li, J., & Zhang, X. (2014). Unitary reduced-dimensional estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques for angle estimation in monostatic multiple-input–multiple-output radar with rectangular arrays. Radar Sonar & Navigation IET,8(6), 575–584.
Haardt, M., & Nossek, J. (1995). Unitary ESPRIT: How to obtain increased estimation accuracy with a reduced computational burden. Piscataway: IEEE Press.
Li, J., Jiang, D., & Zhang, X. (2017). DOA estimation based on combined unitary ESPRIT for coprime MIMO radar. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(1), 96–99.
Funding
This research is supported by China Natural Science Foundation Grants [61631020, 61601167, 61371169], and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NP2018103, NE2017103, NC2017003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, P., Zhang, X. & Zhai, H. Generalized Three Dimensional Coprime Array for Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation. Wireless Pers Commun 110, 1995–2017 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06826-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06826-9