Abstract
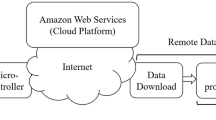
In the automobile sector, the new advancements in technology help the vendors in developing smart vehicles. These smart vehicles are designed to provide all sort of comfort to the society. But still, some improvements are required to make these vehicles smarter in terms of environmental pollution management. The other cause of air pollution is due to the toxic gases released by the industries. The environment pollution is still increasing gradually despite the various efforts of government. A number of solutions are available in the literature to control and monitor environmental pollution. The examination uncovers that there is a necessity of a sensor based embedded system that can screen and control the air contamination with generation of challan from anyplace in the world using IOT. An embedded system prototype has been designed on the concept of an internet of things scenario that uses sensors and actuators around Raspberry Pi board. The system prototype is programmed in python using some standard libraries available on adafruit and github. A web page is also designed to monitor the level of gases remotely at any place in the world. The results demonstrate that the complete system has been successfully tested and implemented.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, D.-D., & Lee, D.-S. (2001). Environmental gas sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 1(3), 214–224.
Sallis, P., Dannheim, C., Icking, C., & Mder M. (2014). Air pollution and fog detection through vehicular sensors. In IEEE Asia modelling symposium (pp. 181–186).
Shah, J., & Mishra, B. (2016). Customized IoT enabled wireless sensing and monitoring platform for smart buildings. Procedia Technology, 23, 256–263.
Fuertes, W., Carrera, D., Toulkeridis, T., Gal, F., & Torres, E. (2015). Distributed system as internet of things for a new low-cost air pollution wireless monitoring on real time. In IEEE/ACM international symposium on distributed simulation and real time applications (DS-RT) (pp. 58–67).
Rushikesh, R., & Sivappagari, C. M. R. (2015). Development of IoT based vehicular pollution monitoring system. In IEEE Green computing and internet of things (pp. 779–783).
Khedo, K. K., Perseedoss, R., & Mungur, A. (2010). A wireless sensor network air pollution monitoring system. International Journal of Wireless & Mobile Networks, 2(2), 31–45.
Al-Haija, Q. A., Al-Qadeeb, H., & Al-Lwaimi, A. (2013). Case study: Monitoring of air quality in King Faisal University using a microcontroller and WSN. Procedia Computer Science, 21, 517–521.
Raju, P. V., Aravind, R. V. R. S., & Kumar, B. S. (2013). Pollution monitoring system using wireless sensor network in Visakhapatnam. International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT), 4(4), 591–595.
Folea, S. C., & Mois, G. (2015). A low-power wireless sensor for online ambient monitoring. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(2), 742–749.
Lay- Ekuakille, A., Vergallo, P., Morello, R., & De Capua, C. (2014). Indoor air pollution system based on LED technology. Measurement, 47, 749–755.
Verma, H., Jain, M., Goel, K., Vikram, A., & Verma, G. (2016). Smart home system based on Internet of Things. In International conference on computing for sustainable global development, New Delhi (pp. 2073–2075).
Kalra, V., Baweja, C., Simranpreet, & Chopra, S. (2016). Influence of temperature and humidity on the output resistance of the MQ-135 sensor. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 6(4), 423–429.
Gao, M., Zhang, F., & Tian, J. (2008). Environmental monitoring system with wireless mesh network based on embedded system. In IEEE international symposium on embedded computing (pp. 174–179).
Al-Ali, A. R., Zualkernan, I., & Aloul, F. (2010). A mobile GPRS-sensors array for air pollution monitoring. IEEE Sensors Journal, 10, 1666–1671.
Chandrasekaran, S. S., Muthukumar, S., & Rajendran, S. (2013). Automated control system for air pollution detection in vehicles. In International conference on intelligent systems modelling and simulation (pp. 49–51).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to submit their gratefulness to Deanship of Scientific Research, King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia for providing administrative, financial and technical support under Grant Number G.R.P 261/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, A., Verma, G., Qamar, S. et al. Vehicle Pollution Monitoring, Control and Challan System Using MQ2 Sensor Based on Internet of Things. Wireless Pers Commun 116, 1071–1085 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06936-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06936-4