Abstract
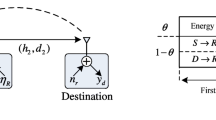
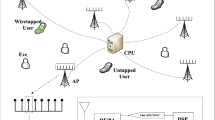
In this paper, the issue of secrecy capacity of wireless powered massive MIMO dual hop relay system with a single antenna eavesdropper having non ideal hardware is addressed. The relay harvests energy in a proportionate manner and passes it to destination through beamforming with classical decode and forward relaying protocol. The relay has no channel state information (CSI) of passive eavesdropper but has CSI of the legitimate channel. The work presented in this paper focuses on the analysis of the difference in system performance with ideal and non ideal hardware, bounded by strict outage probability. The performance (in terms of secrecy outage capacity) is studied with hardware impairments (HWIs) defined for all network elements, i.e., source, relay, destination and passive eavesdropper. It is also observed that compared to ideal hardware, there is significant degradation in performance due to HWIs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, D., Bai, B., Zhao, W., & Han, Z. (2018). A survey of optimization approaches for wireless physical layer security. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 21, 1878–1911.
Schaefer, R. F., Amarasuriya, G., & Poor, H. V. (2017). Physical layer security in massive MIMO systems. In 2017 51st Asilomar conference on signals, systems, and computers (pp. 3–8).
Jensen, B., Clark, B., Flanary, D., Norman, K., Rice, M., & Harrison, W. K. (2018). Physical-layer security: Does it work in a real environment? CoRR. arXiv:1811.06591.
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. The Bell System Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Shiu, Y. S., Chang, S. Y., Wu, H. C., Huang, S. C. H., & Chen, H. H. (2011). Physical layer security in wireless networks: A tutorial. IEEE Wireless Communications, 18(2), 66–74.
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S., & Hellman, M. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Lu, X., Niyato, D., Privault, N., Jiang, H., & Wang, P. (2018). Managing physical layer security in wireless cellular networks: A cyber insurance approach. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 36(7), 1648–1661.
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., & McKay, M. R. (2013). On the design of artificial-noise-aided secure multi-antenna transmission in slow fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(5), 2170–2181.
Zhu, J., Schober, R., & Bhargava, V. K. (2014). Secrecy analysis of multi-cell massive MIMO systems with RCI precoding and artificial noise transmission. In 2014 6th International symposium on communications, control and signal processing (ISCCSP) (pp. 101–104).
Yaacoub, E., & Al-Husseini, M. (2017). Achieving physical layer security with massive MIMO beamforming. In 2017 11th European conference on antennas and propagation (EUCAP) (pp. 1753–1757).
Wang, X., Wang, K., & Zhang, X. D. (2013). Secure relay beamforming with imperfect channel side information. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 62(5), 2140–2155.
Holma, H., & Toskala, A. (2011). LTE for UMTS: Evolution to LTE-advanced. New York: Wiley.
Nasir, A. A., Zhou, X., Durrani, S., & Kennedy, R. A. (2013). Relaying protocols for wireless energy harvesting and information processing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(7), 3622–3636.
Mo, J., Tao, M., & Liu, Y. (2012). Relay placement for physical layer security: A secure connection perspective. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(6), 878–881.
Grover, P., & Sahai, A. (2010). Shannon meets tesla: Wireless information and power transfer. In 2010 IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 2363–2367).
Ng, D. W. K., Lo, E. S., & Schober, R. (2014). Robust beamforming for secure communication in systems with wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(8), 4599–4615.
Qiao, J., Zhang, H., Zhao, F., & Yuan, D. (2018). Secure transmission and self-energy recycling with partial eavesdropper CSI. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 36(7), 1531–1543.
Chen, X., Lei, L., Zhang, H., & Yuen, C. (2014). On the secrecy outage capacity of physical layer security in large-scale MIMO relaying systems with imperfect CSI. In 2014 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 2052–2057).
Matthaiou, M., Papadogiannis, A., Bjornson, E., & Debbah, M. (2013). Two-way relaying under the presence of relay transceiver hardware impairments. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(6), 1136–1139.
Björnson, E., Papadogiannis, A., Matthaiou, M., & Debbah, M. (2013). On the impact of transceiver impairments on AF relaying. In 2013 IEEE International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (pp. 4948–4952).
Son, P. N., & Kong, H. Y. (2017). Energy-harvesting decode-and-forward relaying under hardware impairments. Wireless Personal Communications, 96(4), 6381–6395.
Studer, C., Wenk, M., & Burg, A. (2010). MIMO transmission with residual transmit-RF impairments. In 2010 International ITG workshop on smart antennas (WSA) (pp. 189–196).
Ngo, H. Q., Larsson, E. G., & Marzetta, T. L. (2013). Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(4), 1436–1449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Proof of Theorem 1
Let \(p=(1-\theta )P_S N_R\alpha _{S,R}\), \(\varDelta _p=(1-\theta )N_0+\mu N_0\), \(\kappa _p=\sqrt{\kappa _{1}^2+\kappa _{2}^2}.\) Let \(q=\theta \zeta \alpha _{S,R}\alpha _{R,E}P_S N_R,\) \(\varDelta _q=N_0+\mu N_0\), \(\kappa _q=\sqrt{\kappa _{3}^2+\kappa _{4}^2}\). The term \(\left| \frac{h^H_{R,E}{\hat{h}}_{R,D}}{||{\hat{h}}_{R,D}||^2}\right| ^2\) is \(\chi ^2\) Random Variable with two Degrees of Freedom. Let \(y\sim \left| \frac{h^H_{R,E}{\hat{h}}_{R,D}}{||{\hat{h}}_{R,D}||^2}\right| ^2\) and \(x = 2^\frac{C_D-R_{SOC}}{W}-1\).
As there is no eavesdropping on S-R link, we have \(Pr\left( C_{S,R}>C_{D}-R_{SOC}\right) =1\). Then,
The statistics of Pr \(\left( \frac{q y}{q y\kappa _q^2+\varDelta _q} > x \right)\) are obtained as follows:
Using above relations,
Letting \(\hat{\epsilon } = \exp \left( -\frac{\varDelta _qx}{q-q \kappa _q^2x}\right)\) and rearranging further we get,
Hence, the theorem is proved. \(\square\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K.R., Trivedi, A. Physical Layer Security for Wireless Powered Massive MIMO Decode and Forward Relay Systems with Hardware Impairments: Performance Analysis. Wireless Pers Commun 112, 1537–1547 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07114-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07114-7