Abstract
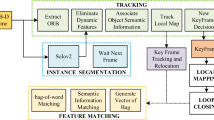
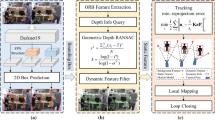
In this paper, a novel dynamic multi-object classification method is proposed based on real-time localization of a robot equipped with a vision sensor that captures a sparse three-dimensional environment. Specifically, we build upon ORB-SLAM2 and improve its formulation to better handle moving objects in a dynamic environment. We propose a feature classification algorithm for ORB (oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF) features in complex environments. Based on inter-frame texture constraints, we add the reprojection error algorithm, which can reduce the influence of illumination and dynamic objects on the simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm. We then propose a new dynamic initialization strategy and apply the proposed feature classification algorithm to the ORB-SLAM2 tracking thread. For real-world implementations, we focus on the robustness and real-time performance of dynamic target segmentation simultaneously, which cannot be satisfied by existing geometric segmentation and semantic segmentation methods. From an engineering point of view, the proposed work can quickly separate dynamic feature points based on traditional methods, which makes the proposed algorithm has better real time in practical applications. We thoroughly evaluate our approach on the TUM and KITTI benchmark database and on a real environment using the Turtlebot platform equipped with a Bumblebee camera. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method is more robust and accurate than current state-of-the-art methods in different environments.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang G, Tang W, Zeng J, Xu J, Yao E (2014) A survey of multi-robot cslam considering communication conditions. Zidonghua Xuebao/acta Automatica Sinica 40(010):2073–2088
Wen S, Hu X, Ma J, Sun F, Fang B (2019) Autonomous robot navigation using retinex algorithm for multiscale image adaptability in low-light environment. Intell Serv Robot 12:359–369
Lu Z, Hu Z, Uchimura K (2009) SLAM Estimation in Dynamic Outdoor Environments: A Review, In: Intelligent robotics and applications, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 255–267
Tian G, Liu L, Ri J, Liu Y, Sun Y (2019) Object Fusion : An object detection and segmentation framework with RGB-D SLAM and convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 345:3–14
Singandhupe A, La HM (2019) A Review of SLAM techniques and security in autonomous driving, In: Third IEEE International conference on robotic computing (IRC) 2019:602–607. https://doi.org/10.1109/IRC.2019.00122
Engel J, Schöps T, Cremers D (2014) LSD-SLAM: Large-Scale Direct Monocular SLAM, In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 834–849
Mur-Artal R, Montiel JMM, Tardós JD (2015) Orb-slam: A versatile and accurate monocular slam system. IEEE Transact Robot 31(5):1147–1163. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671
Mur-Artal R, Tardós JD (2017) ORB-SLAM2: an open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Transact Robot 33(5):1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103
Qin T, Li P, Shen S (2018) VINS-Mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Transact Robot 34(4):1004–1020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729
Wang R, Schwörer M, Cremers D (2017) Stereo DSO: Large-scale direct sparse visual odometry with stereo cameras, In: IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV) 2017:3923–3931. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.421
Xu B, Li W, Tzoumanikas D, Bloesch M, Davison A, Leutenegger S (2019) MID-Fusion: octree-based object-level multi-instance dynamic SLAM, In. International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) 2019:5231–5237. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794371
Wen S, Li P, Zhao Y, Z. H., Z. Wang, (2021) Semantic visual slam in dynamic environment. Autonomous Robots. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-021-09979-4
Xiao L, Wang J, Qiu X, Rong Z, Zou X (2019) Dynamic-SLAM: semantic monocular visual localization and mapping based on deep learning in dynamic environment. Robot Auton Sys 117:1–16
Judd KM, Gammell JD, Newman P (2018) Multimotion visual odometry (MVO): simultaneous estimation of camera and third-party motions, In: IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) 2018:3949–3956. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8594213
Kundu A, Krishna KM, Jawahar CV (2011) Realtime multibody visual SLAM with a smoothly moving monocular camera, In: International conference on computer vision 2011:2080–2087. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126482
Alcantarilla PF, Yebes JJ, Almazán J, Bergasa LM (2012) On combining visual SLAM and dense scene flow to increase the robustness of localization and mapping in dynamic environments, In: IEEE International conference on robotics and automation 2012:1290–1297. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2012.6224690
Wang Y, Huang S (2014) Towards dense moving object segmentation based robust dense RGB-D SLAM in dynamic scenarios, In: 2014 13th International conference on control automation robotics vision (ICARCV), pp. 1841–1846. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICARCV.2014.7064596
Sun D, Geißer F, Nebel B (2016) Towards effective localization in dynamic environments, In: IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) 2016:4517–4523. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2016.7759665
Zou D, Tan P (2013) CoSLAM: Collaborative Visual SLAM in Dynamic Environments. IEEE Transact Pattern Anal Machine Intell 35(2):354–366. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.104
Kim D, Kim J (2016) Effective background model-based RGB-D dense visual odometry in a dynamic environment. IEEE Transact Robot 32(6):1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2016.2609395
Kerl C, Sturm J, Cremers D (2013) Dense visual slam for rgb-d cameras, In: IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems 2013:2100–2106. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696650
Liu G, Zeng W, Feng B, Xu F (2019) Dms-slam: A general visual slam system for dynamic scenes with multiple sensors, Sensors 19 (17) . https://doi.org/10.3390/s19173714 . https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/19/17/3714
Dai W, Zhang Y, Li P, Fang Z, Scherer S (2020) Rgb-d slam in dynamic environments using point correlations. IEEE Transact Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3010942
Bescos B, Fácil JM, Civera J, Neira J (2018) DynaSLAM: tracking, mapping and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Robot Automat Lett 3(4):4076–4083. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask R-CNN, In: IEEE International conference on computer vision (ICCV) 2017:2980–2988. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.322
Yu C, Liu Z, Liu X, Xie F, Yang Y, Wei Q, Fei Q, DS-SLAM: A semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments, year=2018, In: 2018 IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), pp. 1168–1174. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2018.8593691
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transact Pattern Anal Machine Intell 39(12):2481–2495. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615
Zhang J, Henein M, Mahony R, Ila V (2020) VDO-SLAM: A visual dynamic object-aware SLAM system . arXiv:2005.11052
Schörghuber M, Steininger D, Cabon Y, Humenberger M, Gelautz M (2019) Slamantic - leveraging semantics to improve vslam in dynamic environments, In: IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision workshop (ICCVW) 2019:3759–3768. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00468
Wen S, Li P, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Sun F, Wang Z (2021) Semantic visual SLAM in dynamic environment. Autonomous Robots 45:493-504
Zhong F, Wang S, Zhang Z, Chen C, Wang Y (2018) Detect-slam: Making object detection and slam mutually beneficial, In: IEEE Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV) 2018:1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2018.00115
Rünz M, Agapito L (2017) Co-fusion: Real-time segmentation, tracking and fusion of multiple objects, In: IEEE International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) 2017:4471–4478. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2017.7989518
Palazzolo E, Behley J, Lottes P, Giguère P, Stachniss C (2019) Refusion: 3d reconstruction in dynamic environments for rgb-d cameras exploiting residuals, In: IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) 2019:7855–7862. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS40897.2019.8967590
Liu Y, Miura J (2021) Rds-slam: real-time dynamic slam using semantic segmentation methods. IEEE Access 9:23772–23785. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050617
Hassanpour H, Sedighi M, Manashty AR (2011) Video Frame’s Background modeling: reviewing the techniques. J Signal Infor Process 2(2):72–78
Yang G, Chen K, Zhou M, Xu Z, Chen Y (2007) Study on statistics iterative thresholding segmentation based on aviation image, In: Eighth ACIS International conference on software engineering, Artificial intelligence, Networking, and Parallel/Distributed computing (SNPD 2007), Vol. 2, , pp. 187–188. https://doi.org/10.1109/SNPD.2007.512
Hartley R. I, Zisserman A (2004) Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd Edition, Cambridge University Press, ISBN: 0521540518,
Mann H. B, Wald A (1942) On the choice of the number of class intervals in the application of the chi square test, The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 13(3):306–317. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2235942
Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D (2012) A benchmark for the evaluation of rgb-d slam systems, In: IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems 573–580. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2012.6385773
Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R (2012) Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite, In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 2012:3354–3361. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248074
Grupp M, (2017) evo: Python package for the evaluation of odometry and slam., https://github.com/MichaelGrupp/evo
Acknowledgements
The work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Project No. 61773333), the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Royal Society of Britain (NSFC-RS, Project No. 62111530148) and the China Scholarship Council (CSC, Project No.201908130016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, S., Liu, X., Wang, Z. et al. An improved multi-object classification algorithm for visual SLAM under dynamic environment. Intel Serv Robotics 15, 39–55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-021-00400-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11370-021-00400-8