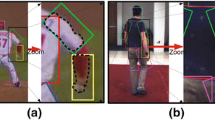
Abstract
A new model-based human body tracking framework with learning-based theory is introduced in this paper. We propose a variable structure multiple model (VSMM) framework to address challenging problems such as uncertainty of motion styles, imprecise detection of feature points, and ambiguity of joint locations. Key human joint points are detected automatically and the undetected points are estimated with Kalman filters. Multiple motion models are learned from motion capture data using a ridge regression method. The model set that covers the total motion set is designed on the basis of topological and compatibility relationships, while the VSMM algorithm is used to estimate quaternion vectors of joint rotation. Experiments using real image sequences and simulation videos demonstrate the high efficiency of our proposed human tracking framework.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mikic I, Trivedi M, Hunter E, et al. Human body model acquisition and tracking using voxel data. Int J Comput Vision, 2003, 53: 199–223
Xu X Y, Li B X. Learning motion correlation for tracking articulated human body with a Rao-Blackwellised particle filter. In: Proceedings of the International ConferenceOn Computer Vision (ICCV07). Rio de Janeiro, 2007. 1–8
Sigal L, Blan A, Black M J. HumanEva: Synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. Int J Comput Vision, 2010, 87: 1–2
Sigal L, Balan A, Black M J. HumanEva: synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. Int J Comput Vision, 2010, 87: 4–27
Tong M L. Three dimensional human motion analysis from uncalibrated monocular image sequences (in Chinese). PhD Thesis. ShangHai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2007. 71–91
Bo L F, Sminchisescu C. Structured output-associative regression. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. 2403–2410
Bo L F, Sminchisescu C. Twin Gaussian processes for structured prediction. Int J Comput Vision, 2010, 87: 28–52
Lee C S, Elgammal A. Coupled visual and kinematic manifold models for tracking. Int J Comput Vision, 2010, 87: 118–139
Li X R, Zhi X R, Zhang Y M. Multiple-model estimation with variable structure-part III: model-group switching algorithm. IEEE Trans Aero Elec Sys, 1999, 35: 225–241
Han H, Yue L C, Jiao L C, et al. Human body motion tracking based on quantum-inspired immune cloning algorithm. P SPIE, 2009, 7496: 1–8
Wang L, Tan T N, Ning H Z, et al. Silhouette analysis based gait recognition for human identification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal, 2003, 25: 1505–1518
Sandhu R, Dambreville S. A nonrigid kernel-based framework for 2D-3D pose estimation and 2D image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal, 2011, 33: 1098–1115
Gupta A, Chen T. Context and observation driven latent variable model for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR08), Anchorage, 2008. 1–8
Okada R, Soatto S. Relevant feature selection for human pose estimation and localization in cluttered images. LNCS, 2008, 5303: 434–445
Urtasun R, Darrell T. Local probabilistic regression for activity-independent human pose inference. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Anchorage, 2008. 1–8
Grauman K, Shakhnarovich G, Darrell T. Inferring 3D structure with a statistical image based shape model. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, 2003. 641–647
Li X R, Zhang Y M, Zhi X R. Multiple-model estimation with variable structure-part IV: design and evaluation of model-group switching algorithm. IEEE Trans Aero Elec Sys, 1999, 35: 242–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Tong, M., Chen, Z. et al. Variable structure multiple model for articulated human motion tracking from monocular video sequences. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 55, 1138–1150 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4529-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4529-8