Abstract
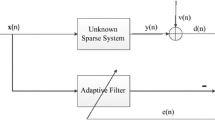
In this paper, two new blind adaptive identification and equalization algorithms based on second-order statistics are proposed. We consider a practical case where the noise statistics of each transmission channel is unknown. Resorting to the technique of antennas array, a single-input double-output channel can be obtained. We further convert the problem of blind identification into an errors-in-variables (EIV) parameter estimation problem, then we apply the normalized least-mean squares (NLMS) algorithms to tackle the problem. To improve the performance of the NLMS algorithms, we also develop a variable step-size NLMS (VSS-NLMS) algorithm that ensures the stability of the algorithm and faster convergence speed at the beginning of the iterations process. Under various practical scenarios, noise affects transmission channels; it is necessary to estimate the variance and remove the bias. By modifying the cost function, we present a bias-compensated NLMS (BC-NLMS) algorithm and a bias-compensated NLMS algorithm with variable step-size (BC-VSS-NLMS) to eliminate the bias. The proposed algorithms estimate the variances of the noise online, and therefore, the noise-induced bias can be removed. The estimate of the channel characteristics is available for equalization. Simulation results are presented to demonstrate the performance of the proposed algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azim A W, Abrar S, Zerguine A, et al. Performance analysis of a family of adaptive blind equalization algorithms for square-QAM. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 48: 163–177
Huang Y T, Benesty J. A class of frequency-domain adaptive approaches to blind multichannel identification. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2003, 51: 11–24
Sato Y. A method of self-recovering equalization for multilevel amplitude-modulation systems. IEEE Trans Commun, 1975, 23: 679–682
Godard D. Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems. IEEE Trans Commun, 1980, 28: 1867–1875
Tugnait J K. Approaches of FIR system identification with noisy data using higher order statistics. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process, 1990, 38: 1307–1317
Wang G, Kapilan B, Razul S G, et al. Blind equalization in the presence of co-channel interference based on higher-order statistics. Circ Syst Signal Process, 2018, 37: 4150–4161
Li J, Feng D Z, Li B B. A robust adaptive weighted constant modulus algorithm for blind equalization of wireless communications systems under impulsive noise environment. AEU Int J Electron Commun, 2018, 83: 150–155
Gelli G, Verde F. Two-stage interference-resistant adaptive periodically time-varying CMA blind equalization. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2002, 50: 662–672
Chang W C, Yuan J T. CMA adaptive equalization in subspace pre-whitened blind receivers. Digital Signal Process, 2019, 88: 33–40
Yilmaz B B, Erdogan A T. Compressed training adaptive equalization: algorithms and analysis. IEEE Trans Commun, 2017, 65: 3907–3921
Sun J Q, Li X G, Chen K, et al. A novel CMA+DD_LMS blind equalization algorithm for underwater acoustic communication. Comput J, 2020, 63: 974–981
Radenkovic M S, Bose T. A recursive blind adaptive identification algorithm and its almost sure convergence. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2007, 54: 1380–1388
Xie N, Hu H Y, Wang H. A new hybrid blind equalization algorithm with steady-state performance analysis. Digital Signal Process, 2012, 22: 233–237
Diversi R, Guidorzi R, Soverini U. Blind identification and equalization of two-channel FIR systems in unbalanced noise environments. Signal Process, 2005, 85: 215–225
Tong L, Xu G H, Kailath T. Blind identification and equalization based on second-order statistics: a time domain approach. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 1994, 40: 340–349
Abed-Meraim K, Moulines E, Loubaton P. Prediction error method for second-order blind identification. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45: 694–705
Ding Z. Matrix outer-product decomposition method for blind multiple channel identification. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45: 3053–3061
Xu G H, Liu H, Tong L, et al. A least-squares approach to blind channel identification. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1995, 43: 2982–2993
Giannakis G B, Halford S D. Blind fractionally spaced equalization of noisy FIR channels: direct and adaptive solutions. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45: 2277–2292
Xiang Y, Yang L, Peng D Z, et al. A second-order blind equalization method robust to ill-conditioned SIMO FIR channels. Digital Signal Process, 2014, 32: 57–66
Komatsu M, Tanabe N, Furukawa T. Direct blind equalization corresponding to noisy environment using rayleigh quotient. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Its Applications (CSPA), Penang, 2019. 35–38
Mashimo M, Komatsu M, Matsumoto H. Blind equalizer with noise reduction function. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS), Taipei, 2019. 1–2
Chen F J, Kwong S, Kok C W. Blind MMSE equalization of FIR/IIR channels using oversampling and multichannel linear prediction. ETRI J, 2009, 31: 162–172
Haykin S O. Adaptive Filter Theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 2013
Tsuda Y, Shimamura T. An improved nlms algorithm for channel equalization. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2002
Mandic D P. A generalized normalized gradient descent algorithm. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2004, 11: 115–118
Choi Y S, Shin H C, Song W J. Robust regularization for normalized LMS algorithms. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2006, 53: 627–631
Shin H C, Sayed A H, Song W J. Variable step-size NLMS and affine projection algorithms. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2004, 11: 132–135
Benesty J, Rey H, Vega L R, et al. A nonparametric VSS NLMS algorithm. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2006, 13: 581–584
Sayed A H. Normalized LMS Algorithm. Hoboken: Wiley, 2008. 178–182
Lou J, Jia L J, Tao R, et al. Distributed incremental bias-compensated RLS estimation over multi-agent networks. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 032204
Lou J, Jia L J, Wang Y N. Diffusion bias-compensated RLS estimation with quantized measurements over adaptive networks. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2016, 49: 1255–1260
Lou J, Jia L J, Ye Y Z, et al. Distributed bias-compensated recursive least squares estimation over multi-agent networks. In: Proceedings of the 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Chengdu, 2016. 7996–8001
Lou J, Jia L J, Yang Z J. Diffusion bias-compensated RLS estimation in noisy autoregressive process over adaptive networks. In: Proceedings of Society of Instrument and Control Engineers Annual Conference, Hangzhou, 2015. 308–313
Tang T, Jia L J, Lou J, et al. Adaptive EIV-FIR filtering against coloured output noise by using linear prediction technique. IET Signal Process, 2018, 12: 104–112
Fan L, Jia L J, Tao R, et al. Distributed bias-compensated normalized least-mean squares algorithms with noisy input. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 112210
Jia L J, Lou J, Yang Z J. Blind adaptive identification of 2-channel systems using bias-compensated RLS algorithm. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process, 2018, 32: 301–315
Söderström T. Errors-in-variables methods in system identification. Automatica, 2007, 43: 939–958
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41927801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Jia, L., Tao, R. et al. Blind adaptive identification and equalization using bias-compensated NLMS methods. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 152302 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3216-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3216-0