Abstract
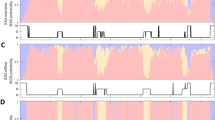
We have compared sleep staging by an automated neural network (ANN) system, BioSleep™ (Oxford BioSignals) and a human scorer using the Rechtschaffen and Kales scoring system. Sleep study recordings from 114 patients with suspected obstructed sleep apnoea syndrome (OSA) were analysed by ANN and by a blinded human scorer. We also examined human scorer reliability by calculating the agreement between the index scorer and a second independent blinded scorer for 28 of the 114 studies. For each study, we built contingency tables on an epoch-by-epoch (30 s epochs) comparison basis. From these, we derived kappa (κ) coefficients for different combinations of sleep stages. The overall agreement of automatic and manual scoring for the 114 studies for the classification {wake | light-sleep | deep-sleep | REM} was poor (median κ=0.305) and only a little better (κ=0.449) for the crude {wake | sleep} distinction. For the subgroup of 28 randomly selected studies, the overall agreement of automatic and manual scoring was again relatively low (κ=0.331 for {wake | light-sleep | deep-sleep | REM} and κ=0.505 for {wake | sleep}), whereas inter-scorer reliability was higher (κ=0.641 for {wake | light-sleep | deep-sleep | REM} and κ=0.737 for {wake | sleep}). We conclude that such an ANN-based analysis system is not sufficiently accurate for sleep study analyses using the R&K classification system.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Tarassenko L, Braithwaite E. BioSleep analysis technique for the evaluation of sleep EEG, http://www.oxford-biosignals.com/admin/files/AASM_response.pdf
References
Andreas S, von Breska B, Magnusson K, Kreuzer H (1993) Validation of automated sleep stage and apnoea analysis in suspected obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Resp J 6(1):48–52
Buchanan F, Wiltshire N, Catterall JR, Kendrick AH (2002) Analysis of sleep stage using a neural network: comparison to manual scoring in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). Thorax 57(P50):48–94
Chen W, Zhu X, Nemoto T, Kanemitsu Y, Kitamura K, Yamakoshi K (2005) Unconstrained detection of respiration rhythm and pulse rate with one under-pillow sensor during sleep. Med Biol Eng Comput 43(2):306–312
Diamantea F, Walker PP, Lowe S, Barr D, Mckown T, Calverley PMA (2002) Comparison of R&K and BioSleep systems for analysis of obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 57(P51):48–94
Gfullner F, Siemon G (2000) Studies with the fully automated EEG sleep analysis system QUISI. Pneumologie 54(12):580–583
Hirshkowitz M, Moore CA (1994) Issues in computerized polysomnography. Sleep 17(2):105–112
McGrogan N, Braithwaite E, Tarassenko L (2001) BioSleep: a comprehensive sleep analysis system. In: Proceedings of the 23rd annual international conference of the IEEE Eng Med Bio Soc 2:1608–1611
Pardey J, Roberts S, Tarassenko L, Stradling J (1996) A new approach to the analysis of the human sleep/wakefulness continuum. J Sleep Res 5:201–210
Penzel T, McNames J, Murray A, de Chazal P, Moody G, Raymond B (2002) Systematic comparison of different algorithms for apnoea detection based on electrocardiogram recordings. Med Biol Eng Comput 40(4):402–407
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Technical report, UCLA
Roberts S, Tarassenko L (1992) New method of automated sleep quantification. Med Biol Eng Comput 30:509–517
Roberts S, Tarassenko L (1995) Automated sleep EEG analysis using an RBF network. In: Applications of neural networks. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 305–322
Royston R, Aldridge M (2002) Clinical evaluation of additional single channel EEG in a home sleep studies programme. Eur Sleep Res Soc JSR 11(Suppl 1):197
Schaltenbrand N, Lengelle R, Toussaint M, Luthringer R, Carelli G, Jacqmin A, Lainey E, Muzet A, Macher JP (1996) Sleep stage scoring using the neural network model: comparison between visual and automatic analysis in normal subjects and patients. Sleep 19(1):26–35
Stores G, Braithwaite E, Crawford C (2002) Evaluation of a single channel neural network sleep analysis system. Eur Sleep Res Soc JSR 11(Suppl 1):217
Villa MP, Piro S, Dotta A, Bonci E, Scola P, Paggi B, Paglietti MG, Midulla F, Ronchetti R (1998) Validation of automated sleep analysis in normal children. Eur Respir J 11:458–461
Zamora M, Tarassenko L (1999) The study of micro-arousals using neural network analysis of the EEG. Artificial Neural Networks 7–10 September
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Professor Janet Wilson and Mr. Mohamed Reda for recruiting the patients for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caffarel, J., Gibson, G.J., Harrison, J.P. et al. Comparison of manual sleep staging with automated neural network-based analysis in clinical practice. Med Bio Eng Comput 44, 105–110 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-005-0002-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-005-0002-4