Abstract
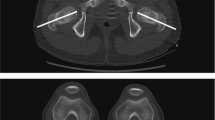
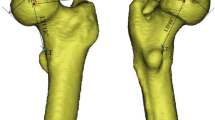
This study provides a robust measuring method of the femoral neck anteversion angle for use in a total hip replacement pre-planning program. The femora of 24 patients (69.3 ± 6.3 years old) were CT-scanned and converted into three-dimensionally volume-rendered models in ORTHODOC® (ISS Inc., CA, USA) which is the pre-planning software for ROBODOC surgery. The Mod.ISS method (the modified ISS method), designed by authors, measures the anteversion angle of the proximal-most femoral neck confluence on the plane perpendicular to the femoral mechanical axis. 3D FNC method proposed by the authors of the present study involves measurement of the anteversion angle of three-dimensional femoral neck center on a plane perpendicular to the posterior femoral plane and parallel to the posterior condylar axis. Here, we found that interobserver reproducibility was 1.8°(SD = 1.3) for the Mod.ISS method and 2.4˚(SD = 1.9) for the proposed 3D FNC method. The anteversion angle of the local femoral neck axis was measured as θ˚ = 25.3(L/D) − 5.4 in L/D = 0.1 ∼ 0.6, where L/D is distance (L) from the proximal-most neck confluence along the femoral mechanical axis, normalized with respect to the diameter of the femoral head (D). At L/D = 0.5, the anteversion angle of the femoral neck axis was coincident with the average femoral neck anteversion determined by the 3D FNC method. We conclude that the 3D FNC method is a gold standard for measuring the femoral neck anteversion applicable during both pre-operative and post-operative stages, because its femoral neck center can be determined in three-dimensional space during both stages.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel MF, Sutherland DH, Wenger DR, Mubarak SJ (1994) Evaluation of CT scans and 3-D reformatted images for quantitative assessment of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 14(1):48–53
Cheng XG, Nicholson PH, Boonen S, Brys P, Lowet G, Nijs J, Dequeker J. (1997) Effects of anteversion on femoral bone mineral density and geometry measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: a cadaver study. Bone 21(1):113–117
Cibulka MT (2004) Determination and significance of femoral neck anteversion. Phys Ther 84(6):550–558
Davids JR, Marshall AD, Blocker ER, Frick SL, Blackhurst DW, Skewes E (2003) Femoral anteversion in children with cerebral palsy. Assessment with two and three-dimensional computed tomography scans. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85(3):481–488
Gill HS, Alfaro-Adrian J, Alfaro-Adrian C, McLardy-Smith P, Murray DW (2002) The effect of anteversion on femoral component stability assessed by radiostereometric analysis. J Arthroplasty 17(8):997–1005
Heller MO, Bergmann G, Deuretzbacher G, Claes L, Haas NP, Duda GN (2001) Influence of femoral anteversion on proximal femoral loading: measurement and simulation in four patients. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 16(8):644–649
Hoiseth A, Reikeras O, Fonstelien E (1989) Evaluation of three methods for measurement of femoral neck anteversion. Femoral neck anteversion, definition, measuring methods and errors. Acta Radiol 30(1):69–73
Khang G, Choi K, Kim C S, Yang JS, Bae TS (2003) A study of Korean femoral geometry. Clin Orthop Relat Res 406:116–122
Kim JS, Park TS, Park SB, Kim IY, Kim SI (2000a) Measurement of femoral neck anteversion in 3D. Part1: 3D imaging method. Med Biol Eng Comput 38(6):603–609
Kim JS, Park TS, Park SB, Kim IY, Kim SI (2000b) Measurement of femoral neck anteversion in 3D. Part 2: 3D modelling method. Med Biol Eng Comput 38(6):610–616
Kingsley PC, Olmsted KL (1948) A study to determine the angle of anteversion of the neck of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 30:745–751
Kuo TY, Skedros JG, Bloebaum RD (2003) Measurement of femoral anteversion by biplane radiography and computed tomography imaging: comparison with an anatomic reference. Invest Radiol 38(4):221–229
Mahaisavariya B, Sitthiseripratip K, Tongdee T, Bohez EL, Vander Sloten J, Oris P (2002) Morphological study of the proximal femur: a new method of geometrical assessment using 3-dimensional reverse engineering. Med Eng Phys 24(9):617–622
Miller F, Merlo M, Liang Y, Kupcha P, Jamison J, Harcke HT (1993) Femoral version and neck shaft angle. J Pediatr Orthop 13(3):382–388
Murphy SB, Simon SR, Kijewski PK, Wilkinson RH, Griscom NT (1987) Femoral anteversion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(8):1169–1176
Ruwe PA, Gage JR, Ozonoff MB, DeLuca PA (1992) Clinical determination of femoral anteversion. A comparison with established techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am 74(6):820–830
Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E (1998) A comparison of alternative methods of measuring femoral anteversion. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22(4):610–614
Tonnis D, Heinecke A (1999) Acetabular and femoral anteversion: relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81(12):1747–1770
Umeda N, Saito M, Sugano N, Ohzono K, Nishii T, Sakai T, Yoshikawa H, Ikeda D, Murakami A (2003) Correlation between femoral neck version and strain on the femur after insertion of femoral prosthesis. J Orthop Sci 8(3):381–386
Yoshioka Y, Siu D, Cooke TD (1987) The anatomy and functional axes of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69(6):873–880
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported by Chonnam National University in 2005, and the second stage of Brain Korea 21 Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0148-8
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Oh, S.H., Seon, J.K. et al. 3D femoral neck anteversion measurements based on the posterior femoral plane in ORTHODOC® system. Med Bio Eng Comput 44, 895–906 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0104-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0104-7