Abstract
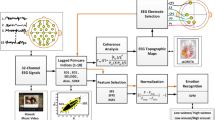
EEG signals have been widely explored in emotional processing analyses, both in time and frequency domains. However, in such studies, habituation phenomenon is barely considered in the discrimination of different emotional responses. In this work, spectral features of the event-related potentials (ERPs) are studied by means of event-related desynchronization/synchronization computation. In order to determine the most relevant ERP features for distinguishing how positive and negative affective valences are processed within the brain, support vector machine-recursive feature elimination is employed. The proposed approach was applied for investigating in which way the familiarity of stimuli affects the affective valence processing as well as which frequency bands and scalp regions are more involved in this process. In a group composed of young adult women, results prove that parietooccipital region and theta band are especially involved in the processing of novelty in emotional stimuli. Furthermore, the proposed method has shown to perform successfully using a moderated number of trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCI:
-
Brain–computer interface
- ERPs:
-
Event-related potentials
- ERD/ERS:
-
Event-related desynchronization/synchronization
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- SVM-RFE:
-
Support vector machine-recursive feature elimination
- IAPS:
-
International affective picture system
- NNC:
-
Novel negative condition
- NPC:
-
Novel positive condition
- FNC:
-
Familiar negative condition
- FPC:
-
Familiar positive condition
- LR:
-
Left–right
- FP:
-
Frontal–parietooccipital
- LOO:
-
Leave one out
References
Aftanas LI, Varlamow AA, Pavlov SV, Makhnev VP, Reva NV (2001) Affective picture processing: event-related synchronization within individually defined human theta band is modulated by valence dimension. Neurosci Lett 303:115–118
Bradley MM, Lang PJ, Cuthbert BN (1993) Emotion, novelty, and the startle reflex: habituation in humans. Behav Neurosci 107:970–980
Carretié L, Hinojosa JA, Mercado F (2003) Cerebral patterns of attentional habituation to emotional visual stimuli. Psychophysiology 40:381–388
Cesarei AD, Codispoti M (2011) Affective modulation of the LPP and alpha-ERD during picture viewing. Psychophysiology 48:1397–1404
Codispoti M, Ferrari V, Bradley MM (2007) Repetition and event-related potentials: distinguishing early and late processes in affective picture perception. J Cogn Neurosci 19:577–586
Ferrari V, Bradley MM, Codispoti M, Lang PJ (2011) Repetitive exposure: brain and reflex measures of emotion and attention. Psychophysiology 48:515–522
Frantzidis CA, Bratsas C, Papadelis CL, Konstantinidis E, Pappas C, Bamidis PD (2010) Toward emotion aware computing: an integrated approach using multichannel neurophysiological recordings and affective visual stimuli. IEEE Trans Inf Technol B 14:589–597
Fuentes A, Farina D, Dremstrup K (2010) Comparison of feature selection and classification methods for a brain–computer interface driven by non-motor imagery. Med Biol Eng Comput 48:123–132
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach Learn 46:389–422
Hidalgo-Muñoz AR, López MM, Santos IM, Pereira AT, Vázquez-Marrufo M, Galvao-Carmona A, Tomé AM (2013) Application of SVM-RFE on EEG signals for detecting the most relevant scalp regions linked to affective valence processing. Expert Syst Appl 40:2102–2108
Huang D, Guan C, Ang KK, Zhang H, Pan Y (2012) Asymmetric spatial pattern for EEG-based emotion detection. In: World Congress on Computational Intelligence. WCCI 2012. IEEE
Klados MA, Frantzidis C, Vivas AB, Papadelis C, Lithari C, Pappas C, Bamidis PD (2009) A framework combining delta event-related oscillations (EROs) and synchronisation effects (ERD/ERS) to study emotional processing. Comput Intell Neurosci 2009, Article ID 549419. doi:10.1155/2009/549419
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (2008) International affective picture system (IAPS): instruction manual and affective ratings. Technical Report A-8, The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida
Lithari C, Frantzidis C, Papadelis C, Vivas AB, Klados M, Kourtidou-Papadeli C, Pappas C, Ioannides A, Bamidis P (2010) Are females more responsive to emotional stimuli? A neurophysiological study across arousal and valence dimensions. Brain Topogr 23:27–40
López MM, Ramírez J, Górriz JM, Álvarez I, Salas-Gonzalez D, Chaves R (2009) SVM-based CAD system for early detection of the Alzheimer’s disease using kernel PCA and LDA. Neurosci Lett 464:233–238
Macas M, Vavrecka M, Gerla V, Lhotska, L (2009) Classification of the emotional states based on the EEG signal processing. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Applications in Biomedicine, Larnaca, Cyprus, pp 1–4
Mu Y, Fan Y, Mao L, Han S (2008) Event-related theta and alpha oscillations mediate empathy for pain. Brain Res 1234:128–136
Nielen M, Heslenfeld D, Heinen K, Strien JV, Witter M, Jonker C, Veltman D (2009) Distinct brain systems underlie the processing of valence and arousal of affective pictures. Brain Cogn 71:387–396
Olofsson JK, Nordin S, Sequeira H, Polich J (2008) Affective picture processing: an integrative review of ERP findings. Biol Psychol 77:247–265
Pfurtscheller G, Da Silva FHL (1999) Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1842–1857
Rankin CH, Abrams T, Barry RJ, Bhatnagar S, Clayton D, Colombo J, Coppola G, Geyer MA, Glanzman DL, Marsland S, McSweeney F, Wilson DA, Wu CF, Thompson RF (2009) Habituation revisited: an updated and revised description of the behavioral characteristics of habituation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92:135–138
Rozenkrants B, Olofsson JK, Polich J (2008) Affective visual event- related potentials: arousal, valence, and repetition effects for normal and distorted pictures. Int J Psychophysiol 67:114–123
Shawe-Taylor J, Sun S (2011) A review of optimization methodologies in support vector machines. Neurocomputing 74(17):3609–3618
Sun S (2008) The extreme energy ratio criterion for EEG feature extraction. Lect Notes Comput Sci 5164:919–928
Sun S (2010) Extreme energy difference for feature extraction of EEG signals. Expert Syst Appl 37(6):4350–4357
Sun S, Zhang C (2006) Adaptive feature extraction for EEG signal classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 44:931–935
Tomé AM, Hidalgo-Muñoz AR, López MM, Teixeira AR, Santos IM, Pereira AT, Vázquez-Marrufo M, Lang EW (2013) Feature extraction and classification of biosignals: emotion valence detection from EEG signals. In: proceedings of International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal. BIOSIGNALS 2013, pp 54–60
Weierich MR, Wright CI, Negreira A, Dickerson BC, Barrett LF (2010) Novelty as a dimension in the affective brain. Neuroimage 49:2871–2878
Xu H, Plataniotis KN (2012) Affect recognition using EEG signal. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing. Banff, Canada, pp 299–304
Yoon HJ, Chung SY (2011) EEG spectral analysis in valence and arousal dimensions of emotion. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Kintex, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, pp 1319–1322
Acknowledgments
This work is partially funded by FEDER through the Operational Program Competitiveness Factors—COMPETE and by National Funds through FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology in the context of the project FCOMP-01-0124-FEDER-022682 (FCT reference PEst-C/EEI/UI0127/2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidalgo-Muñoz, A.R., López, M.M., Galvao-Carmona, A. et al. EEG study on affective valence elicited by novel and familiar pictures using ERD/ERS and SVM-RFE. Med Biol Eng Comput 52, 149–158 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1126-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1126-6