Abstract
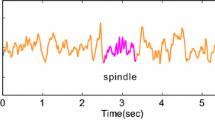
Detection of sleep spindles is of major importance in the field of sleep research. However, manual scoring of spindles on prolonged recordings is very laborious and time-consuming. In this paper, we introduce a new algorithm based on synchrosqueezing transform for detection of sleep spindles. Synchrosqueezing is a powerful time–frequency analysis tool that provides precise frequency representation of a multicomponent signal through mode decomposition. Subsequently, the proposed algorithm extracts and compares the basic features of a spindle-like activity with its surrounding, thus adapting to an expert’s visual criteria for spindle scoring. The performance of the algorithm was assessed against the spindle scoring of one expert on continuous electroencephalogram sleep recordings from two subjects. Through appropriate choice of synchrosqueezing parameters, our proposed algorithm obtained a maximum sensitivity of 96.5 % with 98.1 % specificity. Compared to previously published works, our algorithm has shown improved performance by enhancing the quality of sleep spindle detection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babadi B, McKinney SM, Tarokh V, Ellenbogen JM (2012) DiBa: a data-driven Bayesian algorithm for sleep spindle detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:483–493. doi:10.1109/TBME.2011.2175225
Berger H (1933) Uber das Elektroenkephalogramm des Menschen. Sechste mitteilung. Arch Phychiatr Nervenkr 99:555–574
Boivin DB, Boudreau P, Tremblay GM (2012) Phototherapy and orange-tinted goggles for night-shift adaptation of police officers on patrol. Chronobiol Int 29:629–640
Campbell K, Kumar A, Hofman W (1980) Human and automatic validation of a phase-locked loop spindle detection system. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 48:602–605
Clemens Z, Fabo D, Halasz P (2005) Overnight verbal memory retention correlates with the number of sleep spindles. Neuroscience 132:529–535. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.011
Daubechies I, Lu J, Wu HT (2011) Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: an empirical mode decomposition-like tool. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 30:243–261. doi:10.1016/j.acha.2010.08.002
Devuyst S, Dutoit T, Stenuit P, Kerkhofs M (2011) Automatic sleep spindles detection—overview and development of a standard proposal assessment method. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:1713–1716. doi:10.1109/iembs.2011.6090491
Diekelmann S, Born J (2010) The memory function of sleep. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:114–126. doi:10.1038/nrn2762
Duman F, Erdamar A, Erogul O, Telatar Z, Yetkin S (2009) Efficient sleep spindle detection algorithm with decision tree. Expert Syst Appl 36:9980–9985. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2009.01.061
Durka PJ, Matysiak A, Montes EM, Sosa PV, Blinowska KJ (2005) Multichannel matching pursuit and EEG inverse solutions. J Neurosci Methods 148:49–59. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.04.001
Estevez PA, Held CM, Holzmann CA, Perez CA, Perez JP, Heiss J, Garrido M, Peirano P (2002) Polysomnographic pattern recognition for automated classification of sleep-waking states in infants. Med Biol Eng Comput 40:105–113
Fogel SM, Smith CT (2011) The function of the sleep spindle: a physiological index of intelligence and a mechanism for sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:1154–1165. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.12.003
Grigg-Damberger M, Gozal D, Marcus CL, Quan SF, Rosen CL, Chervin RD, Wise M, Picchietti DL, Sheldon SH, Iber C (2007) The visual scoring of sleep and arousal in infants and children. J Clin Sleep Med 3:201–240
Güneş S, Dursun M, Polat K, Yosunkaya Ş (2011) Sleep spindles recognition system based on time and frequency domain features. Expert Syst Appl 38:2455–2461. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.08.034
Hao YL, Ueda Y, Ishii N (1992) Improved procedure of complex demodulation and an application to frequency analysis of sleep spindles in EEG. Med Biol Eng Comput 30:406–412
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Q, Yen N-C, Tung CC, Liu HH (1998) The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc R Soc Lond. Ser A 454:903–995 doi:10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
Huupponen E, Gomez-Herrero G, Saastamoinen A, Varri A, Hasan J, Himanen SL (2007) Development and comparison of four sleep spindle detection methods. Artif Intell Med 40:157–170. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2007.04.003
Huupponen E, Himanen SL, Hasan J, Varri A (2003) Automatic analysis of electro-encephalogram sleep spindle frequency throughout the night. Med Biol Eng Comput 41:727–732
Huupponen E, Varri A, Himanen SL, Hasan J, Lehtokangas M, Saarinen J (2000) Optimization of sigma amplitude threshold in sleep spindle detection. J Sleep Res 9:327–334
Iber C, Ancoli-Israel S, Chesson A Jr, Quan SF (2007) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Westchester, IL
Jaleel A, Ahmed B, Tafreshi R, Boivin DB, Streletz L, Haddad N (2014) Improved spindle detection through intuitive pre-processing of electroencephalogram. J Neurosci Methods 233:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.05.009
Klemm M, Haueisen J, Ivanova G (2009) Independent component analysis: comparison of algorithms for the investigation of surface electrical brain activity. Med Biol Eng Comput 47:413–423. doi:10.1007/s11517-009-0452-1
Ktonas PY, Golemati S, Xanthopoulos P, Sakkalis V, Ortigueira MD, Tsekou H, Zervakis M, Paparrigopoulos T, Bonakis A, Economou NT, Theodoropoulos P, Papageorgiou SG, Vassilopoulos D, Soldatos CR (2009) Time-frequency analysis methods to quantify the time-varying microstructure of sleep EEG spindles: possibility for dementia biomarkers? J Neurosci Methods 185:133–142. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.09.001
Loomis AL, Harvey EN, Hobart G (1935) Potential rhythms of the cerebral cortex during sleep. Science (New York, NY) 81:597–598. doi:10.1126/science.81.2111.597
Meignen S, Oberlin T, McLaughlin S (2012) A new algorithm for multicomponent signals analysis based on synchrosqueezing: with an application to signal sampling and denoising. IEEE Trans Signal Process 60:5787–5798. doi:10.1109/TSP.2012.2212891
Noachtar S, Binnie C, Ebersole J, Mauguiere F, Sakamoto A, Westmoreland B (1999) A glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and proposal for the report form for the EEG findings. The international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 52:21–41
Nobach H, Tropea C, Cordier L, Bonnet J-P, Delville J, Lewalle J, Farge M, Schneider K, Adrian R (2007) Review of some fundamentals of data processing. In: Tropea C, Yarin A, Foss J (eds) Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1337–1398
Nonclercq A, Urbain C, Verheulpen D, Decaestecker C, Van Bogaert P, Peigneux P (2013) Sleep spindle detection through amplitude-frequency normal modelling. J Neurosci Methods 214:192–203. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.01.015
Page ES (1954) Continuous inspection schemes. Biometrika 41:100–115. doi:10.1093/biomet/41.1-2.100
Petit D, Gagnon JF, Fantini ML, Ferini-Strambi L, Montplaisir J (2004) Sleep and quantitative EEG in neurodegenerative disorders. J Psychosom Res 56:487–496. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychores.2004.02.001
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Public Health Service, US Government Printing Office, Washington DC
Schabus M, Gruber G, Parapatics S, Sauter C, Klosch G, Anderer P, Klimesch W, Saletu B, Zeitlhofer J (2004) Sleep spindles and their significance for declarative memory consolidation. Sleep 27:1479–1485
Schonwald SV, de Santa-Helena EL, Rossatto R, Chaves ML, Gerhardt GJ (2006) Benchmarking matching pursuit to find sleep spindles. J Neurosci Methods 156:314–321. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.01.026
Schönwald SV, Gerhardt GJL, de Santa-Helena EL, Chaves MLF (2003) Characteristics of human EEG sleep spindles assessed by Gabor transform. Physica A 327:180–184. doi:10.1016/S0378-4371(03)00473-4
Sciarretta G, Bricolo A (1970) Automatic detection of sleep spindles by analysis of harmonic components. Med Biol Eng 8:517–519
Shimada T, Shiina T, Saito Y (2000) Detection of characteristic waves of sleep EEG by neural network analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 47:369–379. doi:10.1109/10.827301
Thakur G, Brevdo E, Fuckar NS, Wu H-T (2013) The synchrosqueezing algorithm for time-varying spectral analysis: robustness properties and new paleoclimate applications. Signal Process 93:1079–1094. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.11.029
Ventouras EM, Monoyiou EA, Ktonas PY, Paparrigopoulos T, Dikeos DG, Uzunoglu NK, Soldatos CR (2005) Sleep spindle detection using artificial neural networks trained with filtered time-domain EEG: a feasibility study. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 78:191–207. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.02.006
Wilson SB, Harner RN, Duffy FH, Tharp BR, Nuwer MR, Sperling MR (1996) Spike detection. I. Correlation and reliability of human experts. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 98:186–198
Yi-Hsin C, Hau-Tieng W, Shu-Shya H, Chi-Tai K, Yung-Hsin Y (2011) ECG-derived respiration and instantaneous frequency based on the synchrosqueezing transform: application to patients with atrial fibrillation. arXiv:1105.1571 [math.NA]
Zeitlhofer J, Gruber G, Anderer P, Asenbaum S, Schimicek P, Saletu B (1997) Topographic distribution of sleep spindles in young healthy subjects. J Sleep Res 6:149–155
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabir, M.M., Tafreshi, R., Boivin, D.B. et al. Enhanced automated sleep spindle detection algorithm based on synchrosqueezing. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 635–644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1265-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1265-z