Abstract
Purpose
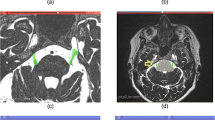
Visualization of pathological contact between cranial nerves and vascular structures at the surface of the brainstem is important for diagnosis and treatment of neurovascular compression (NVC) syndromes. We developed a method for improved visualization of this abnormality.
Methods
Distance fields were computed using preoperative MRI scans of individuals with NVC syndromes to support the topological representation of brainstem surface structures with quantitative information. Polygonal models of arteries, cranial nerves and the brainstem were generated using segmented T2 weighted MR data. After color-coding the polygonal models with the respective distances, enhanced color visualization of vessel-nerve locations with possible contacts was achieved.
Results
The proposed method was implemented and applied to surgical planning in a dozen cases of NVC syndrome. Two selected cases were chosen to demonstrate the feasibility and subjective improvement provided by our visualization technique. Expert neurosurgeons found the improvement valuable and useful for these cases.
Conclusion
Color-encoded distance information significantly improves the perceptibility of potential nerve-vessel contacts. This method contributes to a better understanding of the complex anatomical situation at the surface of the brainstem and assists in planning of surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto H, Nagaoka T, Nariai T, Takada Y, Ohno K, Yoshino N (2002) Preoperative evaluation of neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia by use of three-dimensional reconstruction from two types of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 51(4): 956–961
Barker FG II, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Shields PT, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1995) Microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 82: 201–210
Boecher-Schwarz HG, Bruehl K, Kessel G, Guenthner M, Perneczky A, Stoeter P (1998) Sensitivity and specificity of MRA in the diagnosis of neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a correlation of MRA and surgical findings. Neuroradiology 40: 88–95
De Ridder D, Moller A, Verlooy J, Cornelissen M, De Ridder L (2002) Is the root entry/exit zone important in microvascular compression syndromes?. Neurosurgery 51: 427–434
Dijkstra EW (1959) A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numerische Mathematik 1: 269–271
Hadwiger M, Sigg C, Scharsach H, Bühler K, Gross M (2005) Real-time ray-casting and advanced shading of discrete isosurfaces. Comput Graph Forum 24(3): 303–312
Hastreiter P, Naraghi R, Tomandl B, Bauer M, Fahlbusch R (2002) 3D-Visualization and registration for neurovascular compression syndrome analysis. MICCAI 396–403
Hastreiter P, Naraghi R, Tomandl B, Bonk A, Fahlbusch R (2003) Analysis and 3-dimensional visualization of neurovascular compression syndromes. Acad Radiol 10(12): 1369–1379
Hastreiter P, Vega-Higuera F, Tomandl B, Fahlbusch R, Naraghi R (2004) Advanced and standardized evaluation of neurovascular compression syndromes. SPIE Med Imaging 5367: 267–274
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26(1): 159–162
Jannetta PJ (1980) Neurovascular compression in cranial nerve and systemic disease. Ann Surg 192: 518–525
Kin T, Oyama H, Kamada K, Aoki S, Ohtomo K, Saito N (2009) Prediction of surgical view of neurovascular decompression using interactive computer graphics. Neurosurgery 65(1): 121–128
Kobbelt L, Campagna S, Vorsatz J, Seidel H-P (1998) Interactive multi-resolution modeling on arbitrary meshes. SIGGRAPH 105–114
Krüger J, Westermann R (2003) Acceleration techniques for GPU-based volume rendering. IEEE Vis 287–292
Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. SIGGRAPH 163–169
McLaughlin MR, Jannetta PJ, Clyde BL, Subach BR, Comey CH, Resnick DK (1999) Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves: lessons learned after 4,400 operations. J Neurosurg 90: 1–8
Miller J, Acar F, Hamilton B, Burchiel K (2008) Preoperative visualization of neurovascular anatomy in trigeminal. J Neurosurg 108(3): 477–482
Mortensen EN, Barrett WA (1998) Interactive segmentation with intelligent scissors. Graph Models Image Process 60(5): 349–384
Naraghi R, Hastreiter P, Tomandl B, Bonk A, Huk W, Fahlbusch R (2004) Three dimensional visualization of neurovascular relationship in the posterior fossa. Technique and clinical application. J Neurosurg 100(6): 1025–1035
Naraghi R, Tanrikulu L, Troescher-Weber R, Bischoff B, Hecht M, Buchfelder M, Hastreiter P (2007) Classification of neurovascular compression in typical hemifacial spasm: three-dimensional visualization of the facial and the vestibulocochlear nerves. J Neurosurg 107(6): 1154–1163
Ni S, Su W, Li X, Zeng Q, Liu Y, Zhu S, Wu C (2009) Enhanced three-dimensional fast spoiled gradient recalled MRI combined with magnetic resonance angiography for preoperative assessment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci 16(12): 1555–1559
Peker S, Dinçer A, Necmettin Pamir M. (2009) Vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve is a frequent finding in asymptomatic individuals: 3-T MR imaging of 200 trigeminal nerves using 3D CISS sequences. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151(9): 1081–1088
Raslan AM, DeJesus R, Berk C, Zacest A, Anderson JC, Burchiel KJ (2009) Sensitivity of high-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography and three-dimensional spoiled-gradient recalled imaging in the prediction of neurovascular compression in patients with hemifacial spasm. J Neurosurg 111(4): 733–736
Satoh T, Omi M, Nabeshima M, Onoda K, Date I (2009) Severity analysis of neurovascular contact in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: assessment with the inner view of the 3D MR cisternogram and angiogram fusion imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 30(3): 603–607
Süßmuth J, Piazza A, Enders F, Naraghi R, Greiner G, Hastreiter P (2009) Analysis and visualization of nerve vessel contacts for neurovascular decompression. Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin (BVM) 21–25
Takao T, Oishi M, Fukuda M, Ishida G, Sato M, Fujii Y (2008) Three-dimensional visualization of neurovascular compression: presurgical use of virtual endoscopy created from magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery 63: 139–145
Tanrikulu L, Hastreiter P, Troescher-Weber R, Buchfelder M, Naraghi R (2007) Intraoperative three-dimensional visualization in microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg 107(6): 1137–1143
Tessmann M, Eisenacher C, Enders F, Stamminger M, Hastreiter P (2008) GPU accelerated normalized mutual information and B-spline transformation. EG VCBM 117–124
Vega-Higuera F, Hastreiter P, Fahlbusch R, Greiner G (2005) High performance volume splatting for visualization of neurovascular data. IEEE Vis 271–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Süßmuth, J., Protogerakis, WD., Piazza, A. et al. Color-encoded distance visualization of cranial nerve-vessel contacts. Int J CARS 5, 647–654 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0410-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-010-0410-2