Abstract
Purpose
The goal of this study was to investigate the impact of reduced k-space sampling rates on the visualization of a moving MR-compatible puncture needle and to demonstrate the feasibility of keyhole imaging in interventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Material and methods
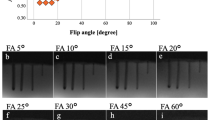
All experiments were performed in an open 1.0 Tesla MRI. MR images of a moving puncture needle were taken with different keyhole sampling rates from 15–100%, in 10% increments. The needle was submerged in a water-filled basin and was imaged in motion with a T1-weighted gradient-echo sequence with an initial acquisition rate of 1.4 s per image. An apparatus operated by a compressor unit enabled needle rotation and ensured reproducible needle movements. The median forward velocity of the needle tip was 2 cm/s. To evaluate the depiction of the needle, artifact diameter of the needle, contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and needle tip profiles (delineation) were measured.
Results
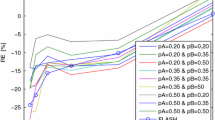
The needle position was determined with an longitudinal error of 3 mm and a transverse error of 0.8 mm with respect to the needle’s orientation and the theoretically calculated trajectory. No significant correlation was found between the CNR and velocity. A reduction of k-space update rates caused neither a significant reduction of CNR nor a significant increase in artifact diameter or blurring of the needle profile.
Conclusion
The application of keyhole imaging with update rates of greater than 15% is sufficient for the MR guidance of interventions with an signal-to-noise ratio >9 of the surrounding tissue and a target accuracy of >1 mm. Keyhole imaging can increase temporal resolution while ensuring unimpaired spatial resolution and image quality of the depicted instrument.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clasen S, Pereira PL (2008) Magnetic resonance guidance for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(2): 421–433
Carrino JA, Jolesz FA (2005) MRI-guided interventions. Acad Radiol 12(9): 1063–1064
Edelman RR, Wielopolski P, Schmitt F (1994) Echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 192(3): 600–612
Bishop JE, Santyr GE, Kelcz F, Plewes DB (1997) Limitations of the keyhole technique for quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 7(4): 716–723
Yutzy SR, Duerk JL (2008) Pulse sequences and system interfaces for interventional and real-time MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(2): 267–275
Yerly J, Lauzon ML, Chen HS, Frayne R (2010) A simulation-based analysis of the potential of compressed sensing for accelerating passive MR catheter visualization in endovascular therapy. Magn Reson Med 63(2): 473–483
Chen Z, Zhang J, Pang K (2005) Adaptive K-space updating methods for dynamic MRI sequence estimation. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 7: 7401–7404
Busch M, Bornstedt A, Wendt M, Duerk JL, Lewin JS, Gronemeyer D (1998) Fast “real time” imaging with different k-space update strategies for interventional procedures. J Magn Reson Imaging 8(4): 944–954
Shankaranarayanan A, Wendt M, Aschoff AJ, Lewin JS, Duerk JL (2001) Radial keyhole sequences for low field projection reconstruction interventional MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(1): 142–151
Willinek WA, Hadizadeh DR, von Falkenhausen M, Urbach H, Hoogeveen R, Schild HH, Gieseke J (2008) 4D time-resolved MR angiography with keyhole (4D-TRAK): more than 60 times accelerated MRA using a combination of CENTRA, keyhole, and SENSE at 3.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(6): 1455–1460
Beranek-Chiu J, Froehlich JM, Wentz KU, Doert AN, Zollikofer CL, Eckhardt BP (2009) Improved vessel delineation in keyhole time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiography using a gadolinium doped flush. J Magn Reson Imaging 29(5): 1147–1153
Hadizadeh DR, Gieseke J, Beck G, Geerts L, Kukuk GM, Bostrom A, Urbach H, Schild HH, Willinek WA (2010) View-sharing in keyhole imaging: partially compressed central k-space acquisition in time-resolved MRA at 3.0T. Eur J Radiol [Epub ahead of print]
Duerk JL, Lewin JS, Wu DH (1996) Application of keyhole imaging to interventional MRI: a simulation study to predict sequence requirements. J Magn Reson Imaging 6(6): 918–924
Wonneberger U, Schnackenburg B, Streitparth F, Walter T, Rump J, Teichgraber UK (2010) Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging-compatible needles and interactive sequences for musculoskeletal interventions using an open high-field magnetic resonance imaging scanner. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33(2): 346–351
Streitparth F, Walter T, Wonneberger U, Chopra S, Wichlas F, Wagner M, Hermann KG, Hamm B, Teichgraber U (2010) Image-guided spinal injection procedures in open high-field MRI with vertical field orientation: feasibility and technical features. Eur Radiol 20(2): 395–403
Terashima M, Hyon M, de la Pena-Almaguer E, Yang PC, Hu BS, Nayak KS, Pauly JM, McConnell MV (2005) High-resolution real-time spiral MRI for guiding vascular interventions in a rabbit model at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 22(5): 687–690
Fischer U, Schwethelm L, Baum FT, Luftner-Nagel S, Teubner J (2009) Effort, accuracy and histology of MR-guided vacuum biopsy of suspicious breast lesions–retrospective evaluation after 389 interventions. Rofo 181(8): 774–781
Langen HJ, Stutzer H, Kugel H, Krug B, Hesselmann V, Schulte O, Walter C, Landwehr P (2000) Precision of MRI-guided needle placement–experimental results. Rofo 172(11): 922–926
Perlet C, Schneider P, Amaya B, Grosse A, Sittek H, Reiser MF, Heywang-Kobrunner SH (2002) MR-guided vacuum biopsy of 206 contrast-enhancing breast lesions. Rofo 174(1): 88–95
Stattaus J, Maderwald S, Baba HA, Gerken G, Barkhausen J, Forsting M, Ladd ME (2008) MR-guided liver biopsy within a short, wide-bore 1.5 Tesla MR system. Eur Radiol 18(12): 2865–2873
Moche M, Zajonz D, Kahn T, Busse H (2010) MRI-guided procedures in various regions of the body using a robotic assistance system in a closed-bore scanner: preliminary clinical experience and limitations. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(4): 964–974
Testing, ASTM (2001) Standard test method for evaluation of MR-image artifacts from passive implants. In: Annual book of ASTM standards. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
Gurleyik K, Haacke EM (2002) Quantification of errors in volume measurements of the caudate nucleus using magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 15(4): 353–363
Davis SC, Pogue BW, Dehghani H, Paulsen KD (2005) Contrast-detail analysis characterizing diffuse optical fluorescence tomography image reconstruction. J Biomed Opt 10(5): 050501
Leung DA, Debatin JF, Wildermuth S, Heske N, Dumoulin CL, Darrow RD, Hauser M, Davis CP, von Schulthess GK (1995) Real-time biplanar needle tracking for interventional MR imaging procedures. Radiology 197(2): 485–488
Scott AD, Keegan J, Firmin DN (2009) Motion in cardiovascular MR imaging. Radiology 250(2): 331–351
Yang RK, Roth CG, Ward RJ, deJesus JO, Mitchell DG (2010) Optimizing abdominal MR imaging: approaches to common problems. Radiographics 30(1): 185–199
Itou D, Nagasaka T, Yanagawa I, Yoshida S, Takase K (2008) Use of the keyhole technique for 3.0T MRI dynamic imaging. Jpn J Radiol Technol 64(12): 1562–1567
Ruhl KM, Katoh M, Langer S, Mommertz G, Guenther RW, Niendorf T, Spuentrup E (2008) Time-resolved 3D MR angiography of the foot at 3 T in patients with peripheral arterial disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190(6): W360–W364
Suga M, Matsuda T, Komori M, Minato K, Takahashi T (1999) Keyhole method for high-speed human cardiac cine MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 10(5): 778–783
Patel NK, Khan S, Gill SS (2008) Comparison of atlas- and magnetic-resonance-imaging-based stereotactic targeting of the subthalamic nucleus in the surgical treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 86(3): 153–161
Puri BK (2006) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging sinc-interpolation-based subvoxel registration and semi-automated quantitative lateral ventricular morphology employing threshold computation and binary image creation in the study of fatty acid interventions in schizophrenia, depression, chronic fatigue syndrome and Huntington’s disease. Int Rev Psychiatry 18(2): 149–154
Ladd ME, Erhart P, Debatin JF, Romanowski BJ, Boesiger P, McKinnon GC (1996) Biopsy needle susceptibility artifacts. Magn Reson Med 36(4): 646–651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rump, J.C., Jonczyk, M., Seebauer, C.J. et al. Reduced k-space acquisition to accelerate MR imaging of moving interventional instruments: a phantom study. Int J CARS 6, 713–719 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0554-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0554-8