Abstract
Purpose
Since pre-processing and initial segmentation steps in medical images directly affect the final segmentation results of the regions of interesting, an automatic segmentation method of a parameter-adaptive pulse-coupled neural network is proposed to integrate the above-mentioned two segmentation steps into one. This method has a low computational complexity for different kinds of medical images and has a high segmentation precision.
Methods
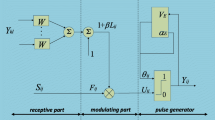
The method comprises four steps. Firstly, an optimal histogram threshold is used to determine the parameter \(\alpha \) for different kinds of images. Secondly, we acquire the parameter \(\beta \) according to a simplified pulse-coupled neural network (SPCNN). Thirdly, we redefine the parameter V of the SPCNN model by sub-intensity distribution range of firing pixels. Fourthly, we add an offset \(A\times S_{\mathrm{off}}\) to improve initial segmentation precision.
Results
Compared with the state-of-the-art algorithms, the new method achieves a comparable performance by the experimental results from ultrasound images of the gallbladder and gallstones, magnetic resonance images of the left ventricle, and mammogram images of the left and the right breast, presenting the overall metric UM of 0.9845, CM of 0.8142, TM of 0.0726.
Conclusion
The algorithm has a great potential to achieve the pre-processing and initial segmentation steps in various medical images. This is a premise for assisting physicians to detect and diagnose clinical cases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hareendranathan A, Mabee M, Punithakumar K, Noga M, Jaremko J (2016) A technique for semiautomatic segmentation of echogenic structures in 3D ultrasound, applied to infant hip dysplasia. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(1):31–42. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1239-5
Nobel J, Boukerroui D (2006) Ultrasound image segmentation: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25(8):987–1010. doi:10.1109/TMI.2006.877092
Gupta J, Gosain B, Kaushal S (2010) A comparison of two algorithms for automated stone detection in clinical B-mode ultrasound images of the abdomen. Int J Clin Monit Comput 24(5):341–362. doi:10.1007/s10877-010-9254-0
Lian J, Ma Y, Ma Y, Shi B, Liu J, Yang Z, Guo Y (2017) Automatic gallbladder and gallstone regions segmentation in ultrasound image. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. doi:10.1007/s11548-016-1515-z
Yang X, Ye X, Slabaugh G (2015) Multilabel region classification and semantic linking for colon segmentation in CT colonography. IEEE Trans B Biomed Eng 62(3):948–959. doi:10.1109/TBME.2014.2374355
Zou X, Li Z (2016) TV-based correction for beam hardening in computed tomography. J Med Imaging Heal Inf 6(7):1701–1707. doi:10.1166/jmihi.2016.1875
Dandin O, Teomete U, Osman O, Tulum G, Ergin T, Sabuncuoglu M (2016) Automated segmentation of the injured spleen. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(3):351–368. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1288-9
Hanaoka S, Masutani Y, Nenoto M, Nomura Y, Miki S, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi N, Ohtomo K, Shimizu A (2017) Landmark-guided diffeomorphic demons algorithm and its application to automatic segmentation of the whole spine and pelvis in CT images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12(3):413–430. doi:10.1007/s11548-016-1507-z
Wang Z, Zhang X, Dou W, Zhang M, Chen H, Lu M, Li S (2016) Best Window Width Determination and Glioma Analysis Application of Dynamic Brain Network Measure on Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Med Imaging Heal Inf 6(7):1735–1740. doi:10.1166/jmihi.2016.1881
Ma Y, Wang L, Ma Y, Dong M, Du S, Sun S (2016) Novel automatic segmentation of left ventricle in cardiac cine MR images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(11):1951–1964. doi:10.1007/s11548-016-1429-9
Faghih Roohi S, Aghaeizadeh Zoroofi R (2013) 4D statistical shape modeling of the left ventricle in cardiac MR images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8(3):335–351. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0787-1
Sezgin M, Sankur B (2004) Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J Electron Imaging 13(1):146–165. doi:10.1117/1.1631315
Lee S, Chung S, Park R (1990) A comparative performance study of several global thresholding techniques for segmentation. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 52(2):171–190. doi:10.1016/0734-189X(90)90053-X
Feng Y, Zhao H, Li X, Zhang X, Li H (2016) A multi-scale 3D Otsu thresholding algorithm for medical image segmentation. Digit Signal Process 60:186–199. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2016.08.003
Yang Z, Dong M, Guo Y, Gao X, Wang K, Shi B, Ma Y (2016) A new method of micro-calcifications detection in digitized mammograms based on improved simplified PCNN. Neurocomputing. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.068
Musrrat A, Ch W, Pant M (2013) Multi-level image thresholding by synergetic differential evolution. Appl Soft Comput 17(3):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2013.11.018
Guo Y, Dong M, Yang Z, Gao X, Wang K, Luo C, Ma Y, Zhang J (2016) A new method of detecting micro-calcification clusters in mammograms using contourlet transform and non-linking simplified PCNN. Comput Methods Progam Biomed 130:31–45. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.02.019
Zhan K, Shi J, Wang H, Xie Y, Li Q (2016) Computational mechanisms of pulse-coupled neural networks: a comprehensive review. Arch Comput Methods Eng. doi:10.1007/s11831-016-9182-3
Ma H, Cheng X (2014) Automatic image segmentation with PCNN algorithm based on grayscale correlation. Int J Signal Process 7(5):249–258. doi:10.14257/ijsip.2014.7.5.22
Zhuang H, Low K, Yau W (2012) Multichannel Pulse-Coupled-Neural-Network-Based Color Image Segmentation for Object Detection. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(8):3299–3308. doi:10.1109/TIE.2011.2165451
Zheng W, Pu T, Chen J, Zeng H (2012) Image contrast enhancement by contour let transform and PCNN. In: Audio lang image process (ICALIP) international conference, pp 735–739. doi:10.1109/ICALIP.2012.6376711
Xu G, Li C, Zhao J, Lei B (2014) Multiplicative decomposition based image contrast enhancement method using PCNN factoring model. In : Intelligent control and automation (WCICA), pp 1511–1566. doi:10.1109/WCICA.2014.7052943
Yu B, Zhang L (2004) Pulse-coupled neural networks for contour and motion matchings. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(5):1186–1201. doi:10.1109/TNN.2004.832830
Chen Y, Ma Y, Park S (2015) Region-based object recognition by color segmentation using a simplified PCNN. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(8):1682–1697. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2351418
Berg H, Olsson R, Lindblad T, Chilo J (2008) Automatic design of pulse coupled neurons for image segmentation. Neurocomputing 71(10):1980–1993. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2007.10.018
Ma Y, Qi C (2006) Study of automated PCNN system based on genetic algorithm. J Syst Simul 18(3):722–725
Chen Y, Park S, Ma Y, Ala R (2011) A new automatic parameter setting method of a simplified PCNN for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):880–892. doi:10.1109/TNN.2011.2128880
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Suckling J, Parker J, Dance D, Astley S, Hutt I, Boggis C, Ricketts I, Stamatakis E, Cerneaz N, Kok S (1994) The mammographic image analysis society digital mammogram database. In :Excerpta medica international congress series, pp 375–378
Zhan K, Zhang H, Ma Y (2009) New spiking cortical model for invariant texture retrieval and image processing. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(12):1980–1986. doi:10.1109/TNN.2009.2030585
Zhan K, Shi J, Li Q, Teng J (2015) Image segmentation using fast linking SCM. Int Jt Confere Neural Netw (IJCNN). doi:10.1109/IJCNN.2015.7280579
Kittler J, Illingworth J (1986) Minimum error thresholding. Pattern Recognit 19(1):41–47. doi:10.1016/0031-3203(86)90030-0
Sahoo P, Soltani S, Wong A (1988) A survey of thresholding techniques. Comput Graph Vis Image Process 41(2):233–260. doi:10.1016/0734-189X(88)90022-9
Levine M, Naxif A (1985) Dynamic measurement of computer generated image segmentation. IEEE Transactions Pattern Anal Mach Intell 7(2):155–164. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.1985.4767640
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the reviewers for their valuable comments, which further improved the quality of the paper. This study was funded National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 61175012 & 61201422), Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (Grant Number 148RJZA044) and Youth Foundation of Lanzhou Jiaotong University of China (Grant Numbers 2013004 & 2014005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, J., Shi, B., Li, M. et al. An automatic segmentation method of a parameter-adaptive PCNN for medical images. Int J CARS 12, 1511–1519 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1597-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1597-2