Abstract
Purpose
This work aims to develop a unified methodology for the false positives reduction in lung nodules computer-aided detection schemes.
Methods
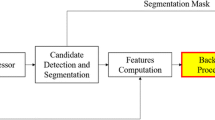
The 3D region of each detected nodule candidate is first reconstructed using the sparse field method for accurately segmenting the objects. This technique enhances the level set modeling by restricting the computations to a narrow band near the evolving curve. Then, a set of 2D and 3D relevant features are extracted for each segmented candidate. Subsequently, a hybrid undersampling/boosting algorithm called RUSBoost is applied to analyze the features and discriminate real nodules from non-nodules.
Results
The performance of the proposed scheme was evaluated by using 70 CT images, randomly selected from the Lung Image Database Consortium and containing 198 nodules. Applying RUSBoost classifier exhibited a better performance than some commonly used classifiers. It effectively reduced the average number of FPs to only 3.9 per scan based on a fivefold cross-validation.
Conclusion
The practical implementation, applicability for different nodule types and adaptability in handling the imbalanced data classification insure the improvement in lung nodules detection by utilizing this new approach.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin JH, Muller NL, Friedman PJ, Hansell DM, Naidich DP, Remy-Jardin M, Webb WR, Zerhouni EA (1996) Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the nomenclature committee of the Fleischner society. Radiology 200(2):327–331
Lee SLA, Kouzani AZ, Hu EJ (2012) Automated detection of lung nodules in computed tomography images: a review. Mach Vis Appl 23:151–163
Suarez-Cuenca JJ, Tahoces PG, Souto M, Lado MJ, Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Vidal JJ (2009) Application of the iris filter for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules on computed tomography images. Comput Biol Med 39:921–933
Saien S, Pilevar AH, Abrishami Moghaddam H (2014) Refinement of lung nodule candidates based on local geometric shape analysis and Laplacian of Gaussian kernels. Comput Biol Med 54:188–198
Choi W-J, Choi T-S (2014) Automated pulmonary nodule detection based on three dimensional shape-based feature descriptor. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 113:37–54
Ma Z, Tavares JM, Jorge RN, Mascarenhas T (2010) A review of algorithms for medical image segmentation and their applications to the female pelvic cavity. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 13(2):235–246
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Wileye, Hoboken
Javaid M, Javid M, Rehman MZU, Shah SIA (2016) A novel approach to CAD system for the detection of lung nodules in CT images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 135:125–139
Ye X, Lin X, Dehmeshki J, Slabaugh G, Beddoe G (2009) Shape based computer aided detection of lung nodules in thoracic CT images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56:1810–1820
Suzuki K, Armato III SG, Li F, Sone S, Doi K (2003) Massive training artificial neural network (MTANN) for reduction of false positives in computerized detection of lung nodules in low-dose computed tomography. Med Phys 30(7):1602–1617
Golosio B, Masala GL, Piccioli A, Oliva P, Carpinelli M, Cataldo R, Cerello P, De Carlo F, Gargano G, Falaschi F, Fantacci ME, Kasae P, Torsello M (2009) A novel multi-threshold method for nodule detection in CT. Med Phys 36(8):3607–3618
Tan M, Deklerck R, Jansen B, Bister M, Cornelis J (2011) A novel computer-aided lung nodule detection system for CT images. Med Phys 38(10):5630–5645
Messay T, Hardie RC, Rogers SK (2010) A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med Image Anal 14(3):390–406
Murphy K, van Ginneken B, Schilham AMR, de Hoop BJ, Gietema HA, Prokop M (2009) A large scale evaluation of automatic pulmonary nodule detection in chest CT using local image features and k-nearest-neighbour classification. Med Image Anal 13:757–770
Santos AM, de Carvalho Filho AO, Silva AC, de Paiva AC, Nunes RA, Gattass M (2014) Automatic detection of small lung nodules in 3D CT data using Gaussian mixture models, Tsallis entropy and SVM. Eng Appl Artif Intel 36:27–39
Han H, Li L, Han F, Song B, Moore W, Liang Z (2015) Fast and adaptive detection of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT images using a hierarchical vector quantization scheme. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19(2):648–659
Wu P, Xia K, Yu H (2016) Correlation coefficient based supervised locally linear embedding for pulmonary nodule recognition. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 136:97–106
Papa JP, FalcãO AX, De Albuquerque VH, Tavares JM (2012) Efficient supervised optimum-path forest classification for large datasets. Pattern Recognit 45(1):512–520
Rebouças Filho PP, Cortez PC, da Silva Barros AC, Albuquerque VH, Tavares JM (2017) Novel and powerful 3D adaptive crisp active contour method applied in the segmentation of CT lung images. Med Image Anal 35:503–516
Cao P, Yang J, Li W, Zhao D, Zaiane O (2014) Ensemble-based hybrid probabilistic sampling for imbalanced data learning in lung nodule CAD. Comput Med Imaging Graph 38(3):137–150
Bagci U, Bray M, Caban J, Yao J, Mollura DJ (2012) Computer-assisted detection of infectious lung diseases: a review. Comput Med Imaging Graph 36:72–84
Whitaker R (1998) A level-set approach to 3D reconstruction from range data. Int J Comput Vis 29(3):203–231
Yang X, Gao X, Tao D, Li X, Li J (2015) An efficient MRF embedded level set method for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(1):9–21
Awad J, Wilson L, Parraga G, Fenster A (2011) Lung tumours segmentation on CT using sparse field active model. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging computer-aided diagnosis vol 7963, p 79632Y
Chan T, Vese L (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277
Li Q, Sone S, Doi K (2003) Selective enhancement filters for nodules, vessels, and airway walls in two and three-dimensional CT scans. Med Phys 30(8):2040–2051
Theodoridis S, Koutroumbas K (2006) Pattern recognition, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London
Seiffert C, Khoshgoftaar TM, Van Hulse J, Napolitano J (2010) Rusboost: a hybrid approach to alleviating class imbalance. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern A, Syst Hum 40(1):185–197
McNitt-Gray MF, Armato SG, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, McLennan G, Pais RC, Freymann J, Brown MS, Engelmann RM, Bland PH, Laderach GE, Piker C, Piker C, Guo J, Towfic Z, Qing DP, Yankelevitz DF, Aberle DR, van Beek EJ, MacMahon H, Kazerooni EA, Croft BY, Clarke LP (2007) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) data collection process for nodule detection and annotation. Acad Radiol 14:1464–1474
Armato SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, Zhao B, Aberle DR, Henschke CI, Hoffman EA, Kazerooni EA, MacMahon H, Beek EJRV, Yankelevitz D, Biancardi AM, Bland PH, Brown MS, Engelmann RM, Laderach GE, Max D, Pais RC, Qing DPY, Roberts RY, Smith AR, Starkey A, Batrah P, Caligiuri P, Farooqi A, Gladish GW, Jude CM, Munden RF, Petkovska I, Quint LE, Schwartz LH, Sundaram B, Dodd LE, Fenimore C, Gur D, Petrick N, Freymann J, Kirby J, Hughes B, Casteele AV, Gupte S, Sallamm M, Heath MD, Kuhn MH, Dharaiya E, Burns R, Fryd DS, Salganicoff M, Anand V, Shreter U, Vastagh S, Croft BY (2011) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys 38:915–931
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Campadelli P, Casiraghi E, Valentini G (2005) Support vector machines for candidate nodules classification. Neurocomputing 68:281–288
Liu X-Y, Wu J, Zhou Z-H (2009) Exploratory undersampling for class imbalance learning. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Appl Rev 39(2):539–550
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2000) Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting. Ann Stat 28(2):337–407
Cao P, Liu X, Yang J, Zhao D, Li W, Huang M, Zaiane O (2017) A multi-kernel based framework for heterogeneous feature selection and over-sampling for computer-aided detection of pulmonary nodules. Pattern Recognit 64:327–346
Jacobs C, van Rikxoort EM, Twellmann T, Scholten ET, de Jong PA, Kuhnigk JM, Oudkerk M, de Koning HJ, Prokop M, Schaefer-Prokop C, van Ginneken B (2014) Automatic detection of subsolid pulmonary nodules in thoracic computed tomography images. Med Image Anal 18(2):374–384
Chang C, Lin C (2013) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/cjlin/libsvm/
Galar M, Fernández A, Barrenechea E, Bustince H, Herrera F (2012) A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C Appl Rev 42(4):3358–3378
Netto SM, Silva AC, Nunes RA, Gattass M (2012) Automatic segmentation of lung nodules with growing neural gas and support vector machine. Comput Biol Med 42(11):1110–21
Pu J, Zheng B, Leader JK, Wang X-H, Gur D (2008) An automated CT based lung nodule detection scheme using geometric analysis of signed distance field. Med Phys 35(8):3453–3461
Li Q, Li F, Doi K (2008) Computerized detection of lung nodules in thin-section CT images by use of selective enhancement filters and an automated rule-based classifier. Acad Radiol 15(2):165–175
Riccardi A, Petkov TS, Ferri G, Masotti M, Campanini R (2011) Computer-aided detection of lung nodules via 3D fast radial transform, scale space representation, and Zernike MIP classification. Med Phys 38(4):1962–1971
Camarlinghi N, Gori I, Retico A, Bellotti R, Bosco P, Cerello P, Gargano G, Lopez Torres E, Megna R, Peccarisi M, Fantacci M (2011) Combination of computer-aided detection algorithms for automatic lung nodule identification. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7:455–464
Keshani M, Azimifar Z, Tajeripour F, Boostani R (2013) Lung nodule segmentation and recognition using svm classifier and active contour modeling: a complete intelligent system. Comput Biol Med 43:287–300
Teramoto A, Fujita H (2013) Fast lung nodule detection in chest CT images using cylindrical nodule-enhancement filter. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8:193–205
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Mahsa Fathian and Dr. Roya Fallahian for their clinical guidance and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saien, S., Moghaddam, H.A. & Fathian, M. A unified methodology based on sparse field level sets and boosting algorithms for false positives reduction in lung nodules detection. Int J CARS 13, 397–409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1656-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1656-8