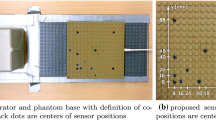
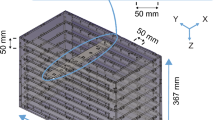
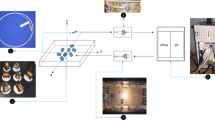
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the accuracy of medical electromagnetic tracking systems, reference positioning systems are generally required. Errors are unavoidable in such systems, and despite how tiny they may be, prevent the ground truth from being known. In this work, a simulator was developed and used to analyze the theoretical system performances in electromagnetic tracking.
Methods
To simulate the entire tracking process, the magnetic dipole model, Faraday’s law, and a mathematical optimization algorithm are applied. With the simulator, we optimized the spatial placement of the transmitter coils, analyzed the tracking accuracy by applying stochastic and optimized coil placement. Additionally, the performance of the calibration of transmitter coils’ measurement error and Kalman filtering was tested.
Results
The results show that, after optimizing the spatial arrangement of the transmitter coils, the tracking accuracy is significantly improved to a much higher level compared with applying statistical arrangement. The measurement errors of the transmitter coils’ positions and orientations can be totally rectified by the developed calibration algorithm when no noises are introduced. The Kalman filter reduces the sensor jitter errors caused by noise, which potentially allows the EM tracking system to reach a larger volume of interest.
Conclusions
We proposed a simulator for advanced analysis in electromagnetic tracking without hardware requirements. Grounded on this, we performed an optimization of the spatial arrangement of the transmitter coils to improve the tracking accuracy further. The performances of the calibration algorithm and Kalman filtering were also evaluated. The developed simulator can also be applied for other analysis in electromagnetic tracking.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loke WF, Choi TY, Maleki T, Papiez L, Ziaie B, Jung B (2010) Magnetic tracking system for radiation therapy. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 4(4):223–231. doi:10.1109/TBCAS.2010.2046737
Franz AM, März K, Hummel J, Birkfellner W, Bendl R, Delorme S, Schlemmer HP, Meinzer HP, Maier-Hein L (2012) Electromagnetic tracking for us-guided interventions: standardized assessment of a new compact field generator. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7(6):813–818. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0740-3
Shahriari N, Hekman E, Oudkerk M, Misra S (2015) Design and evaluation of a computed tomography (ct)-compatible needle insertion device using an electromagnetic tracking system and ct images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10(11):1845–1852. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1176-3
Franz AM, Haidegger T, Birkfellner W, Cleary K, Peters TM, Maier-Hein L (2014) Electromagnetic tracking in medicine—a review of technology, validation, and applications. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(8):1702–1725. doi:10.1109/TMI.2014.2321777
Wood BJ, Zhang H, Durrani A, Glossop N, Ranjan S, Lindisch D, Levy E, Banovac F, Borgert J, Krueger S, Kruecker J, Viswanathan A, Cleary K (2005) Navigation with electromagnetic tracking for interventional radiology procedures: a feasibility study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16(4):493–505. doi:10.1097/01.RVI.0000148827.62296.B4
Krücker J, Xu S, Glossop N, Viswanathan A, Borgert J, Schulz H, Wood BJ (2007) Electromagnetic tracking for thermal ablation and biopsy guidance: clinical evaluation of spatial accuracy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18(9):1141–1150. doi:10.1016/j.jvir.2007.06.014
Yaniv Z, Wilson E, Lindisch D, Cleary K (2009) Electromagnetic tracking in the clinical environment. Med Phys 36(3):876–892. doi:10.1118/1.3075829
Hummel J, Figl M, Birkfellner W, Bax MR, Shahidi R, Maurer C Jr, Bergmann H (2006) Evaluation of a new electromagnetic tracking system using a standardized assessment protocol. Phys Med Biol 51(10):N205. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/51/10/N01
Bien T, Li M, Salah Z, Rose G (2014) Electromagnetic tracking system with reduced distortion using quadratic excitation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9(2):323–332. doi:10.1007/s11548-013-0925-4
Bien T, Rose G (2012) Algorithm for calibration of the electromagnetic tracking system. In: 2012 IEEE-EMBS international conference on biomedical and health informatics (BHI), IEEE, pp 85–88. doi:10.1109/BHI.2012.6211512
Fitzpatrick JM, West JB, Maurer CR (1998) Predicting error in rigid-body point-based registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(5):694–702. doi:10.1109/42.736021
Frantz DD, Wiles A, Leis S, Kirsch S (2003) Accuracy assessment protocols for electromagnetic tracking systems. Phys Med Biol 48(14):2241
Nafis C, Jensen V, Beauregard L, Anderson P (2006) Method for estimating dynamic em tracking accuracy of surgical navigation tools. Proc SPIE Med Image 2006 Vis Image Guided Proc Display 6141:152–167. doi:10.1117/12.653448
Wilson E, Yaniv Z, Zhang H, Nafis C, Shen E, Shechter G, Wiles A, Peters T, Lindisch D, Cleary K (2007) A hardware and software protocol for the evaluation of electromagnetic tracker accuracy in the clinical environment: a multi-center study. Proc SPIE 6509:65092T. doi:10.1117/12.712701
Koivukangas T, Katisko JP, Koivukangas JP (2013) Technical accuracy of optical and the electromagnetic tracking systems. SpringerPlus 2(1):90. doi:10.1186/2193-1801-2-90
O’Donoghue K, Cantillon-Murphy P (2015) Planar magnetic shielding for use with electromagnetic tracking systems. IEEE Trans Magn 51(2):1–12. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2014.2352344
Li M, Hansen C, Rose G (2015) A robust electromagnetic tracking system for clinical applications. In: Proceedings of the annual meeting of the German society of computer- and robot-assisted surgery, pp 31–36
Wiles AD, Thompson DG, Frantz DD (2004) Accuracy assessment and interpretation for optical tracking systems. Proc SPIE 5367:421–432. doi:10.1117/12.536128
Maier-Hein L, Franz A, Birkfellner W, Hummel J, Gergel I, Wegner I, Meinzer HP (2012) Standardized assessment of new electromagnetic field generators in an interventional radiology setting. Med Phys 39(6):3424–3434
Plotkin A, Shafrir O, Paperno E, Kaplan DM (2010) Magnetic eye tracking: a new approach employing a planar transmitter. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(5):1209–1215. doi:10.1109/TBME.2009.2038495
O’Donoghue K, Eustace D, Griffiths J, O’Shea M, Power T, Mansfield H, Cantillon-Murphy P (2014) Catheter position tracking system using planar magnetics and closed loop current control. IEEE Trans Magn 50(7):1–9. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2014.2304271
Raab FH, Blood EB, Steiner TO, Jones HR (1979) Magnetic position and orientation tracking system. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst AES 15(5):709–718. doi:10.1109/TAES.1979.308860
Schneider M, Stevens C (2007) Development and testing of a new magnetic-tracking device for image guidance. In: Medical imaging, International society for optics and photonics, pp 65.090I–65.090I. doi:10.1117/12.713249
Sherman JT, Lubkert JK, Popovic RS, DiSilvestro MR (2007) Characterization of a novel magnetic tracking system. IEEE Trans Magn 43(6):2725–2727. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2007.893314
Stenger B, Mendonça PR, Cipolla R (2001) Model-based hand tracking using an unscented Kalman filter. BMVC 1:63–72. doi:10.5244/C.15.8
Bertozzi M, Broggi A, Fascioli A, Tibaldi A, Chapuis R, Chausse F (2004) Pedestrian localization and tracking system with Kalman filtering. In: Intelligent vehicles symposium, IEEE, pp 584–589. doi:10.1109/IVS.2004.1336449
Schenderlein M, Rasche V, Dietmayer K (2011) Three-dimensional catheter tip tracking from asynchronous biplane X-ray image sequences using non-linear state filtering. In: Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2011, Springer, pp 234–238. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19335-4_49
Li M, Song S, Hu C, Chen D, Meng MQH (2010) A novel method of 6-dof electromagnetic navigation system for surgical robot. In: 2010 8th world congress on intelligent control and automation (WCICA), IEEE, pp 2163–2167. doi:10.1109/WCICA.2010.5554348
Harris PG, Pendlebury J (2006) Dipole-field contributions to geometric-phase-induced false electric-dipole-moment signals for particles in traps. Phys Rev A 73(1):014101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.73.01410
Li M, Hansen C, Rose G (2017) A software solution to dynamically reduce metallic distortions of electromagnetic tracking systems for image-guided surgery. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2:1–13. doi:10.1007/s11548-017-1546-0
Aron M, Kerrien E, Berger MO, Laprie Y (2006) Coupling electromagnetic sensors and ultrasound images for tongue tracking: acquisition setup and preliminary results. In: 7th international seminar on speech production-ISSP’06, CEFALA-Centro de Estudos da Fala, Acústica, Linguagem e músicA
Acknowledgements
The work of this paper is partly funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the Forschungscampus STIMULATE under Grant number ‘13GW0095A’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors Mengfei Li, Christian Hansen and Georg Rose declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Hansen, C. & Rose, G. A simulator for advanced analysis of a 5-DOF EM tracking systems in use for image-guided surgery. Int J CARS 12, 2217–2229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1662-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1662-x