Abstract
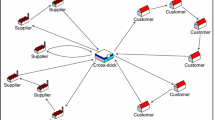
This paper deals with a multi-source vehicle routing problem with a cross-docking facility, and studies open and closed network configurations as well as practically relevant dependency rules and consolidation decisions. Given a set of supplier–customer pairs with known demands, the aim is to design minimum cost routes for the transportation of products via a cross-dock. Vehicles cannot travel directly from suppliers to customers, and thus, products arriving from inbound vehicles are sorted and consolidated onto outbound vehicles. The proposed method utilizes an adaptive multi-restart local search framework. For this purpose, a Tabu Search algorithm is employed, while the execution of the re-starting mechanism is based on the information extracted from a reference set of solutions. Computational experiments illustrate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared to existing results, new improved upper bounds are reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, P., Guo, Y.S., Lim, A., Rodriguesd, B.: Multiple crossdocks with inventory and time windows. Comput. Oper. Res. 33(1), 43–63 (2006)
Dondo, R., Mèndez, C.A., Cerdá, J.: The multi-echelon vehicle routing problem with cross docking in supply chain management. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(12), 3002–3024 (2011)
Perboli, G., Tadei, R., Vigo, D.: The two-echelon capacitated vehicle routing problem: models and math-based heuristics. Trans. Sci. 45, 364–380 (2011)
Tarantilis, C.D., Zachariadis, E.E., Kiranoudis, C.T.: A hybrid guided local search for the vehicle routing problem with intermediate replenishment facilities. INFORMS J. Comput. 20(1), 154–168 (2008)
Van Belle, J., Valckenaers, P., Cattrysse, D.: Cross-docking: state of the art. OMEGA 40, 827–846 (2012)
Repoussis, P.P., Tarantilis, C.D., Ioannou, G.: A hybrid evolution strategy for the open vehicle routing problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 37, 443–455 (2010)
Sung, C.S., Song, S.H.: Integrated service network design ofr a cross-docking supply chain network. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 54(12), 1283–1295 (2003)
Jagannathan, A.K.R.: Vehicle routing with cross docks, split deliveries, and multiple use of vehicles. MSc Thesis, Auburn University, Alabama (2011)
Boysen, N., Fliedner, M.: Cross dock scheduling: classification, literature review and research agenda. Omega 38(6), 413–422 (2010)
Musa, R., Arnaout, J.-P., Jung, H.: Ant colony optimization algorithm to solve for the transportation problem of cross-docking network. Comput. Ind. Eng. 59, 85–92 (2010)
Ma, H., Miao, Z., Lim, A., Rodrigues, B.: Crossdocking distribution networks with setup cost and time window constraint. Omega 39, 64–72 (2011)
Miao, Z., Yang, F., Fu, K., Xu, D.: Transshipment service through crossdocks with both soft and hard time windows. Ann. Oper. Res. 192, 21–47 (2012)
Lee, Y.H., Jung, J.W., Lee, K.M.: Vehicle routing scheduling for cross-docking in the supply chain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 51(2), 247–256 (2006)
Liao, Ch-J, Lin, Y., Shih, S.C.: Vehicle routing with cross-docking in the supply chain. Expert Sys. Appl. 37, 6868–6873 (2010)
Wen, M., Larsen, J., Clausen, J., Cordeau, J.-F., Laporte, G.: Vehicle routing with cross-docking. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 60, 1708–1718 (2009)
Soltani, R., Sadjadi, S.J.: Scheduling trucks in cross-docking systems: a robust meta-heuristics approach. Trans. Res. E 46, 650–666 (2010)
Martí, R.: Handbook of metaheuristics. In: Glover, F., Kochenberger, G.A. (eds.) Multi-Start Methods. Kluwer Academic Publishers, USA (2003)
Tarantilis, C.D., Kiranoudis, C.T.: BoneRoute: an adaptive memory-based method for effective fleet management. Ann. Oper. Res. 115, 227–241 (2002)
Tarantilis, C.D.: Solving the vehicle routing problem with adaptive memory programming methodology. Comput. Oper. Res. 32, 2309–2327 (2005)
Ho, S.C., Gendreau, M.: Path relinking for the vehicle routing problem. J. Heuristics 12, 55–72 (2006)
Gendreau, M., Tarantilis, C.D.: Solving large-scale vehicle routing problems with time windows: The state-of-the-art. Technical Report CIRRELT-2010-04 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Research Center of the Athens University of Economics and Business. The author also wishes to thank the guest editors for handling the paper, and the two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarantilis, C.D. Adaptive multi-restart Tabu Search algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. Optim Lett 7, 1583–1596 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-012-0558-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-012-0558-5