Abstract
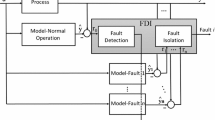
According to the fault characteristic of the imperial smelting process (ISP), a novel intelligent integrated fault diagnostic system is developed. In the system fuzzy neural networks are utilized to extract fault symptom and expert system is employed for effective fault diagnosis of the process. Furthermore, fuzzy abductive inference is introduced to diagnose multiple faults. Feasibility of the proposed system is demonstrated through a pilot plant case study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Keen. Regional Issues in the Global Lead Market. Journal of Power Sources, vol. 133, no. 1, pp. 8–13, 2004.
X. Y. Liu. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Technology on Complex Process and Its Application to Large Industrial Kilns, Ph.D. thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, Chapter 5, 2003.
X. H. Wu, M. Wu, S. P. Xiao, Y. X. Du. An Intelligent Optimization Operation Guide System for Furnace State of ISP. Development & Innovation of Machinery & Electrical Products, vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 97–99, 2004.
W. H. Gui, X. Y. Liu. Fault Diagnosis Technologies Based on Artificial Intelligence for Complex Process. Control Engineering of China, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 1–6, 2002.
X. Ding, L. Guo. Optimization of Observer Based Fault Detection Systems. In Proceedings Of IFAC Symposium On System Identification, Kushu, Japan, pp. 1201–1206, 1997.
L. L. Li, D. H. Zhou. Fast and Robust Fault Diagnosis for a Class of Nonlinear Systems. Computers and Chemical Engineering, vol. 18, no. 12, pp. 2635–2646, 2004.
E. A. Mohamed, A. Y. Abdelaziz, A. S. Mostafa. A Neural Network-based Scheme for Fault Diagnosis of Power Transformers. Electric Power Systems Research, vol. 75, no. 11, pp. 29–39, 2005.
S. Y. Chang, C. T. Chang. A fuzzy-logic based fault diagnosis strategy for process control loops. Chemical Engineering Science, vol. 58, no. 15, pp. 3395–3411, 2003.
X. Y. Liu, W. H. Gui, M. Wu. Synthetic Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Technology for Complex Process. High Technology Letters, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 72–75, 2002
Y. Miyata, T. Furuhashi, Y. Uchikawa. A Study of Fuzzy Abductive Inference. In Proceedings of 1995 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Orlando, Florida, vol. 1, pp. 337–342, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by National 973 Program (No. 2002CB312200) and National Natural Science Foundation of PRC (No. 60634020).
Wei-Hua Gui received his B.Eng. degree in control science and engineering and the M. Eng. degree in control science and engineering both from Central South University, Changsha, China in 1976 and 1981, respectively. From 1986 to 1988 he was a visiting scholar at Universität-GH-Duisburg, Germany. He has been a professor in the School of Information Science & Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, China, since 1991.
His main research interests include modeling and optimal control of complex industrial process, distributed robust control, and fault diagnoses of complex industrial process.
Chun-Hua Yang received her M. Eng. degree in automatic control engineering and the Ph. D. degree in control science and engineering both from Central South University, China in 1988 and 2002, respectively, and was with the Electrical Engineering Department, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium from 1999 to 2001. She is currently a professor in the School of Information Science & Engineering, Central South University.
Her research interests include modeling and optimal control of complex industrial process, intelligent control system, and fault-tolerant computing of real-time systems.
Jing Teng received her B. Eng. in electronic information engineering from Central South University, Changsha, China in 2003. From 2003 to 2006 she was a Ph. D. student in Central South University and currently transferring to University of Technology of Troyes, France, to finish her Ph. D. degree.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gui, WH., Yang, CH. & Teng, J. Intelligent fault diagnosis in lead-zinc smelting process. Int J Automat Comput 4, 135–140 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-007-0135-z
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-007-0135-z