Abstract
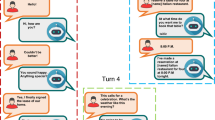
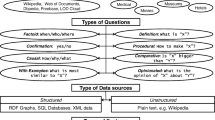
Contextual question answering (CQA), in which user information needs are satisfied through an interactive question answering (QA) dialog, has recently attracted more research attention. One challenge is to fuse contextual information into the understanding process of relevant questions. In this paper, a discourse structure is proposed to maintain semantic information, and approaches for recognition of relevancy type and fusion of contextual information according to relevancy type are proposed. The system is evaluated on real contextual QA data. The results show that better performance is achieved than a baseline system and almost the same performance as when these contextual phenomena are resolved manually. A detailed evaluation analysis is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuneaki K, Junichi F, Fumito M, Kando N. Handling information access dialogue through QA technologies — a novel challenge for open domain question answering. In: Proceedings of HLT-NAACL 2004 Workshop on Pragmatics in Question Answering. 2004, 70–77
Chai J, Jin R. Discourse structure for context question answering. In: Proceedings of HLT-NAACL 2004 Workshop on Pragmatics of Question Answering. 2004, 23–30
Carbonell J G. Discourse pragmatics and ellipsis resolution in taskoriented natural language interfaces. In: Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. 1983, 164–168
Nils D, Jonsson A. Empirical studies of discourse representations for natural language interfaces. In: Proceedings of 4th Conference of the European Chapter of the ACL. 1989, 291–298
Wang D S. A domain-specific question answering system based on ontology and question templates. In: Proceedings of 11th ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering. 2010, 151–156
Fernlcndez R, Katagiri Y, Komatani K, Lemon O, Nakano M, eds. Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2010
Chai J Y, Moore J D, Passonneau R J, Traum, D R, et al, eds. Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2011
Mitkov R, Boguraev B K, Tait J I, Palmer M, eds. Journal of Natural Language Engineering, Special Issue on Interactive Question Answering, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009
Voorhees E M. Overview of the TREC 2001 question answering track. In: Proceedings of 10th Text Retrieval Conference. 2001, 42–51
Mori T, Kawaguchi S, Ishioroshi M. Answering contextual questions based on the cohesion with knowledge. International Journal of Computer Processing Of Languages, 2007, 20(2/3): 115–135
Bernardi R, Kirschner M. From artificial questions to real user interaction logs: real challenges for interactive question answering systems. In: Proceedings of Workshop on Web Logs and Question Answering. 2010, 8–15
Yang F, Feng J, DiFabbrizio G. A data driven approach to relevancy recognition for contextual question answering. In: Proceedings of HLT-NAACL 2006 Workshop on Interactive Question Answering. 2006, 33–40
Kirschner M, Bernardi R, Baroni M, Dinh L T. Analyzing interactive QA dialogues using logistic regression models. In: Proceedings of XIth International Conference of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence Reggio Emilia on Emergent Perspectives in Artificial Intelligence. 2009, 334–344
Bernardi R, Kirschner M, Ratkovic Z. Context fusion: the role of discourse structure and centering theory. In: Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation. 2010, 2014–2021
Kirschner M, Bernardi R. Towards an empirically motivated typology of follow-up questions: the role of dialogue context. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue. 2010, 322–331
Kato T, Fukumoto J, Masui F, Kando N. Are open-domain question answering technologies useful for information access dialogues? — an empirical study and a proposal of a novel challenge. ACM Transactions on Asian Language Information Processing, 2005, 4 (3): 243–262
Van schooten B W, Op den akker R, Rosset S, Galibert O, Max A, Illouz G. Follow-up question handling in the IMIX and Ritel systems: A comparative study. Journal of Natural Language Engineering, 2009, 15(1):97–118
Murata Y, Akiba T, Fujii A, Itou K. Question answering experiments at NTCIR-5: Acquisition of answer evaluation patterns and context processing using passage retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 5th NTCIR Workshop Meeting. 2005, 394–401
Matsuda M, Fukumoto J. Answering questions of IAD task using reference resolution of follow-up questions. In: Proceedings of the 5th NTCIR Workshop Meeting. 2005, 414–421
Hobbs J R. On the coherence and structure of discourse. Center for the Study of Language and Information from Leland Stanford Junior University. Report No. CSLI-85-37, 1985
Mann WC, Thompson S A. Rhetorical structure theory: a theory of text organization. USC/ISI Technical Report ISI/RS-87-190, 1987
Grosz B J, Sidner C. Attention, intention, and the structure of discourse. Computational Linguistics, 1986, 12(3): 175–204
Kamp H, Reyle U. From Discourse To Logic. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993
Lars A, Nils D, Jagonsson A. Discourse representation and discourse management for natural language interfaces. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Nordic Conference on Text Comprehension in Man and Machine. 1990, 1–14
Quarteroni S, Manandhar S. Adaptivity in question answering with user modeling and a dialogue interface. In: Proceedings of the 11th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. 2006, 199–202
Quarteroni S, Manandhar S. Designing an interactive open-domain question answering system. Journal of Natural Language Engineering, 2009, 15(1): 73–95
Quarteroni S, Manandhar S. User modeling for personalized question answering. In: Proceedings of the 10th Congress of the Italian Association for Artificial Intelligence (AI*IA). 2007, 386–397
Sun M, Chai J J. Towards intelligent QA interfaces: discourse processing for context questions. In: Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. 2006, 163–170
Noy N F, McGuinnes D L. Ontology development 101: a guide to creating your first ontology. Stanford Knowledge Systems Laboratory Technical Report KSL-01-05 and Stanford Medical Informatics Technical Report. 2001
De Boni M, Manandhar S. Implementing clarification dialogues in open domain question answering. Journal of Natural Language Engineering, 2005, 11(4): 343–361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dongsheng Wang received his bachelor and masters degree from Jiangsu University of Science and Technology in 2005 and 2007, respectively. Now he is a PhD candidate in Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Science. His primary research interest is question answering and natural language understanding.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D. Answering contextual questions based on ontologies and question templates. Front. Comput. Sci. China 5, 405–418 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-011-1031-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-011-1031-9