Abstract
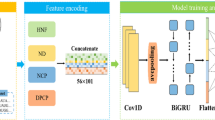
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are RNAs with closed circular structure involved in many biological processes by key interactions with RNA binding proteins (RBPs). Existing methods for predicting these interactions have limitations in feature learning. In view of this, we propose a method named circ2CBA, which uses only sequence information of circRNAs to predict circRNA-RBP binding sites. We have constructed a data set which includes eight sub-datasets. First, circ2CBA encodes circRNA sequences using the one-hot method. Next, a two-layer convolutional neural network (CNN) is used to initially extract the features. After CNN, circ2CBA uses a layer of bidirectional long and short-term memory network (BiLSTM) and the self-attention mechanism to learn the features. The AUC value of circ2CBA reaches 0.8987. Comparison of circ2CBA with other three methods on our data set and an ablation experiment confirm that circ2CBA is an effective method to predict the binding sites between circRNAs and RBPs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Liu J, Li D, Luo H, Zhu X. Circular RNAs: the star molecules in cancer. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 2019, 70: 141–152
Sanger H L, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross H J, Kleinschmidt A K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1976, 73(11): 3852–3856
Pamudurti N R, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E, Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, Shenzis S, Samson M, Dittmar G, Landthaler M, Chekulaeva M, Rajewsky N, Kadener S. Translation of CircRNAs. Molecular Cell, 2017, 66(1): 9–21.e7
Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R. Circular transcripts of the testisdetermining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell, 1993, 73(5): 1019–1030
Hansen T B, Jensen T I, Clausen B H, Bramsen J B, Finsen B, Damgaard C K, Kjems J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 384–388
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak S D, Gregersen L H, Munschauer M, Loewer A, Ziebold U, Landthaler M, Kocks C, Le Noble F, Rajewsky N. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 333–338
Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 2020, 98(1): 87–97
Wang Z, Lei X, Wu F X. Identifying cancer-specific circRNA-RBP binding sites based on deep learning. Molecules, 2019, 24(22): 4035
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T, Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M, Glock C, Quedenau C, Wang X, Hou J, Liu H, Sun W, Sambandan S, Chen T, Schuman E M, Chen W. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nature Neuroscience, 2015, 18(4): 603–610
Conn S J, Pillman K A, Toubia J, Conn V M, Salmanidis M, Phillips C A, Roslan S, Schreiber A W, Gregory P A, Goodall G J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell, 2015, 160(6): 1125–1134
Du W W, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P, Yang B B. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(6): 2846–2858
Zhang K, Pan X, Yang Y, Shen H B. CRIP: predicting circRNA-RBP-binding sites using a codon-based encoding and hybrid deep neural networks. RNA, 2019, 25(12): 1604–1615
van Nostrand E L, Pratt G A, Shishkin A A, Gelboin-Burkhart C, Fang M Y, Sundararaman B, Blue S M, Nguyen T B, Surka C, Elkins K, Stanton R, Rigo F, Guttman M, Yeo G W. Robust transcriptome-wide discovery of RNA-binding protein binding sites with enhanced CLIP (eCLIP). Nature Methods, 2016, 13(6): 508–514
Ray D, Kazan H, Cook K B, Weirauch M T, Najafabadi H S, Li X, Gueroussov S, Albu M, Zheng H, Yang A, Na H, Irimia M, Matzat L H, Dale R K, Smith S A, Yarosh C A, Kelly S M, Nabet B, Mecenas D, Li W M, Laishram R S, Qiao M, Lipshitz H D, Piano F, Corbett A H, Carstens R P, Frey B J, Anderson R A, Lynch K W, Penalva L O F, Lei E P, Fraser A G, Blencowe B J, Morris Q D, Hughes T R. A compendium of RNA-binding motifs for decoding gene regulation. Nature, 2013, 499(7457): 172–177
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA, 2014, 20(11): 1666–1670
Dudekula D B, Panda A C, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. CircInteractome: a web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biology, 2016, 13(1): 34–42
Yao D, Zhang L, Zheng M, Sun X, Lu Y, Liu P. Circ2Disease: a manually curated database of experimentally validated circRNAs in human disease. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 11018
Xia S, Feng J, Chen K, Ma Y, Gong J, Cai F, Jin Y, Gao Y, Xia L, Chang H, Wei L, Han L, He C. CSCD: a database for cancer-specific circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(D1): D925–D929
Licatalosi D D, Mele A, Fak J J, Ule J, Kayikci M, Chi S W, Clark T A, Schweitzer A C, Blume J E, Wang X N, Darnell J C, Darnell R B. HITS-CLIP yields genome-wide insights into brain alternative RNA processing. Nature, 2008, 456(7221): 464–469
Li B, Zhang X Q, Liu S R, Liu S, Sun W J, Lin Q, Luo Y X, Zhou K R, Zhang C M, Tan Y Y, Yang J H, Qu L H. Discovering the Interactions between Circular RNAs and RNA-binding Proteins from CLIP-seq Data using circScan. bioRxiv, 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/115980
Liu X, Yang M. Research on conversational machine reading comprehension based on dynamic graph neural network. Journal of Integration Technology, 2022, 11(2): 67–78
Lei X, Tie J, Pan Y. Inferring metabolite-disease association using graph convolutional networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2022, 19(2): 688–698
Zhang S, Gong Y H, Wang J J. The development of deep convolution neural network and its applications on computer vision. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(3): 453–482
Alipanahi B, Delong A, Weirauch M T, Frey B J. Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA- and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(8): 831–838
Pan X, Shen H B. RNA-protein binding motifs mining with a new hybrid deep learning based cross-domain knowledge integration approach. BMC Bioinformatics, 2017, 18(1): 136
Pan X, Shen H. Predicting RNA-protein binding sites and motifs through combining local and global deep convolutional neural networks. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(20): 3427–3436
Pan X Y, Rijnbeek P, Yan J C, Shen H B. Prediction of RNA-protein sequence and structure binding preferences using deep convolutional and recurrent neural networks. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 511
Jia C, Bi Y, Chen J, Leier A, Li F, Song J. PASSION: an ensemble neural network approach for identifying the binding sites of RBPs on circRNAs. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(15): 4276–4282
Wang Z, Lei X. Matrix factorization with neural network for predicting circRNA-RBP interactions. BMC Bioinformatics, 2020, 21(1): 229
Tahir M, Tayara H, Hayat M, Chong K T. kDeepBind: prediction of RNA-Proteins binding sites using convolution neural network and k-gram features. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2021, 208: 104217
Du Z, Xiao X, Uversky V N. DeepA-RBPBS: a hybrid convolution and recurrent neural network combined with attention mechanism for predicting RBP binding site. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 2022, 40(9): 4250–4258
Li Z, Zhao S, Zhu S, Fan Y. MicroRNA-153–5p promotes the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via direct targeting of AGO1. Cell Death & Disease, 2021, 12(1): 33
Liu C, Yao M D, Li C P, Shan K, Yang H, Wang J J, Liu B, Li X M, Yao J, Jiang Q, Yan B. Silencing of circular RNA-ZNF609 ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction. Theranostics, 2017, 7(11): 2863–2877
Pan L, Xu C, Mei J, Chen Y, Wang D. Argonaute 3 (AGO3) promotes malignancy potential of cervical cancer via regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Reproductive Biology, 2021, 21(1): 100479
Liu Z, Wang Q, Wang X, Xu Z, Wei X, Li J. Circular RNA cIARS regulates ferroptosis in HCC cells through interacting with RNA binding protein ALKBH5. Cell Death Discovery, 2020, 6: 72
Tian X Y, Li J, Liu T H, Li D N, Wang J J, Zhang H, Deng Z L, Chen F J, Cai J P. The overexpression of AUF1 in colorectal cancer predicts a poor prognosis and promotes cancer progression by activating ERK and AKT pathways. Cancer Medicine, 2020, 9(22): 8612–8623
Khlghatyan J, Evstratova A, Bozoyan L, Chamberland S, Chatterjee D, Marakhovskaia A, Silva T S, Toth K, Mongrain V, Beaulieu J M. Fxr1 regulates sleep and synaptic homeostasis. The EMBO Journal, 2020, 39(21): e103864
Shen M, Guo Y, Dong Q, Gao Y, Stockton M E, Li M, Kannan S, Korabelnikov T, Schoeller K A, Sirois C L, Zhou C, Le J, Wang D, Chang Q, Sun Q Q, Zhao X. FXR1 regulation of parvalbumin interneurons in the prefrontal cortex is critical for schizophrenia-like behaviors. Molecular Psychiatry, 2021, 26(11): 6845–6867
Yang Y, Cai B, Shi X, Duan C, Tong T, Yu C. circ_0044516 functions in the progression of gastric cancer by modulating MicroRNA-149–5p/HuR axis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-04026-9
Su Y, Jin C, Sun S M, Li Z H, Xia S W, Zhang Z L, Zhang F, Shao J J, Zheng S Z. Progress in RNA-binding protein HuR and its roles in development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology, 2020, 36(12): 2283–2288
Singh A K, Kapoor V, Thotala D, Hallahan D E. TAF15 contributes to the radiation-inducible stress response in cancer. Oncotarget, 2020, 11(27): 2647–2659
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W. CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencingdata. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(23): 3150–3152
Zhang Y, Qiao S, Ji S, Li Y. DeepSite: bidirectional LSTM and CNN models for predicting DNA—protein binding. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(4): 841–851
Yang Y, Hou Z, Ma Z, Li X, Wong K C. iCircRBP-DHN: identification of circRNA-RBP interaction sites using deep hierarchical network. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2020, 22(4): bbaa274
Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Wu C H, Barker W C, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Huang H, Lopez R, Magrane M, Martin M J, Natale D A, O’Donovan C, Redaschi N, Yeh L S L. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(S1): D115–D119
Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, Frith M, Grant C E, Clementi L, Ren J, Li W W, Noble W S. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(S2): W202–W208
Hong J, Gao R, Yang Y. CrepHAN: cross-species prediction of enhancers by using hierarchical attention networks. Bioinformatics, 2021, 37(20): 3436–3443
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61972451, 61902230) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Shaanxi Normal University (GK202103091). We would like to express our gratitude to EditSprings for the expert linguistic services provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yajing Guo received the BS degree in School of Computer Science from Shaanxi Normal University, China in 2020, where she is currently pursuing the MS degree. Her current research interests include bioinformatics and deep learning.
Xiujuan Lei received the MS and PhD degrees from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China in 2001 and 2005, respectively. She is currently a Professor at the School of Computer Science, Shaanxi Normal University, China. Her research interests include bioinformatics, swarm intelligent optimization, data mining, and deep learning.
Lian Liu, received the PhD from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China in 2018. She is currently an associate research fellow at the School of Computer Science, Shaanxi Normal University, China. Her current research interests include bioinformatics, pattern recognition and machine learning.
Yi Pan is currently a professor of the Faculty of Computer Science and Control Engineering, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. He has served as Chair of Computer Science Department at Georgia State University, USA during 2005 to 2020. He received his Bachelor’s degree and Master’s degree in computer engineering from Tsinghua University, China in 1982 and 1984, respectively, and his PhD degree in computer science from the University of Pittsburgh, USA in 1991. His current research interests mainly include bioinformatics and health informatics using big data analytics, cloud computing, and machine learning technologies.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Lei, X., Liu, L. et al. circ2CBA: prediction of circRNA-RBP binding sites combining deep learning and attention mechanism. Front. Comput. Sci. 17, 175904 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-2151-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-2151-0