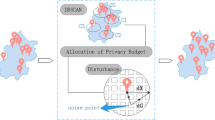
Abstract
Since smartphones embedded with positioning systems and digital maps are widely used, location-based services (LBSs) are rapidly growing in popularity and providing unprecedented convenience in people’s daily lives; however, they also cause great concern about privacy leakage. In particular, location queries can be used to infer users’ sensitive private information, such as home addresses, places of work and appointment locations. Hence, many schemes providing query anonymity have been proposed, but they typically ignore the fact that an adversary can infer real locations from the correlations between consecutive locations in a continuous LBS. To address this challenge, a novel dual privacy-preserving scheme (DPPS) is proposed that includes two privacy protection mechanisms. First, to prevent privacy disclosure caused by correlations between locations, a correlation model is proposed based on a hidden Markov model (HMM) to simulate users’ mobility and the adversary’s prediction probability. Second, to provide query probability anonymity of each single location, an advanced k-anonymity algorithm is proposed to construct cloaking regions, in which realistic and indistinguishable dummy locations are generated. To validate the effectiveness and efficiency of DPPS, theoretical analysis and experimental verification are further performed on a real-life dataset published by Microsoft, i.e., GeoLife dataset.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Hua J, Liu Y, Shen Y, Tian X, Luo Y, Jin C. A privacy-enhancing scheme against contextual knowledge-based attacks in location-based services. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2020, 14(3): 143605
Zhang S, Li X, Tan Z, Peng T, Wang G. A caching and spatial K-anonymity driven privacy enhancement scheme in continuous location-based services. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 94: 40–50
Lim K H, Chan J, Karunasekera S, Leckie C. Tour recommendation and trip planning using location-based social media: a survey. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2019, 60(3): 1247–1275
Liu H, Jin C, Zhou A. Popular route planning with travel cost estimation from trajectories. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2020, 14(1): 191–207
Yu H, Jia X, Zhang H, Yu X, Shu J. PSRide: Privacy-preserving shared ride matching for online ride hailing systems. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 18(3): 1425–1440
Jiang H, Li J, Zhao P, Zeng F, Xiao Z, Iyengar A. Location privacy-preserving mechanisms in location-based services: a comprehensive survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 2021, 54(1): 4
Zhang J, Li C, Wang B. A performance tunable CPIR-based privacy protection method for location based service. Information Sciences, 2022, 589: 440–458
Vidyalakshmi B S, Wong R K, Chi C H. Health mentions on twitter: a case study to identify privacy leaks. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 2020, 9(5): 85–90
Wang H, Xu Z, Zhang X, Peng X, Li K. An optimal differentially private data release mechanism with constrained error. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2022, 16(1): 161608
Zhao P, Li J, Zeng F, Xiao F, Wang C, Jiang H. ILLIA: Enabling K-anonymity-based privacy preserving against location injection attacks in continuous LBS queries. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(2): 1033–1042
Wang N, Fu J, Zeng J, Bhargava B K. Source-location privacy full protection in wireless sensor networks. Information Sciences, 2018, 444: 105–121
Yang Y, Zheng X, Guo W, Liu X, Chang V. Privacy-preserving smart IoT-based healthcare big data storage and self-adaptive access control system. Information Sciences, 2019, 479: 567–592
Zhang Z, Qi X, Wang Y, Jin C, Mao J, Zhou A. Distributed top-k similarity query on big trajectory streams. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2019, 13(3): 647–664
Zhang S, Mao X, Choo K K R, Peng T, Wang G. A trajectory privacy-preserving scheme based on a dual-K mechanism for continuous location-based services. Information Sciences, 2020, 527(2): 406–419
Kido H, Yanagisawa Y, Satoh T. An anonymous communication technique using dummies for location-based services. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pervasive Services, 2005. 2005, 88–97
Niu B, Li Q, Zhu X, Cao G, Li H. Achieving k-anonymity in privacy-aware location-based services. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2014-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. 2014, 754–762
Sun G, Chang V, Ramachandran M, Sun Z, Li G, Yu H, Liao D. Efficient location privacy algorithm for Internet of Things (IoT) services and applications. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2017, 89: 3–13
Sun G, Cai S, Yu H, Maharjan S, Chang V, Du X, Guizani M. Location privacy preservation for mobile users in location-based services. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 87425–87438
Sun Y, Chen M, Hu L, Qian Y, Hassan M M. ASA: Against statistical attacks for privacy-aware users in Location Based Service. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017, 70: 48–58
Peng T, Liu Q, Wang G. Enhanced location privacy preserving scheme in location-based services. IEEE Systems Journal, 2014, 11(1): 219–230
Zhang S, Choo K K R, Liu Q, Wang G. Enhancing privacy through uniform grid and caching in location-based services. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 86: 881–892
Yadav V K, Verma S, Venkatesan S. Linkable privacy-preserving scheme for location-based services. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 7998–8012
Peng T, Liu Q, Meng D, Wang G. Collaborative trajectory privacy preserving scheme in location-based services. Information Sciences, 2017, 387: 165–179
Shaham S, Ding M, Liu B, Lin Z H, Li J. Transition-Entropy: a novel metric for privacy preservation in location-based services. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). 2019, 1–6
Shaham S, Ding M, Liu B, Dang S, Lin Z, Li J. Privacy preservation in location-based services: A novel metric and attack model. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 20(10): 3006–3019
Wu Z, Wang R, Li Q, Lian X, Xu G, Chen E, Liu X. A location privacy-preserving system based on query range cover-up or location-based services. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(5): 5244–5254
Kuang L, Wang Y, Zheng X, Huang L, Sheng Y. Using location semantics to realize personalized road network location privacy protection. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2020, 2020(1): 1
Tan Z, Wang C, Yan C, Zhou M, Jiang C. Protecting privacy of location-based services in road networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(10): 6435–6448
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62172350), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 21621028) and the Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education (No. 2022YCXS083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Long Li received his PhD degree from Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China in 2018. He is now a lecturer with the School of Computer Science and Information Security, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, and undertakes postdoctoral research in Jinan University, China. His research interests include cryptographic protocols, privacy-preserving technologies and AI security.
Jianbo Huang received his MS degree from Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China in 2020. He is currently working in Nanning Campus, Guilin University of Technology, China. His research interests include location privacy protection and big data processing.
Liang Chang received his PhD degree in computer science from the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. He is currently a Professor with the School of Computer Science and Information Security, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China. His research interests include information security, knowledge representation and reasoning, description logics, and the semantic Web.
Jian Weng received his PhD degree from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China in 2008. He is a professor with the College of Information Science and Technology, Jinan University, China. His research interests include public key cryptography, cloud security, etc. He has published 80 papers in international conferences and journals such as CRYPTO, EUROCRYPT, ASIACRYPT, TCC, PKC, CT-RSA, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing.
Jia Chen, PhD candidate. He is now a lecturer with the Department of Computer Applications, Guilin University of Technology, China. His main research interests include network architecture, network security and big data processing.
Jingjing Li received her PhD degree from Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China in 2020. She is now a lecturer with the College of Cyber Security, Jinan University, China. Her research interests include cryptographic protocols, machine learning and AI security.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Huang, J., Chang, L. et al. DPPS: A novel dual privacy-preserving scheme for enhancing query privacy in continuous location-based services. Front. Comput. Sci. 17, 175814 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-2155-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-2155-9