Abstract
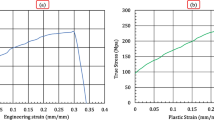
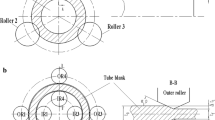
This paper describes the peculiarities encountered in the numerical modeling of non-circular spinning processes using motion-controlled roller tools and applying the Finite Element Method (FEM). This process is suitable for producing non-circular, hollow components in small to medium-sized production lots. Numerical simulation can be used to optimize the process. Therefore, it is necessary to make a realistic sheet thinning and wrinkling calculation by using the FEM. This can be achieved through the definition of the real kinematics, a suitable flow curve and an optimal sheet meshing strategy using solid elements. An optimal sheet meshing strategy is particularly necessary in order to realistically calculate the process within an acceptable computing time. Reference experiments with the rotationally non-symmetric mandrel types, the “Tripode” and “Pagoda”, were carried out to compare simulations and experiments. A comparison of the reference experiments with the “Tripode” mandrel demonstrated that it is possible to simulate non-circular spinning with a deviation of less than 5% with respect to minimum sheet thickness. It is also possible to predict wrinkling in critical, non-circular spinning processes. This has been confirmed by comparing the “Pagoda” reference experiment with the FEM simulation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lange K (1990) Umformtechnik. Handbuch für Industrie und Wissenschaft. Springer, Heidelberg
Tschaetsch H (2005) Metal forming practise. Springer, Heidelberg
Awiszus B, Härtel S (2010) Drücken unrunder Bauteile. Blech Rohre Profile 3:10–11. ISSN 0006-4688
Awiszus B. Meyer F (2005) Metal spinning of non-circular hollow parts. In: Proceedings of 8th ICTP, October 9–13, 2005, Verona/Italy, p 353 ff. ISBN 88-87331-74-X
Arai H (2006) Force-controlled metal spinning machine using linear motors. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 15–19 May 2006, Orlando, Florida, pp 4031–4036
Awiszus B, Härtel S (2010) Es läuft rund—„Das Unrunddrücken“, UTFscience 1. http://www.utfscience.de
Härtel S, Awiszus B (2010) Numerical and experimental investigations of production of non-rotationally symmetric hollow parts using sheet metal spinning. In: Steel research international, 81, No. 9, Special Edition Metal Forming 2010, September 19–22, 2010, Toyohashi, Japan, pp 998–1002. ISBN 978-3-514-00774-1
Röcker O (2008) Untersuchungen zur Anwendung hoch- und höchstfester Stähle für walzprofilierte Fahrzeugstrukturkomponenten. Dissertation. TU Berlin
Beyer U, Awiszus B (2010) Flat-clinching—a new possibility for joining different kinds of components in a flexible and effective way to a planar material com-pound. In: Steel research international, 81, No. 9, Special Edition Metal Forming 2010, September 19–22, 2010, Toyohashi, Japan, pp 1124–1127. ISBN 978-3-514-00774-1
Acknowledgments
The authors are extremely grateful to the German Research Foundation DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft e.V.) for supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awiszus, B., Härtel, S. Numerical simulation of non-circular spinning: a rotationally non-symmetric spinning process. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 5, 605–612 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-011-0335-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-011-0335-9