Abstract
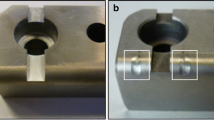
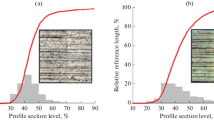
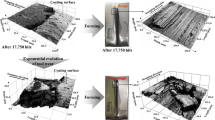
Residual stresses in the substrate material are significantly influencing the performance of PVD-coated parts and tools which are exposed to high forces. Especially for forming operations, such as sheet-bulk metal forming, during which normal contact pressures of 1.4 GPa can occur, the reduction of friction and, at the same time, the wear protection by means of thin Cr-based coatings are essential. To ensure a long service life of forming tool and tool coating, each step of the substrate pre-treatment, as well as the magnetron-sputtering process, has to be coordinated and compatible. Therefore, polished as well as nitrided samples consisting of high-speed steel (AISI M3:2) are exposed to a sequence of plasma-based pre-treatments prior to depositing a CrAlN coating. Hardness and Young’s modulus of the substrate and the coating are analysed by means of nanoindentation. To determine the adhesion between coating and substrate, scratch tests are conducted and analysed using a scanning electron microscope. For each step, the residual stresses are determined using sin2ψ measurements, which are correlated to the mechanical properties. A plasma-nitriding process before the CrAlN coating induces high compressive residual stresses into the sample subsurface and at the same time increases the hardness of the surface. This results in higher critical loads during the scratch tests and therefore a better adhesion of the coating on the substrate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas K, Merklein M (2014) Improvement of surface integrity of cold forging tools by adaption of tool making process. Prod Eng 8:131–141
Bagcivan N, Bobzin K, Theiß S (2013) (Cr1−xAlx)N: a comparison of direct current, middle frequency pulsed and high power pulsed magnetron sputtering for injection molding components. Thin Solid Films 528:180–186
Behrens B-A, Yilkiran T (2012) Influence of the fabrication method on the wear resistance of hot forging dies. Prod Eng 6:267–276
Biermann D, Freiburg D, Hense R, Tillmann W, Stangier D (2015) Surface modifications to influence friction, using high-feed milling and wear resistant PVD-coatings for sheet-bulk metal forming tools. Key Eng Mater 639:275–282
Bobzin K, Lugscheider E, Nickel R, Immich P (2006) (Cr1−x, Alx)N ein Review über ein vielseitig einsetzbares Schichtsystem. Materialwiss Werkstofftech 37(10):833–841
Brecher C, Spachtholz G, Bobzin K, Lugscheider E, Knotek O, Maes M (2005) Superelastic, (Cr, Al) N coatings for high end spindle bearings. Surf Coat Technol 200:1738–1744
Breidenstein B, Denkena B (2013) Significance of residual stress in PVD-coated carbide cutting tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62(1):67–70
Bußmann M (2000) Beitrag zur Grenzflächenkonditionierung im Plasmanitrier-Arc-PVD-Hybridprozeß. Dr. Ing., Dissertation, TU Dortmund
Eigenmann B, Macherauch E (1995) Röntgenographische Untersuchungen von Spannungszuständen in Werkstoffen, Teil I. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstoffstechnik 3:148–160
Eigenmann B, Macherauch E (1996) Röntgenographische Untersuchungen von Spannungszuständen in Werkstoffen, Teil III. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstoffstechnik 9:426–437
Kimura A, Kawate M, Hiroyuki H, Suzuki T (2003) Anisotropic lattice expansion and shrinkage of hexagonal TiAlN and CrAlN films. Surf Coat Technol 169–170:367–370
Kurz SJB, Meka SR, Schell N, Ecker W, Keckes J, Mittemeijera EJ (2015) Residual stress and microstructure depth gradients in nitrided iron-based alloys revealed by dynamical cross-sectional transmission X-ray microdiffraction. Acta Mater 87:100–110
Lange K, Kammerer M, Pöhlandt K, Schöck J (2008) Fließpressen, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin
Lin J, Mishra B, Moore JJ, Sproul WD (2006) Mircrostructure, mechanical and tribological properties of Cr1−xAlxN films deposited by pulsed-closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering (P-CFUBMS). Surf Coat Technol 201:4329–4334
Lv Y, Ji L, Liu X, Li H, Zhou H, Chen J (2012) Influence of substrate bias voltage on structure and properties of the CrAlN films deposited by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Appl Surf Sci 258:3864–3870
Martin PM (2010) Handbook of deposition technologies for films and coatings: science, applications and technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Merklein M, Andreas K, Engel U (2011) Influence of machining process on residual stresses in the surface of cemented carbides. Procedia Eng 19:252–257
Ozbek YY, Sarioglu C, Durman M (2014) The effect of plasma detonation parameters on residual stresses developed in the plasma modified layer. Vacuum 106:11–15
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1583
Sieczkarek P, Kwiatkowski L, Tekkaya AE, Krebs E, Biermann D, Tillmann W, Herper J (2012) Improved tool surfaces for incremental bulk forming processes of sheet metals. Key Eng Mater 504–506:975–980
Sieczkarek P, Kwiatkowski L, Tekkaya AE, Krebs E, Kersting P, Tillmann W, Herper J (2013) Innovative tools to improve incremental bulk forming processes. Key Eng Mater 554:1490–1497
Tillmann W, Dildrop M, Sprute T (2014) Influence of nitriding parameters on the tribological properties and the adhesion of Ti- and Cr- based multilayer designs. Surf Coat Technol 260:380–385
Vierzigmann HU, Merklein M, Engel U (2010) Tailored surfaces in sheet-bulk metal forming. In: Proceedings of 4th international conference on tribology in manufacturing processes, pp. 541–550
Wilson A, Matthews A, Housden J, Turner R, Garside B (1993) A comparison of the wear and fatigue properties of plasma-assisted physical vapour deposition TiN, CrN and duplex coatings on Ti–6Al–4V. Surf Coat Technol 62:600–607
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the transregional collaborative research center TR73 “Manufacturing of complex functional components with variants by using a new sheet metal forming process—Sheet Bulk Metal Forming”. This work is a cooperation of the subprojects B5 (Application of nanostructured bionic thin layers to enhance the wear and friction behaviour of forming tools by thin-walled sheet forming) and B8 (Grinding strategies for local and stress orientated subsurface-modification of sheet-bulk metal forming tools).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tillmann, W., Stangier, D., Denkena, B. et al. Influence of PVD-coating technology and pretreatments on residual stresses for sheet-bulk metal forming tools. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 10, 17–24 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-015-0653-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-015-0653-4