Abstract
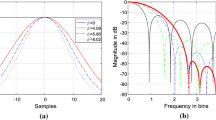
Linear canonical transform is a four-parameter class of integral transform that plays an important role in many fields of optics and signal processing. Well-known transforms such as the Fourier transform, the fractional Fourier transform, and the Fresnel transform can be seen as the special cases of the linear canonical transform. This paper presents a new mathematical model for obtaining the linear canonical transforms of Dirichlet, Generalized “Hamming”, and Triangular window functions. The different window function parameters are also obtained from the simulations. By changing the value of four parameters and then changing the adjustable parameter, the main-lobe width, −3 dB bandwidth, −6 dB bandwidth and correspondingly, the minimum stop-band attenuation of the resulting window functions can be controlled. It has been shown that by using linear canonical transform, we are able to obtain all window parameters successfully as compared to fractional Fourier transform.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alieva T., Bastiaans M.J.: Powers of transfer matrices determined by means of eigenfunctions. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 16(10), 2413–2418 (1999)
Moshinsky M., Quesne C.: Linear canonical transformations and their unitary representations. J. Math. Phys. 12(8), 1772–1783 (1971)
Nazarathy M., Shamir J.: First-order optics—a canonical operator representation: lossless systems. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 72(3), 356–364 (1982)
Pei S.C., Ding J.J.: Relations between fractional operations and time-frequency distributions, and their applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(8), 1638–1655 (2001)
Pei S.C., Ding J.J.: Eigenfunctions of linear canonical transform. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech. Signal Process. 50(1), 11–26 (2002)
Hennelly B.M., Sheridan J.T.: Generalizing, optimizing, and inventing numerical algorithms for the fractional Fourier, Fresnel, and linear canonical transforms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 22(5), 917–927 (2005)
Stern A.: Sampling of linear canonical transformed signals. Signal Process. 86(7), 1421–1425 (2006)
Tao R., Qi L., Wang Y.: Theory and Applications of the Fractional Fourier Transform. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2004)
Ozaktas H.M., Kutay M.A., Zalevsky Z.: The Fractional Fourier Transform with Applications in Optics and Signal Processing. Wiley, New York (2000)
Almeida L.B.: The fractional Fourier transform and time-frequency representations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(11), 3084–3091 (1994)
Barshan B., Ozaktas H.M., Kutay M.A.: Optimal filters with linear canonical transformations. Opt. Commun. 135(1–3), 32–36 (1997)
Sharma K.K., Joshi S.D.: Signal separation using linear canonical and fractional Fourier transforms. Opt. Commun. 265(2), 454–460 (2006)
Deng B., Tao R., Wang Y.: Convolution theorem for the linear canonical transform and their applications. Sci. China F 49(5), 592–603 (2006)
Li B.Z., Tao R., Wang Y.: New sampling formulae related to linear canonical transform. Signal Process. 87(5), 983–990 (2007)
Koc A., Ozaktas H.M., Candan C., Kutay M.A.: Digital computation of linear canonical transforms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(6), 2383–2394 (2008)
Healy J.J., Sheridan J.T.: Cases where the linear canonical transform of a signal has compact support or is band-limited. Opt. Lett. 33(3), 228–230 (2008)
Tao R., Li B.Z., Wang Y., Aggrey G.K.: On sampling of band-limited signals associated with the linear canonical transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(11), 5454–5464 (2008)
Pei S.C., Ding J.J.: Closed-form discrete fractional and affine Fourier transforms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 48(5), 1338–1353 (2002)
Hennelly B.M., Sheridan J.T.: Fast numerical algorithm for the linear canonical transform. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 22(5), 928–937 (2005)
Healy J.J., Sheridan J.T.: Sampling and discretization of the linear canonical transform. Signal Process. 89(4), 641–648 (2009)
Oktem F.S., Ozaktas H.M.: Equivalence of linear canonical transform domains to fractional Fourier domains and the bicanonical width product: a generalization of the space-bandwidth product. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 27(8), 1885–1895 (2010)
Weisstein E.W.: CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2003)
Harris, F.J.: On the use of windows for harmonic analysis with discrete Fourier transform. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 66(1), pp. 51–83 (1978)
Liu Y., Kou K., Ho I.: New sampling formulae for non-band limited signals associated with linear canonical transform and non linear Fourier atoms. Signal Process. 90, 933–945 (2010)
Alieva T., Bastiaans M.J.: Properties of the linear canonical integral transformation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 24(11), 3658– 3665 (2007)
Kumar S., Singh K., Saxena R.: Analysis of Dirichlet and generalized “Hamming” window functions in the fractional Fourier transform domains. Signal Process. 91, 600–606 (2010)
James D.F.V., Agarwal G.S.: The generalized Fresnel transform and its applications to optics. Opt. Commun. 126(4–6), 207–212 (1996)
Bernardo L.M.: ABCD matrix formalism of fractional Fourier optics. Opt. Eng. 35(3), 732–740 (1996)
Abe S., Sheridan J.T.: Optical operations on wave functions as the Abelian subgroups of the special affine Fourier transformation. Opt. Lett. 19(22), 1801–1803 (1994)
Zhao J., Tao R., Wang Y.: Sampling rate conversion for linear canonical transform. Signal Process. 88, 2825–2832 (2008)
Dainty, J.C.: Current Trends in Optics. Academic Press, New York, Ch. 10, pp. 139–148 (1994)
Abramowitz M., Stegun I.A.: Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs and Mathematical Tables, vol. 55 of National Bureau of Standards Applied Mathematics Series. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC (1964)
Saxena R., Singh K.: Fractional Fourier transform—a review. IETE J. Educ. 48, 13–30 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, N., Singh, K. Analysis of Dirichlet, Generalized Hamming and Triangular window functions in the linear canonical transform domain. SIViP 7, 911–923 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-011-0280-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-011-0280-2