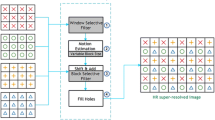
Abstract
An enhanced fusion algorithm for generating a super-resolution image from a sequence of low-resolution images captured from identical scene apparently a video based on adaptive normalized convolution has been designed and analyzed. The algorithm for fusing the images is based on the supporting structure of normalized convolution. Here the idea is projection of local signals onto a subspace. The adaptive nature of the window function in adaptive normalized convolution helps to gather more samples for processing and increases signal-to-noise ratio, decreases diffusion through discontinuities. The validation of proposed method is done using simulated experiments and real-time experiments. These experimental results are compared with various latest techniques using performance measures like peak signal-to-noise ratio, sharpness index and blind image quality index. In both the cases of experiments, the proposed adaptive normalized convolution-based super-resolution image reconstruction has proved to be highly efficient which is needed for satellite imaging, medical imaging diagnosis, military surveillance, remote sensing, etc.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liyakathunisa, L., Kumar, C.N.R, Ananthashayana, V.K.: Super resolution reconstruction of compressed low resolution images using wavelet lifting schemes. Presented at the 2009 International Conference on Computer and Electrical Engineering, Dubai, Dec 28–30 (2009). doi:10.1109/ICCEE.2009.221
Hardeep, P., Prashant, B., Joshi, S.M.: A survey on techniques and challenges in image super resolution reconstruction. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 2(1), 317–325 (2013)
Babacan, S.D., Molina, R., Katsaggelos, K.: Total variation super resolution using a variational approach. Presented at the 2008 \(15{{\rm th}}\) IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, California, Oct 12–15 (2008). doi:10.1109/ICIP.2008.4711836
Tom, B.C., Katsaggelos, A.K.: Reconstruction of a high-resolution image by simultaneous registration, restoration, and interpolation of low-resolution images. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Image Processing, Washington, Oct. 23–26, pp. 539–542 (1995). doi:10.1109/ICIP.1995.537535
Schultz, R.R., Stevenson, R.L.: Extraction of high-resolution frames from video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 5(6), 996–1011 (1996). doi:10.1109/83.503915
Belekos, S.P., Galatsanos, N.P., Katsaggelos, A.K.: Maximum a posteriori video super-resolution using a new multichannel image prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(6), 1451–1464 (2010). doi:10.1109/TIP.2010.2042115
Elad, M., Feuer, A.: Restoration of a single super resolution image from several blurred, noisy, and under sampled measured images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 6(12), 1646–1658 (1997). doi:10.1109/83.650118
Nguyen, N., Milanfar, P.: A wavelet-based interpolation-restoration method for super resolution (wavelet super resolution). Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 19(4), 321–338 (2000). doi:10.1007/BF01200891
Ji, H., Fermüller, C.: Robust wavelet-based super-resolution reconstruction: theory and algorithm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31(4), 649–660 (2009). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2008.103
Pham, T.Q., Van Vliet, L.J., Schutte, K.: Robust fusion of irregularly sampled data using adaptive normalized convolution. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. (2006). doi:10.1155/ASP/2006/83268
Déniz, O., Bueno, G., Salido, J., De La Torre, F.: Face recognition using histograms of oriented gradients. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 32(12), 1598–1603 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2011.01.004
Vandewalle, P., Süsstrunk, S., Vetterll, M.: A frequency domain approach to registration of aliased images with application to super-resolution. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. (2006). doi:10.1155/ASP/2006/71459
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(5), 513–516 (2010)
Feichtenhofer, C., Fassold, H., Schallauer, P.: A perceptual image sharpness metric based on local edge gradient analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 20(4), 379–382 (2013)
Milanfar, P.: MDSP Super-Resolution and Demosaicing Datasets [Online]. http://users.soe.ucsc.edu/~milanfar/software/srdatasets.html. Accessed 29 Mar 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abraham Sundar, K.J., Vaithiyanathan, V. Multi-frame super-resolution using adaptive normalized convolution. SIViP 11, 357–362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0952-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0952-z