Abstract
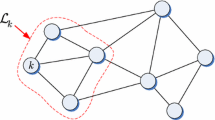
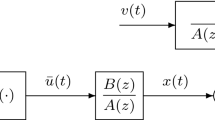
In this paper, we propose a distributed adaptive learning algorithm to train the coefficients of a widely linear autoregressive moving average model by measurements collected by the nodes of a network. We assume that each node uses the augmented complex adaptive infinite impulse response (ACA-IIR) filter as the learning rule, and nodes interact with each other under an incremental mode of cooperation. To derive the proposed algorithm, called the incremental ACAIIR (IACA-IIR), we firstly formulate the distributed adaptive learning problem as an unconstrained minimization problem. Then, we apply stochastic gradient optimization argument to solve it and derive the proposed algorithm. We further find the step size range where the stability of the proposed algorithm is guaranteed. We also introduce a reduced-complexity version of the IACA-IIR algorithm. Since the proposed algorithm relies on the augmented complex statistics, it can be used to model both types of complex-valued signals (proper and improper signals). To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, we use both synthetic and real-world complex signals in our simulations. The results exhibit superior performance of the proposed algorithm over the non-cooperative ACA-IIR algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The wind data are available at www.commsp.ee.ic.ac.uk/~mandic/wind-dataset.zip
References
Adali, T., Schreier, P., Scharf, L.: Complex-valued signal processing: the proper way to deal with impropriety. Signal Process. IEEE Trans. 59(11), 5101–5125 (2011)
Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Bazzi, W.: A collaborative adaptive algorithm for the filtering of noncircular complex signals. In: Telecommunications (IST): 7th International Symposium on, pp. 96–99 (2014)
Xia, Y., Mandic, D., Sayed, A.: An adaptive diffusion augmented CLMS algorithm for distributed filtering of noncircular complex signals. Signal Process. Lett. IEEE 18(11), 659–662 (2011)
Kanna, S., Talebi, S., Mandic, D.: Diffusion widely linear adaptive estimation of system frequency in distributed power grids, In: Energy Conference (ENERGYCON), 2014 IEEE International, pp. 772–778 (2014)
Jahanchahi, C., Mandic, D.: An adaptive diffusion quaternion lms algorithm for distributed networks of 3d and 4d vector sensors, In: Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), 2013 Proceedings of the 21st European, pp. 1–5 (2013)
Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Sanei, S.: Robust frequency estimation in three-phase power systems using correntropy-based adaptive filter. IET Science, Measurement and Technology (2015)
Picinbono, B.: On circularity. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(12), 3473–3482 (1994)
Picinbono, B.: Second-order complex random vectors and normal distributions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(10), 2637–2640 (1996)
Mandic, D., Goh, V.S.L.: Complex Valued Nonlinear Adaptive Filters: Noncircularity, Widely Linear and Neural Models. Wiley, New Jersey (2009)
Schober, R., Gerstacker, W., Lampe, L.H.-J.: Data-aided and blind stochastic gradient algorithms for widely linear mmse mai suppression for ds-cdma. Signal Process. IEEE Trans. 52(3), 746–756 (2004)
Javidi, S., Pedzisz, M., Goh, S.L., Mandic, D.P.: The augmented complex least mean square algorithm with application to adaptive prediction problems. In: 1st IARP Workshop Congress Information Processing, pp. 54–57 (2008)
Xia, Y., CheongTook, C., Mandic, D.P.: An augmented affine projection algorithm for the filtering of noncircular complex signals. Signal Process. 90(6), 1788–1799 (2010)
Douglas, S.: Widely-linear recursive least-squares algorithm for adaptive beamforming. In: Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009. IEEE International Conference on, pp. 2041–2044 (2009)
Xia, Y., Javidi, S., Mandic, D.: A regularised normalised augmented complex least mean square algorithm, In: Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS): 7th International Symposium on, pp. 355–359 (2010)
Took, C., Mandic, D.: Adaptive iir filtering of noncircular complex signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(10), 4111–4118 (2009)
Wang, X., Wang, S., Ma, J.-J., Bi, D.-W.: Energy-efficient organization of wireless sensor networks with adaptive forecasting. Sensors 8(4), 2604–2616 (2008)
Wang, X., Wang, S., Bi, D.-W., Ma, J.-J.: Distributed peer-to-peer target tracking in wireless sensor networks. Sensors 7(6), 1001–1027 (2007)
Gharavi, H., Hu, B.: Cooperative diversity routing and transmission for wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Sens. Syst. IET 3(4), 277–288 (2013)
Mohamed, M., Wu, W., Moniri, M.: Data reduction methods for wireless smart sensors in monitoring water distribution systems. Procedia Engineering, 70, pp. 1166 – 1172, (2014), 12th International Conference on Computing and Control for the Water Industry, CCWI2013
Harb, H., Makhoul, A., Tawil, R., Jaber, A.: Energy-efficient data aggregation and transfer in periodic sensor networks. Wirel. Sens. Syst. IET 4(4), 149–158 (2014)
Rabbat, M., Nowak, R.: Quantized incremental algorithms for distributed optimization. IEEE J. Select. Areas Commun. 23(4), 798–808 (2005)
Lopes, C., Sayed, A.: Incremental adaptive strategies over distributed networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(8), 4064–4077 (2007)
Liu, Y., Tang, W.K.: Enhanced incremental LMS with norm constraints for distributed in-network estimation. Signal Process. 94, 373–385 (2014)
Abadi, M.S.E., Danaee, A.-R.: Low computational complexity family of affine projection algorithms over adaptive distributed incremental networks. AEU - Int. J. Electron. Commun. 68(2), 97–110 (2014)
Rastegarnia, A., Khalili, A.: Incorporating observation quality information into the incremental lms adaptive networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(2), 987–995 (2014)
Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Bazzi, W., Yang, Z.: Derivation and analysis of incremental augmented complex least mean square algorithm. Signal Process. IET 9(4), 312–319 (2015)
Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Bazzi, W.: Incremental augmented affine projection algorithm for collaborative processing of complex signals. In: Information and Communication Technology Research (ICTRC), 2015 International Conference on, pp. 60–63 (2015)
Rahmati, R.G., Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Mohammadi, H.: An adaptive incremental algorithm for distributed filtering of hypercomplex processes. Am. J. Signal Process. 5(2A), 9–15 (2015)
Rastegarnia, A., Khalili, A., Bazzi, W.M., Sanei, S.: An incremental lms network with reduced communication delay. Signal Image Video Process. 10(4), 769–775 (2016)
Rastegarnia, A., Tinati, M.A., Khalili, A.: Steady-state analysis of quantized distributed incremental lms algorithm without gaussian restriction. Signal Image Video Process. 7(2), 227–234 (2013)
Sayed, A.H., Tu, S.-Y., Chen, J., Zhao, X., Towfic, Z.: Diffusion strategies for adaptation and learning over networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(3), 155–171 (2013)
Lopes, C., Sayed, A.: Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: formulation and performance analysis. Signal Process. IEEE Trans. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008)
Cattivelli, F., Sayed, A.: Diffusion lms strategies for distributed estimation. Signal Process. IEEE Trans. 58(3), 1035–1048 (2010)
Abdolee, R., Champagne, B., Sayed, A.H.: Diffusion LMS strategies for parameter estimation over fading wireless channels. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications (2013)
Kreutz-Delgado, K.: The Complex Gradient Operatorand the CR-Calculus, Lecture Suppl. ECE275A, pp. 1–74, (2006)
Tsitsiklis, J., Bertsekas, D., Athans, M.: Distributed asynchronous deterministic and stochastic gradient optimization algorithms. Autom. Control IEEE Trans. 31(9), 803–812 (1986)
Treichler, J.R., Johnson Jr., C.R., Larimore, M.J.: Theory and Design of Adaptive Filters. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1987)
Regalia, P.A.: Adaptive IIR Filtering in Signal Processing and Control. Marcel Dekker, New York (1994)
Navarro-Moreno, J.: Arma prediction of widely linear systems by using the innovations algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3061–3068 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalili, A., Rastegarnia, A., Bazzi, W.M. et al. Incremental augmented complex adaptive IIR algorithm for training widely linear ARMA model. SIViP 11, 493–500 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0986-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0986-2