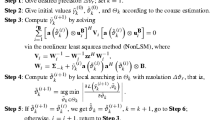Abstract
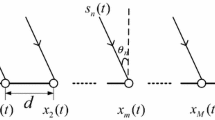
We investigated the problem of source enumeration in array signal processing. The conventional batch estimating methods do not yield satisfactory tracking performance in a dynamic environment. In order to solve this problem, an online source number estimation method is proposed in this paper. The developed algorithm exploits subspace tracking and hypothesis test to update the estimation of the signal number sequentially. Simulation results validate the superiority of the new method in terms of tracking capacity and computation efficiency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, L., Liu, Z., Jiang, W.: A direction finding method for spatial optical beam-forming network based on sparse Bayesian learning. Signal Image Video Process 11(2), 203–209 (2017)
Ta, S., Wang, H.: Propagator-based computationally efficient direction finding via low-dimensional equation rooting. Signal Image Video Process 12(1), 83–90 (2018)
Salvati, D., Drioli, C., Foresti, G.L.: Frequency map selection using a RBFN-based classifier in the MVDR beamformer for speaker localization in reverberant rooms. In: INTERSPEECH 2015, 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, pp. 3298–3301, Dresden, Germany (2015)
Ma, L., Tsoi, A.C.: A variational bayesian approach to number of sources estimation for multichannel blind deconvolution. Signal Image Video Process 2(2), 107–127 (2018)
Kritchman, S., Nadler, B.: Non-parametric detection of the number of signals: hypothesis testing and random matrix theory. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57(10), 3930–3941 (2009)
Akaike, H.: A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6), 716–723 (1974)
Schwarz, G.: Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6(2), 15–18 (1978)
Fishler, E., Poor, H.V.: Estimation of the number of sources in unbalanced arrays via information theoretic criteria. IEEE Trans Signal Process 53(9), 3543–3553 (2005)
Wong, M.K., Zhang, Q.T., Reilly, J.P., Yip, P.C.: On information theoretic criteria for determining the number of signals in high resolution array processing. IEEE Trans Signal Process 38(11), 1959–1971 (1990)
Tsinos, C.G., Berberidis, K.: Decentralized adaptive eigenvalue-based spectrum sensing for multiantenna cognitive radio systems. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 14(3), 1703–1716 (2015)
Zou, Q., Zheng, S., Sayed, A.: Cooperative sensing via sequential detection. IEEE Trans Signal Process 58(12), 6266–6283 (2010)
Renard, J., Lampe, L., Horlin, F.: Sequential likelihood ratio test for cognitive radios. IEEE Trans Signal Process 64(24), 6627–6639 (2016)
Zeng, Y., Liang, Y.C.: Eigenvalue-based spectrum sensing algorithms for cognitive radio. IEEE Trans Commun 57(6), 1784–1793 (2009)
Kortun, A., Ratnarajah, T., Sellathurai, M., Zhong, C., Papadias, C.: On the performance of eigenvalue-based cooperative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 5(1), 49–55 (2011)
Yang, B.: Projection approximation subspace tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 43(1), 95–107 (1995)
Abed-Meraim, K., Chkeif, A., Hua, Y.: Fast orthonormal past algorithm. IEEE Signal Process Lett 7(3), 60–63 (2000)
Miao, Y., Hua, Y.: Fast subspace tracking and neural network learning by a novel information criterion. IEEE Trans Signal Process 46(7), 1967–1980 (1998)
Doukopoulos, X., Moustakides, G.: Fast and stable subspace tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 56(4), 1452–1465 (2008)
Badeau, R., David, B., Richard, G.: Fast approximated power iteration subspace tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process 53(8), 2931–2941 (2005)
Doukopoulos, X.: Power techniques for blind channel estimation in wireless communications systems. Ph.D. Thesis, IRISA-INRIA, University of Rennes, France (2004)
Oja, E.: A simplified neuron model as a principal component analyzer. J Math Biol 15(3), 267–273 (1982)
Abed-Meraim, K., Attallah, S., Chkeif, A., Hua, Y.: Orthogonal Oja algorithm. IEEE Signal Process Lett 7(5), 116–120 (2000)
Kavcic, A., Yang, B.: Adaptive rank estimation for spherical subspace trackers. IEEE Trans Signal Process 44(6), 1573–1579 (1996)
Yang, B.: An extension of the pastd algorithm to both rank and subspace tracking. IEEE Signal Process Lett 2(9), 179–182 (1995)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61302141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, LL., Liu, Zm. & Huang, Zt. Online source number estimation based on sequential hypothesis test and subspace tracking. SIViP 13, 307–311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1358-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1358-x