Abstract
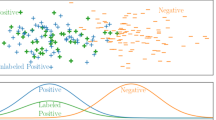
The current success of supervised learning is limited on large amounts of labeled training data. Transfer learning aims to learn an adaptive classifier for the unlabeled target domain data from the labeled source domain data, which is sampled from diverse probability distributions under changing conditions. Most previous works focus on how to reduce the distribution discrepancy between two involved domains, or exploit the shared common feature by preserving the local geometric structure of samples. In this paper, we propose a modified method jointly optimizing the local and global structure preservation. The main idea is to explore common features with manifold regularization. Discriminative repulsive force model is used to improve maximum mean discrepancy, which keeps discriminative property in the local sense via labeled source domain data and alleviates the global distribution discrepancy of the different domains. Quantitative results indicate that our method performs better than other methods on 16 cross-domain experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy, K.P.: Machine Learning: a Probabilistic Perspective. MIT press, Cambridge (2012)
Wei, Z., Chu, Y., Zhao, L.: An effective two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis with locality preserving approach for image recognition. Signal Image Video Process. 11(8), 1577–1584 (2017)
Tang, Z., Wu, X., Leng, X., Chen, W.: A fast face recognition method based on fractal coding. Signal Image Video Process. 11(7), 1221–1228 (2017)
Ghosn, J., Bengio, Y.: Bias learning, knowledge sharing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(4), 748–765 (2003)
Bishop, M.C.: Pattern recognition. Mach. Learn. 128, 1–58 (2006)
Pan, S.J., Yang, Q.: A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 22(10), 1345–1359 (2010)
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Pan, S.J., Philip, S.Y.: Adaptation regularization: a general framework for transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(5), 1076–1089 (2014)
Zhuang, F., Luo, P., Shen, Z., He, Q., Xiong, Y., Shi, Z., Xiong, H.: Mining distinction and commonality across multiple domains using generative model for text classification. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 24(11), 2025–2039 (2012)
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Shen, D., Yang, Q.: Transfer learning with graph co-regularization. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(7), 1805–1818 (2014)
Pan, S.J., Tsang, I.W., Kwok, J.T., Yang, Q.: Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(2), 199 (2011)
Rohrbach, M., Stark, M., Szarvas, G., Gurevych, I., Schiele, B.: What helps where and why? semantic relatedness for knowledge transfer. In: CVPR, pp. 910–917 (2010)
Weiss, K., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Wang, D.: A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 3(1), 1–40 (2016)
Chattopadhyay, R., Ye, J., Sun, P., Fan, W., Davidson, I.: Multi-source domain adaptation and its application to early detection of fatigue. SIGKDD 6(4), 18 (2011)
Duan, L., Xu, D., Tsang, I.W.: Domain adaptation from multiple sources: a domain-dependent regularization approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 23(3), 504–18 (2012)
Tommasi, T., Orabona, F., Caputo, B.: Learning categories from few examples with multi model knowledge transfer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(5), 928–941 (2014)
Pan, S.J., Kwok, J.T., Yang, Q.: Transfer learning via dimensionality reduction. In: AAAI, pp. 677–682 (2008)
Jiang, M., Huang, W., Huang, Z., Yen, G.G.: Integration of global and local metrics for domain adaptation learning via dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(1), 38–51 (2017)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) (2015)
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Sun, J., Yu, P.S.: Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: ICCV, pp. 2200–2207 (2013)
Long M., Zhu, H., Wang, J., Jordan, M.I.: Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 136–144 (2016)
Belkin, M., Niyogi, P., Sindhwani, V.: Manifold regularization: a geometric framework for learning from labeled and unlabeled examples. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7, 2399–2434 (2006)
Ge, Q., Shen, F., Jing, X.Y., Wu, F., Xie, S.P., Yue, D., Li, H.B.: Active contour evolved by joint probability classification on riemannian manifold. Signal Image Video Process. 10(7), 1257–1264 (2016)
Liu, X., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Yin, J., Liu, H.: Global and local structure preservation for feature selection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 25(6), 1083–1095 (2014)
Fisher, R.A.: The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann. Eugen. 7(2), 179–188 (1936)
Jiang, M., Huang, W., Huang, Z., Yen, G.G.: Integration of global and local metrics for domain adaptation learning via dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(1), 38–51 (2017)
Borgwardt, K.M., Gretton, A., Rasch, M.J., Kriegel, H.P., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14), e49–e57 (2006)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 513 (2007)
Zhao, Z., Wang, L., Liu, H., Ye, J.: On similarity preserving feature selection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 25(3), 619–632 (2013)
Saenko, K., Kulis, B., Fritz, M., Darrell, T.: Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: ECCV, pp. 213–226 (2010)
Griffin, G., Holub, A., Perona, P.: Caltech-256 object category dataset. (2007)
LeCun, Y., Cortes, C.: Mnist Handwritten Digit Database. AT&T Labs, Atlanta (2010)
Nene, S.A., Nayar, S.K., Murase, H.: Columbia object image library (coil-20). Technical Report CUCS-005-96 (1996)
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding G., S.J., Yu, P.S.: Transfer joint matching for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp. 1410–1417 (2014)
Gong, B., Shi, Y., Sha, F., Grauman, K.: Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: CVPR, (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Natural Science Foundation (No. 61673262), National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB744903) and Aerospace Sci.and Tech. Foundation (No. 15GFZ-JJ02-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Tuo, H., Wang, J. et al. Discriminative transfer learning via local and global structure preservation. SIViP 13, 753–760 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1405-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1405-7