Abstract
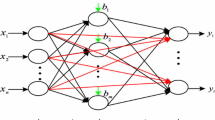
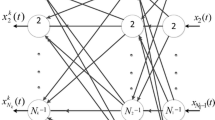
The conventional perceptron with the sign type activation function can be used for performing the linearly separable pattern recognition with its weight vector being found by the conventional perceptron training algorithm. On the other hand, the perceptron with the multi-pulse type activation function can be used for performing the piecewise linearly separable pattern recognition. This paper proposes a training algorithm for finding its weight vector. Moreover, some application examples of this perceptron are given for the demonstration purpose.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenblatt, F.: The perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 65(6), 386–408 (1958)
Novikoff, A.: On the convergence proofs on perceptrons. Proc. Symp. Math. Theory Autom. 12, 615–622 (1962)
Minsky, M.L., Papert, S.A.: Perceptrons. MIT Press, London (1969)
Gallant, S.I.: Perceptron-based learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1(2), 179–191 (1990)
Freund, Y., Schapire. R.E.: Large margin classification using the perceptron algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory. ACM Press (1998)
Li, Y.Y., Zaragoza, H., Herbrich, R., Shawe-Taylor, J., Kandola, J.: The perceptron algorithm with uneven margins. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 379-386 (2002)
Wan, S.J.: Cone algorithm: an extension of the perceptron algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 24(10), 1571–1576 (1994)
Widrow, B., Lehr, M.A.: 30 years of adaptive neural networks: perceptron, madaline, and backpropagation. Proc. IEEE 78(9), 1415–1442 (1990)
Greenwood, G.W.: Training multiple-layer perceptrons to recognize attractors. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1(4), 244–248 (1997)
Gurney, K.: An introduction to neural networks. UCL Press, London (1997)
Gas, B.: Self-organizing multilayer perceptron. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 21(11), 1766–1779 (2010)
Li, Y.Z., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Jiang, T.: Marine wireless big data: efficient transmission, related applications, and challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 25(1), 19–25 (2018)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Chen, F.Y., Chen, G.R., He, G.L., Xu, X.B., He, Q.B.: Universal perceptron and DNA-like learning algorithm for binary neural networks: LSBF and PBF implementations. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 20(10), 1645–1658 (2009)
Chen, F.Y., Chen, G.R., He, Q.B., He, G.L., Xu, X.B.: Universal perceptron and DNA-like learning algorithm for binary neural networks: non-LSBF implementations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20(8), 1293–1301 (2009)
Chen, F.Y., Tang, W.H., Chen, G.R.: Single-layer perceptron and dynamic neuron implementing linearly non-separable Boolean functions. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 37(3), 433–451 (2009)
Czerniak, J., Zarzycki, H: Application of rough sets in the presumptive diagnosis of urinary system diseases. In: Artificial Intelligence and Security in Computing Systems, pp. 41–51 (2003)
Li, Y., Ling, B.W.K., Xie, L.X., Dai, Q.Y.: Using LASSO for formulating constraint of least-squares programming for solving one-norm equality constrained problem. SIViP 11, 179–186 (2017)
Li, Y.Z., Xie, P.C., Tang, Z.S., Jiang, T., Qi, P.H.: SVM-based sea-surface small target detection: a false-alarm-rate-controllable approach. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 16(8), 1225–1229 (2019)
Abid, F.B., Zgarni, S., Braham, A.: Distinct bearing faults detection in induction motor by a hybrid optimized SWPT and aiNet-DAG SVM. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 33(4), 1692–1699 (2018)
Ho, C.Y.F., Ling, B.W.K., Lam, H.K., Nasir, M.H.U.: Global convergence and limit cycle behavior of weights of perceptron. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 19(6), 938–947 (2008)
Fu, X.G., Li, S.H., Fairbank, M., Wunsch, D.C.: Training recurrent neural networks with the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for optimal control of a grid-connected converter. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 19(9), 1900–1912 (2015)
https://github.com/zishengwu/audio-data-set-of-multi-piece-domain-perceptron
Zhao, Y., Deng, B., Wang, Z.: Analysis and study of perceptron to solve XOR problem. In: The 2nd International Workshop on Autonomous Decentralized System, pp. 168–173 (2002)
Maimaitiyiming, M., Sagan, V., Sidike, P., Kwasniewski, M.T.: Dual activation function-based extreme learning machine (ELM) for estimating Grapevine berry yield and quality. Remote Sens. 11, 7 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported partly by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1701266, 61372173 and 61671163), the Team Project of the Education Ministry of the Guangdong Province (No. 2017KCXTD011), the Guangdong Higher Education Engineering Technology Research Center for Big Data on Manufacturing Knowledge Patent (No. 501130144) and Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, Enterprise Support Scheme (No. S/E/070/17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Ling, B.WK. Training algorithm for perceptron with multi-pulse type activation function. SIViP 14, 925–933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01624-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01624-z