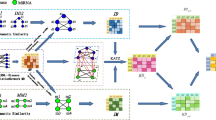
Abstract
MiRNA-disease association is important to disease diagnosis and treatment. Prediction of miRNA-disease associations is receiving increasing attention. Using the huge number of known databases to predict potential associations between miRNAs and diseases is an important topic in the field of biology and medicine. In this paper, we propose a novel computational method of with Short Acyclic Connections in Heterogeneous Graph (SACMDA). SACMDA obtains AUCs of 0.8770 and 0.8368 during global and local leave-one-out cross validation, respectively. Furthermore, SACMDA has been applied to three important human cancers for performance evaluation. As a result, 92% (Colon Neoplasms), 96% (Carcinoma Hepatocellular) and 94% (Esophageal Neoplasms) of top 50 predicted miRNAs are confirmed by recent experimental reports. What’s more, SACMDA could be effectively applied to new diseases and new miRNAs without any known associations, which overcomes the limitations of many previous methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros, V. (2004). The functions of animal micrornas. Nature, 431(7006), 350–355.
Bartel, D.P. (2004). Micrornas: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116(2), 281–297.
Bartel, D.P. (2009). Micrornas: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell, 136(2), 215–233.
Chen, J., Bushman, F.D., Lewis, J.D., Wu, G.D., Li, H. (2012). Structure-constrained sparse canonical correlation analysis with an application to microbiome data analysis. Biostatistics, 14(2), 244–258.
Chen, X., Liu, M.X., Yan, G.Y. (2012). Rwrmda: predicting novel human microrna–disease associations. Molecular BioSystems, 8(10), 2792–2798.
Chen, X., Yan, C.C., Zhang, X., Li, Z., Deng, L., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q. (2015). Rbmmmda: predicting multiple types of disease-microrna associations. Scientific Reports, 5(13), 877.
Chen, X., Yan, C.C., Zhang, X., You, Z.H., Deng, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q. (2016). Wbsmda: within and between score for mirna-disease association prediction. Scientific Reports, 6.
Chen, X., Yan, C.C., Zhang, X., You, Z.H., Huang, Y.A., Yan, G.Y. (2016). Hgimda: Heterogeneous graph inference for mirna-disease association prediction. Oncotarget, 7(40), 65,257.
Chen, X., & Yan, G.Y. (2014). Semi-supervised learning for potential human microrna-disease associations inference. Scientific Reports, 4, 5501.
Daly, J.M., Fry, W.A., Little, A.G., Winchester, D.P., McKee, R.F., Stewart, A.K., Fremgen, A.M. (2000). Esophageal cancer: results of an american college of surgeons patient care evaluation study. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 190(5), 562–572.
Drusco, A., Nuovo, G.J., Zanesi, N., Di Leva, G., Pichiorri, F., Volinia, S., Fernandez, C., Antenucci, A., Costinean, S., Bottoni, A., et al. (2014). Microrna profiles discriminate among colon cancer metastasis. PloS One, 9(6), e96,670.
Du, L., Huang, H., Yan, J., Kim, S., Risacher, S., Inlow, M., Moore, J., Saykin, A., Shen, L. (2016). Structured sparse cca for brain imaging genetics via graph oscar. BMC Systems Biology, 10(3), 68.
Jiang, Q., Wang, Y., Hao, Y., Juan, L., Teng, M., Zhang, X., Li, M., Wang, G. (2009). Liu, y.: mir2disease: a manually curated database for microrna deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Research, 37 (suppl 1), D98–D104.
Kim, T., Grobmyer, S.R., Smith, R., Ben-David, K., Ang, D., Vogel, S.B., Hochwald, S.N. (2011). Esophageal cancer—the five year survivors. Journal of Surgical Oncology, 103(2), 179–183.
van Laarhoven, T., Nabuurs, S.B., Marchiori, E. (2011). Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug–target interaction. Bioinformatics, 27(21), 3036–3043.
Lee, R.C., Feinbaum, R.L., Ambros, V. (1993). The c. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small rnas with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell, 75(5), 843–854.
Li, Y., Qiu, C., Tu, J., Geng, B., Yang, J., Jiang, T., Cui, Q. (2014). Hmdd v2. 0: a database for experimentally supported human microrna and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(D1), D1070–D1074.
Lu, M., Zhang, Q., Deng, M., Miao, J., Guo, Y., Gao, W., Cui, Q. (2008). An analysis of human microrna and disease associations. PloS One, 3(10), e3420.
Ogata-Kawata, H., Izumiya, M., Kurioka, D., Honma, Y., Yamada, Y., Furuta, K., Gunji, T., Ohta, H., Okamoto, H., Sonoda, H., et al. (2014). Circulating exosomal micrornas as biomarkers of colon cancer. PloS One, 9(4), e92,921.
Sohel, M.H. (2016). Extracellular/circulating micrornas: Release mechanisms, functions and challenges. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 10(2), 175–186.
Xu, J., Li, C.X., Lv, J.Y., Li, Y.S., Xiao, Y., Shao, T.T., Huo, X., Li, X., Zou, Y., Han, Q.L., et al. (2011). Prioritizing candidate disease mirnas by topological features in the mirna target–dysregulated network: Case study of prostate cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 10(10), 1857–1866.
Xuan, P., Han, K., Guo, M., Guo, Y., Li, J., Ding, J., Liu, Y., Dai, Q., Li, J., Teng, Z., et al. (2013). Prediction of micrornas associated with human diseases based on weighted k most similar neighbors. PloS One, 8(8), e70,204.
Yan, C., Xie, H., Liu, S., Yin, J., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q. (2017a). Effective uyghur language text detection in complex background images for traffic prompt identification. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Yan, C., Xie, H., Yang, D., Yin, J., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q. (2017b). Supervised hash coding with deep neural network for environment perception of intelligent vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems.
Yan, C., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Dai, F., Li, L., Dai, Q., Wu, F. (2014a). A highly parallel framework for hevc coding unit partitioning tree decision on many-core processors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 21(5), 573–576.
Yan, C., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Dai, F., Zhang, J., Dai, Q., Wu, F. (2014b). Efficient parallel framework for hevc motion estimation on many-core processors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 24(12), 2077–2089.
Yang, Z., Ren, F., Liu, C., He, S., Sun, G., Gao, Q., Yao, L., Zhang, Y., Miao, R., Cao, Y., et al. (2010). dbdemc: a database of differentially expressed mirnas in human cancers. BMC Genomics, 11(4), S5.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (61701149, 61525206, 61671196, 61327902), Zhejiang Province Nature Science Foundation of China LR17F030006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, B., Liu, B. & Yan, C. SACMDA: MiRNA-Disease Association Prediction with Short Acyclic Connections in Heterogeneous Graph. Neuroinform 16, 373–382 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9373-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9373-1