Abstract
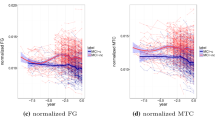
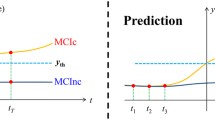
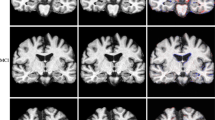
Hippocampal atrophy measures from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are powerful tools for monitoring Alzheimer’s disease (AD) progression. In this paper, we introduce a longitudinal image analysis framework based on robust registration and simultaneous hippocampal segmentation and longitudinal marker classification of brain MRI of an arbitrary number of time points. The framework comprises two innovative parts: a longitudinal segmentation and a longitudinal classification step. The results show that both steps of the longitudinal pipeline improved the reliability and the accuracy of the discrimination between clinical groups. We introduce a novel approach to the joint segmentation of the hippocampus across multiple time points; this approach is based on graph cuts of longitudinal MRI scans with constraints on hippocampal atrophy and supported by atlases. Furthermore, we use linear mixed effect (LME) modeling for differential diagnosis between clinical groups. The classifiers are trained from the average residue between the longitudinal marker of the subjects and the LME model. In our experiments, we analyzed MRI-derived longitudinal hippocampal markers from two publicly available datasets (Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, ADNI and Minimal Interval Resonance Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease, MIRIAD). In test/retest reliability experiments, the proposed method yielded lower volume errors and significantly higher dice overlaps than the cross-sectional approach (volume errors: 1.55% vs 0.8%; dice overlaps: 0.945 vs 0.975). To diagnose AD, the discrimination ability of our proposal gave an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) \(=\) 0.947 for the control vs AD, AUC \(=\) 0.720 for mild cognitive impairment (MCI) vs AD, and AUC \(=\) 0.805 for the control vs MCI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, M.S., DeKosky, S.T., Dickson, D., Dubois, B., Feldman, H.H., Fox, N.C., Gamst, A., Holtzman, D.M., Jagust, W.J., Petersen, R.C., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the national institute on aging-alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 270–279.
Apostolova, L.G., Morra, J.H., Green, A.E., Hwang, K.S., Avedissian, C., Woo, E., Cummings, J.L., Toga, A.W., Jack, C.R., Weiner, M.W., et al. (2010). Automated 3D mapping of baseline and 12-month associations between three verbal memory measures and hippocampal atrophy in 490 ADNI subjects. NeuroImage, 51(1), 488–499.
Artaechevarria, X., Muñoz-barrutia, A., Ortiz-de Solorzano, C. (2009). Combination strategies in multi-atlas image segmentation: Application to brain MR data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28(8), 1266–1277.
Aubert-Broche, B., Fonov, V.S., García-Lorenzo, D., Mouiha, A., Guizard, N., Coupé, P., Eskildsen, S.F., Louis Collins, D. (2013). A new method for structural volume analysis of longitudinal brain mri data and its application in studying the growth trajectories of anatomical brain structures in childhood. NeuroImage, 82, 393–402.
Barnes, C., Shechtman, E., Finkelstein, A., Goldman, D. (2009). Patchmatch: a randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Transactions on Graphics-TOG, 28(3), 24.
Bernal-Rusiel, J.L., Greve, D.N., Reuter, M., Fischl, B., Sabuncu, M.R. (2013). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, et al. Statistical analysis of longitudinal neuroimage data with linear mixed effects models. NeuroImage, 66, 249–260.
Boccardi, M., Ganzola, R., Bocchetta, M., Pievani, M., Redolfi, A., Bartzokis, G., Camicioli, R., Csernansky, J.G., de Leon, M.J., de Toledo-Morrell, L., et al. (2011). Survey of protocols for the manual segmentation of the hippocampus: preparatory steps towards a joint EADC-ADNI harmonized protocol. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 26, 61–75.
Boykov, Y., & Kolmogorov, V. (2004). An experimental comparison of min-cut/max-flow algorithms for energy minimization in vision. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 26(9), 1124–1137.
Bradley, T., Wyman, B.T., Harvey, D.J., Crawford, K., Bernstein, M.A., Carmichael, O., Cole, P.E., Crane, P.K., DeCarli, C., Fox, N.C., Gunter, J.L., et al. (2013). Standardization of analysis sets for reporting results from ADNI MRI data. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 9(3), 332–337.
Chételat, G., Fouquet, M., Kalpouzos, G., Denghien, I., De La Sayette, V., Viader, F., Mézenge, F., Landeau, B., Baron, J.-C., Eustache, F., et al. (2008). Three-dimensional surface mapping of hippocampal atrophy progression from MCI to AD and over normal aging as assessed using voxel-based morphometry. Neuropsychologia, 46(6), 1721–1731.
Chincarini, A., Sensi, F., Rei, L., Gemme, G., Squarcia, S., Longo, R., Brun, F., Tangaro, S., Bellotti, R., Amoroso, N., et al. (2016). Integrating longitudinal information in hippocampal volume measurements for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 125, 834–847.
Clifford, R., Jack, C.R., Bernstein, M.A., Fox, N.C., Thompson, P., Alexander, G., Harvey, D., Borowski, B., Britson, P.J., Whitwell, J.L., Ward, C., et al. (2008). The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): MRI methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27(4), 685–691.
Coupé, P., Manjón, J.V., Fonov, V., Pruessner, J., Robles, M., Louis Collins, D. (2011). Patch-based segmentation using expert priors application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. NeuroImage, 54(2), 940–954.
Cuingnet, R., Gerardin, E., Tessieras, J., Auzias, G., Lehéricy, S., Habert, M.-O., Chupin, M., Benali, H., Colliot, O., et al. (2011). Automatic classification of patients with Alzheimer’s disease from structural MRI: a comparison of ten methods using the ADNI database. NeuroImage, 56(2), 766–781.
DeLong, E.R., DeLong, D.M., Clarke-Pearson, D.L. (1988). Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 837–845.
Devanand, D.P., Pradhaban, G., Liu, X., Khandji, A., De Santi, S., Segal, S., Rusinek, H., Pelton, G.H., Honig, L.S., Mayeux, R., et al. (2007). Hippocampal and entorhinal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment prediction of Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 68(11), 828–836.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H.H., Jacova, C., DeKosky, S.T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., Delacourte, A., Galasko, D., Gauthier, S., Jicha, G., et al. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDS–ADRDA criteria. The Lancet Neurology, 6(8), 734–746.
Eskildsen, S.F., Coupé, P., Fonov, V.S., Pruessner, J.C., Louis Collins, D. (2015). Structural imaging biomarkers of alzheimer’s disease: predicting disease progression. Neurobiology of Aging, 36, S23–S31.
Evans, A.C., Janke, A.L., Louis Collins, D., Baillet, S. (2012). Brain templates and atlases. NeuroImage, 62(2), 911–922.
Fischl, B., Salat, D.H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., Van Der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R., Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Folstein, M.F., Folstein, S.E., McHugh, P.R. (1975). Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Fox, N.C., Ridgway, G.R., Schott, J.M. (2011). Algorithms, atrophy and Alzheimer’s disease: cautionary tales for clinical trials. NeuroImage, 57(1), 15–18.
Frankó, E., & Joly, O. (2013). Evaluating Alzheimer’s disease progression using rate of regional hippocampal atrophy. PloS one, 8(8), e71354.
Fraser, M.A., Shaw, M.E., Cherbuin, N. (2015). A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal hippocampal atrophy in healthy human ageing. NeuroImage, 112, 364–374.
Frisoni, G.B., Fox, N.C., Jack, C.R., Scheltens, P., Thompson, P.M. (2010). The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews Neurology, 6(2), 67–77.
Frisoni, G.B., Jack, C.R., Bocchetta, M., Bauer, C., Frederiksen, K.S., Liu, Y., Preboske, G., Swihart, T., Blair, M., Cavedo, E., et al. (2015). The EADC-ADNI Harmonized Protocol for manual hippocampal segmentation on magnetic resonance: Evidence of validity. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 11(2), 111–125.
Giraud, R., Ta, V.-T., Papadakis, N., Manjón, J.V., Louis Collins, D., Coupé, P., ADNI et al. (2016). An optimized patchmatch for multi-scale and multi-feature label fusion. NeuroImage, 124, 770–782.
Iglesias, J.E., Van Leemput, K., Augustinack, J., Insausti, R., Fischl, B., Reuter, M. (2016). ADNI, et al. Bayesian longitudinal segmentation of hippocampal substructures in brain MRI using subject-specific atlases. NeuroImage, 141, 542–555.
Jack, C.R., Shiung, M.M., Gunter, J.L., Obrien, P.C., Weigand, S.D., Knopman, D.S., Boeve, B.F., Ivnik, R.J., Smith, G.E., Cha, R.H., et al. (2004). Comparison of different MRI brain atrophy rate measures with clinical disease progression in AD. Neurology, 62(4), 591–600.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825–841.
Kim, J., Valdes-Hernandez, M.D.C., Royle, N.A., Park, J. (2015). Hippocampal shape modeling based on a progressive template surface deformation and its verification. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 34(6), 1242–1261.
Klein, A., Andersson, J., Ardekani, B.A., Ashburner, J., Avants, B., Chiang, M.-C., Christensen, G.E., Louis Collins, D., Gee, J., Hellier, P., et al. (2009). Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. NeuroImage, 46(3), 786–802.
Klein, S., Staring, M., Murphy, K., Viergever, M.A., Pluim, J.P.W. (2010). Elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(1), 196–205.
Korolev, I.O., Symonds, L.L., Bozoki, A.C. (2016). Alzheimer?s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, et al. Predicting progression from mild cognitive impairment to alzheimer’s dementia using clinical, mri, and plasma biomarkers via probabilistic pattern classification. Plos One, 11(2), e0138866.
La Joie, R, Fouquet, M, Mézenge, F, Landeau, B, Villain, N, Mevel, K, Pélerin, A, Eustache, F, Desgranges, B, Chételat, G. (2010). Differential effect of age on hippocampal subfields assessed using a new high-resolution 3T MR sequence. Neuroimage, 53(2), 506–514.
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., Pereira, F.C. (2001). Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 282–289).
Lawrence, E., Vegvari, C., Ower, A., Hadjichrysanthou, C., De Wolf, F., Anderson, R.M. (2017). A systematic review of longitudinal studies which measure alzheimers disease biomarkers. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 59(4), 1359–1379.
Leung, K.K., Barnes, J., Ridgway, G.R., Bartlett, J.W., Clarkson, M.J., Macdonald, K., Schuff, N., Fox, N.C., Ourselin, S., et al. (2010). Automated cross-sectional and longitudinal hippocampal volume measurement in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 51(4), 1345–1359.
Lotjonen, J.M.P., Wolz, R., Koikkalainen, J.R., Thurfjell, L., Waldemar, G., Soininen, H., Rueckert, D. (2010). Fast and robust multi-atlas segmentation of brain magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage, 49(3), 2352–2365.
Louis Collins, D., & Pruessner, J.C. (2010). Towards accurate, automatic segmentation of the hippocampus and amygdala from MRI by augmenting ANIMAL with a template library and label fusion. NeuroImage, 52(4), 1355–1366.
Malone, I.B., Cash, D., Ridgway, G.R., MacManus, D.G., Ourselin, S., Fox, N.C., Schott, J.M. (2013). MIRIAD - Public release of a multiple time point Alzheimer’s MR imaging dataset. NeuroImage, 70, 33–36.
Mert, R., Sabuncu, M.R., Desikan, R.S., Sepulcre, J., Yeo, B.T.T., Liu, H., Schmansky, N.J., Reuter, M., Weiner, M.W., Buckner, R.L., Sperling, R.A., et al. (2011). The dynamics of cortical and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer disease. Archives of neurology, 68(8), 1040–1048.
McKhann, G.M., Knopman, D.S., Chertkow, H., Hyman, B.T., Jack, C.R., Kawas, C.H., Klunk, W.E., Koroshetz, W.J., Manly, J.J., Mayeux, R., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 7(3), 263–269.
Moradi, E., Pepe, A., Gaser, C., Huttunen, H., Tohka, J. (2015). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative et al. Machine learning framework for early mri-based alzheimer’s conversion prediction in mci subjects. NeuroImage, 104, 398–412.
Mount, D.M., & Arya, S. (2010). Ann: A library for approximate nearest neighbor searching. http://www.cs.umd.edu/mount/ANN/. (Accessed: 20 January 2015). version 1.1.2 .
Nestor, S.M., Gibson, E., Gao, F.-Q., Kiss, A., Black, S.E. (2013). A direct morphometric comparison of five labeling protocols for multi-atlas driven automatic segmentation of the hippocampus in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 66, 50–70.
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R., Piechor, K. (2004). Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 57, B15. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1760520.
Perrotin, A., de Flores, R., Lamberton, F., Poisnel, G., La Joie, R., de la Sayette, V., Mezenge, F., Tomadesso, C., Landeau, B., Desgranges, B., et al. (2015). Hippocampal subfield volumetry and 3D surface mapping in subjective cognitive decline. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 48(s1), S141–S150.
Platero, C., & Carmen Tobar, M. (2015). A label fusion method using conditional random fields with higher-order potentials Application to hippocampal segmentation. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 64(2), 117–129.
Platero, C., & Carmen Tobar, M. (2016). A fast approach for hippocampal segmentation from t1-MRI for predicting progression in Alzheimer’s disease from elderly controls. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 270, 61–75.
Platero, C., & Tobar, M.C. (2017). Combining a patch-based approach with a non-rigid registration-based label fusion method for the hippocampal segmentation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroinfor matics, 15(2), 165–183.
Reuter, M., Diana Rosas, H., Fischl, B. (2010). Highly accurate inverse consistent registration: a robust approach. NeuroImage, 53(4), 1181–1196.
Reuter, M., Schmansky, N.J., Diana Rosas, H., Fischl, B. (2012). Within-subject template estimation for unbiased longitudinal image analysis. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1402–1418.
Sabuncu, M.R., Bernal-Rusiel, J.L., Reuter, M., Greve, D.N., Fischl, B. (2014). ADNI, et al. Event time analysis of longitudinal neuroimage data. NeuroImage, 97, 9–18.
Schröder, J., & Pantel, J. (2016). Neuroimaging of hippocampal atrophy in early recognition of Alzheimer´s disease–a critical appraisal after two decades of research. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 247, 71–78.
Sled, J.G., Zijdenbos, A.P., Evans, A.C. (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 17(1), 87–97.
Song, Z., Tustison, N., Avants, B., Gee, J. (2006). Integrated graph cuts for brain MRI segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI, 4191, 831–838.
Thompson, W.K., Hallmayer, J., O’Hara, R. (2011). Design considerations for characterizing psychiatric trajectories across the lifespan Application to effects of APOE-ε4 on cerebral cortical thickness in Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Psychiatry, 168(9), 894–903.
van der Lijn, F., den Heijer, T., Breteler, M., Niessen, W.J. (2008). Hippocampus segmentation in MR images using atlas registration, voxel classification, and graph cuts. NeuroImage, 43(4), 708–720.
Viola, P., & Wells, W.M.III. (1997). Alignment by maximization of mutual information. International Journal of Computer Vision, 24(2), 137–154.
Wang, H., Suh, J.W., Das, S.R., Pluta, J.B., Craige, C., Yushkevich, P.A. (2013). Multi-atlas segmentation with joint label fusion. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(3), 611–623.
Wang, L., Guo, Y., Cao, X., Wu, G., Shen, D. (2016). Consistent multi-atlas hippocampus segmentation for longitudinal MR brain images with temporal sparse representation. In International workshop on patch-based techniques in medical imaging (pp. 34–42). Springer.
Wolz, R., Heckemann, R.A., Aljabar, P., Hajnal, J.V., Hammers, A., Lötjönen, J., Rueckert, D. (2010). Measurement of hippocampal atrophy using 4D graph-cut segmentation: application to ADNI. NeuroImage, 52(1), 109–118.
Acknowledgments
Data collection for this study was funded by the ADNI (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering and and through generous contributions from the following: Alzheimer’s Association; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation; BioClinica, Inc.; Biogen Idec Inc.; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Eisai Inc.; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.; GE Healthcare; Innogenetics, N.V.; IXICO Ltd.; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC.; Medpace, Inc.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Meso Scale Diagnostics, LLC.; NeuroRx Research; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Piramal Imaging; Servier; Synarc Inc.; and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platero, C., Lin, L. & Tobar, M.C. Longitudinal Neuroimaging Hippocampal Markers for Diagnosing Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroinform 17, 43–61 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9380-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9380-2