Abstract
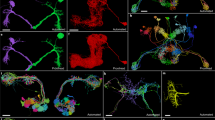
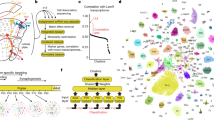
Drosophila melanogaster is one of the most important model animals in neurobiology owing to its manageable brain size, complex behaviour, and extensive genetic tools. However, without a comprehensive map of the brain-wide neural network, our ability to investigate brain functions at the systems level is seriously limited. In this study, we constructed a neuron-to-neuron network of the Drosophila brain based on the 28,573 fluorescence images of single neurons in the newly released FlyCircuit v1.2 (http://www.flycircuit.tw) database. By performing modularity and centrality analyses, we identified eight communities (right olfaction, left olfaction, olfactory core, auditory, motor, pre-motor, left vision, and right vision) in the brain-wide network. Further investigation on information exchange and structural stability revealed that the communities of different functions dominated different types of centralities, suggesting a correlation between functions and network structures. Except for the two olfaction and the motor communities, the network is characterized by overall small-worldness. A rich club (RC) structure was also found in this network, and most of the innermost RC members innervated the central complex, indicating its role in information integration. We further identified numerous loops with length smaller than seven neurons. The observation suggested unique characteristics in the information processing inside the fruit fly brain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, R., & Barabasi, A. L. (2002). Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of Modern Physics, 74(1), 47–97.
Azevedo, F. A. C., Carvalho, L. R. B., Grinberg, L. T., Farfel, J. M., Ferretti, R. E. L., Leite, R. E. P., et al. (2009). Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 513, 532–541. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21974.
Bahlmann, K., So, P. T., Kirber, M., Reich, R., Kosicki, B., McGonagle, W., & Bellve, K. (2007). Multifocal multiphoton microscopy (MMM) at a frame rate beyond 600 Hz. Optics Express, 15, 10991–10998.
Barrat, A., Barthelemy, M., Pastor-Satorras, R., & Vespignani, A. (2004). The architecture of complex weighted networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(11), 3747–3752. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0400087101.
Bassett, D. S., & Bullmore, E. (2006). Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist, 12(6), 512–523. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858406293182.
Bewersdorf, J., Pick, R., & Hell, S. W. (1998). Multifocal multiphoton microscopy. Optics Letters, 23, 655–657.
Bota, M., Dong, H. W., & Swanson, L. W. (2003). From gene networks to brain networks. Nature Neuroscience, 6(8), 795–799. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1096.
Bota, M., Sporns, O., & Swanson, L. W. (2015). Architecture of the cerebral cortical association connectome underlying cognition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(16), E2093–E2101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504394112.
Brandes, U. (2001). A faster algorithm for betweenness centrality. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 25(2), 163–177.
Brin, S., & Page, L. (1998). The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Paper presented at the seventh international world-wide web conference, Brisbane, Australia
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2009). Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems [Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural research support, Non-U.S. Gov't. Review]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(3), 186–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2575.
Chiang, A. S., Lin, C. Y., Chuang, C. C., Chang, H. M., Hsieh, C. H., Yeh, C. W., Shih, C. T., Wu, J. J., Wang, G. T., Chen, Y. C., Wu C. C., Chen, G. Y., Ching, Y. T., Lee, P. C., Lin, C. Y., Lin, H. H., Wu, C. C., Hsu, H. W., Huang, Y. A., Chen, J. Y., Chiang, H. J., Lu, C. F., Ni, R. F., Yeh, C. Y., & Hwang, J. K. (2011). Three-dimensional reconstruction of brain-wide wiring networks in Drosophila at single-cell resolution. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. Current Biology, 21(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.056.
Cleland, T. A., & Linster, C. (2005). Computation in the olfactory system. Chemical Senses, 30, 801–813. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bji072.
Denk, W., & Horstmann, H. (2004). Serial block-face scanning electron microscopy to reconstruct three-dimensional tissue nanostructure. PLOS Biology, 2, e329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020329.
Fagiolo, G. (2007). Clustering in complex directed networks. Physical Review E, 76(2), 026107.
Fornito, A., Zalesky, A., & Bullmore, E. (2016). Fundamentals of brain network analysis (1st ed.). San Diego: Academic.
Gămănuţ, R., Kennedy, H., Toroczkai, Z., Ercsey-Ravasz, M., Van Essen, D. C., Knoblauch, K., et al. (2018). The mouse cortical connectome, characterized by an ultra-dense cortical graph, maintains specificity by distinct connectivity profiles. Neuron, 97(3), 698–715.e610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.12.037.
Guimera, R., & Amaral, L. A. N. (2005). Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature, 433(7028), 895–900.
Harriger, L., van den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2012). Rich club organization of macaque cerebral cortex and its role in network communication. PLoS One, 7(9), e46497. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046497.
Helmstaedter, M. (2013). Cellular-resolution connectomics: Challenges of dense neural circuit reconstruction. Nature Methods, 10, 501–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2476.
Hilgetag, C. C., & Goulas, A. (2016). Is the brain really a small-world network? Brain Structure and Function, 221(4), 2361–2366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1035-6.
Homberg, U. (2008). Evolution of the central complex in the arthropod brain with respect to the visual system. Arthropod Structure and Development, 37(5), 347–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asd.2008.01.008.
Huang, Y.-C., Wang, C.-T., Su, T.-S., Kao, K.-W., Lin, Y.-J., Chuang, C.-C., et al. (2019). A single-cell level and connectome-derived computational model of the Drosophila brain. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 12, 99. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2018.00099.
Huisken, J., Swoger, J., Bene, F. D., Wittbrodt, J., & Stelzer, E. H. K. (2004). Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy. Science, 305, 1007–1009. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1100035.
Jefferis, G. S. X. E., Marin, E. C., Stocker, R. F., & Luo, L. (2001). Target neuron prespecification in the olfactory map of Drosophila. Nature, 414, 204–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/35102574.
Jorgenson, L. A., Newsome, W. T., Anderson, D. J., Bargmann, C. I., Brown, E. N., Deisseroth, K., et al. (2015). The BRAIN initiative: Developing technology to catalyse neuroscience discovery. Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences, 370, 20140164. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0164.
Kaiser, M. (2015). Neuroanatomy: Connectome connects fly and mammalian brain networks. Current Biology, 25(10), R416–R418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.039.
Kaiser, M., & Hilgetag, C. C. (2004). Edge vulnerability in neural and metabolic networks. Biological Cybernetics, 90(5), 311–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-004-0479-1.
Kashiwadani, H., Sasaki, Y. F., Uchida, N., & Mori, K. (1999). Synchronized oscillatory discharges of mitral/tufted cells with different molecular receptive ranges in the rabbit olfactory bulb. Journal of Neurophysiology, 82, 1786–1792.
Knox, J. E., Harris, K. D., Graddis, N., Whitesell, J. D., Zeng, H., Harris, J. A., et al. (2018). High resolution data-driven model of the mouse connectome. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/293019.
Krashes, M. J., Keene, A. C., Leung, B., Armstrong, J. D., & Waddell, S. (2007). Sequential use of mushroom body neuron subsets during Drosophila odor memory processing. Neuron, 53(1), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.11.021.
Landhuis, E. (2017). Neuroscience: Big brain, big data. Nature, 541, 559–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/541559a.
Lee, P. C., Chuang, C. C., Chiang, A. S., & Ching, Y. T. (2012). High-throughput computer method for 3D neuronal structure reconstruction from the image stack of the Drosophila brain and its applications. PLoS Comput Biol, 8(9), e1002658. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002658.
Lee, Y. H., Lin, Y. N., Chuang, C. C., & Lo, C. C. (2014). SPIN: A method of skeleton-based polarity identification for neurons. Neuroinformatics, 12(3), 487–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9225-6.
Levoy, M., Ng, R., Adams, A., Footer, M., & Horowitz, M. (2006) Light Field Microscopy (SIGGRAPH '06, ACM, New York), https://doi.org/10.1145/1179352.1141976.
Lichtman, J. W., Livet, J., & Sanes, J. R. (2008). A technicolour approach to the connectome. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9, 417–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2391.
Lin, C. Y., Chuang, C. C., Hua, T. E., Chen, C. C., Dickson, B. J., Greenspan, R. J., & Chiang, A. S. (2013a). A comprehensive wiring diagram of the protocerebral bridge for visual information processing in the Drosophila brain. Cell Reports, 3(5), 1739–1753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.022.
Lin, H. H., Chu, L. A., Fu, T. F., Dickson, B. J., & Chiang, A. S. (2013b). Parallel neural pathways mediate CO2 avoidance responses in Drosophila. Science, 340(6138), 1338–1341. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1236693.
Lin, Y.-N., Chang, P.-Y., Hsiao, P.-Y., & Lo, C.-C. (2014). Polarity-specific high-level information propagation in neural networks. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 8, 27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2014.00027.
Lo, C.-C., & Chiang, A.-S. (2016). Toward whole-body connectomics. Journal of Neuroscience, 36, 11375–11383. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2930-16.2016.
Markram, H. (2012). The human brain project. Scientific American, 306(6), 50–55.
Mayerich, D., Abbott, L., & McCORMICK, B. (2008). Knife-edge scanning microscopy for imaging and reconstruction of three-dimensional anatomical structures of the mouse brain. Journal of Microscopy, 231, 134–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.2008.02024.x.
Mi, Y., Liao, X., Huang, X., Zhang, L., Gu, W., Hu, G., et al. (2013). Long-period rhythmic synchronous firing in a scale-free network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110, E4931–E4936. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304680110.
Milo, R., Shen-Orr, S., Itzkovitz, S., Kashtan, N., Chklovskii, D., & Alon, U. (2002). Network motifs: Simple building blocks of complex networks. Science, 298(5594), 824–827. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.298.5594.824.
Morgan, J. L., & Lichtman, J. W. (2013). Why not connectomics? Nature Methods, 10, 494–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2480.
Muller, L., Destexhe, A., & Rudolph-Lilith, M. (2014). Brain networks: Small-worlds, after all? New Journal of Physics, 16(10), 105004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/16/10/105004.
Newman, M. E. J. (2006). Modularity and community structure in networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(23), 8577–8582. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601602103.
Newman, M. E. J. (2010). Networks: An introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Olsen, S. R., & Wilson, R. I. (2008). Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Nature, 452, 956–960. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06864.
Pastrana, E. (2013). Focus on mapping the brain. Nature Methods, 10, 481–481. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2509.
Peng, H., Ruan, Z., Long, F., Simpson, J. H., & Myers, E. W. (2010). V3D enables real-time 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of large-scale biological image data sets. Nature Biotechnology, 28(4), 348–353. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1612.
Planchon, T. A., Gao, L., Milkie, D. E., Davidson, M. W., Galbraith, J. A., Galbraith, C. G., & Betzig, E. (2011). Rapid three-dimensional isotropic imaging of living cells using Bessel beam plane illumination. Nature Methods, 8, 417–423. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1586.
Plaza, S. M., Scheffer, L. K., & Chklovskii, D. B. (2014). Toward large-scale connectome reconstructions. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 25, 201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2014.01.019.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage, 52(3), 1059–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.003.
Scannell, J. W., Blakemore, C., & Young, M. P. (1995). Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(2), 1463–1483. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01463.1995.
Schneider-Mizell, C. M., Gerhard, S., Longair, M., Kazimiers, T., Li, F., Zwart, M. F., et al. (2016). Quantitative neuroanatomy for connectomics in Drosophila. Elife, 5. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12059.
Shih, C.-T., Sporns, O., Yuan, S.-L., Su, T.-S., Lin, Y.-J., Chuang, C.-C., Wang, T. Y., Lo, C. C., Greenspan, R. J., & Chiang, A. S. (2015). Connectomics-based analysis of information flow in the Drosophila brain. Current Biology, 25, 1249–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.021.
Sporns, O., NetLibrary 10th Shared Collection, & Perpetual eBook Collection. (2011). Networks of the brain (pp. 1 online resource (xi, 412 p., [418] p. of plates)). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Sporns, O., Tononi, G., & Kotter, R. (2005). The human connectome: A structural description of the human brain. PLoS Computational Biology, 1(4), e42. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010042.
Stocker, R. F. (1994). The organization of the chemosensory system in Drosophila melanogaster: A rewiew. Cell and Tissue Research, 275, 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305372.
Su, T.-S., Lee, W.-J., Huang, Y.-C., Wang, C.-T., & Lo, C.-C. (2017). Coupled symmetric and asymmetric circuits underlying spatial orientation in fruit flies. Nature Communications, 8(1), 139–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00191-6.
Triphan, T., Poeck, B., Neuser, K., & Strauss, R. (2010). Visual targeting of motor actions in climbing Drosophila. Current Biology, 20(7), 663–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.055.
Watts, D. J. (1999). Small worlds: The dynamics of networks between order and randomness. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks. Nature, 393(6684), 440–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/30918.
Wessnitzer, J., & Webb, B. (2006). Multimodal sensory integration in insects--towards insect brain control architectures. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 1(3), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-3182/1/3/001.
Wu, C. L., Shih, M. F., Lai, J. S., Yang, H. T., Turner, G. C., Chen, L., & Chiang, A. S. (2011). Heterotypic gap junctions between two neurons in the Drosophila brain are critical for memory. Current Biology, 21(10), 848–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.041.
Xiao, H., & Peng, H. (2013). APP2: Automatic tracing of 3D neuron morphology based on hierarchical pruning of a gray-weighted image distance-tree. Bioinformatics, 29(11), 1448–1454. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt170.
Zingg, B., Hintiryan, H., Gou, L., Song, M. Y., Bay, M., Bienkowski, M. S., Foster, N. N., Yamashita, S., Bowman, I., Toga, A. W., & Dong, H. W. (2014). Neural networks of the mouse neocortex. Cell, 156(5), 1096–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.023.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Aim for the Top University Project of the Ministry of Education, and by the Higher Education Sprout Project funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology and Ministry of Education in Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CTS, CCL, and ASC designed the study. CTS, YJL, CTW, TYW, CCC, and TSS performed the analysis. CTS and CCL wrote the manuscript. ASC provided the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 3.06 Mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shih, CT., Lin, YJ., Wang, CT. et al. Diverse Community Structures in the Neuronal-Level Connectome of the Drosophila Brain. Neuroinform 18, 267–281 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-019-09443-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-019-09443-w