Abstract
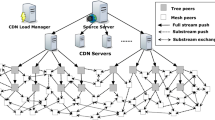
Peer-to-peer live streaming offers plenty of live television programs for users, and has become one of the most popular Internet applications. However, some ubiquitous problems such as long startup delay and unsmooth playback seriously restrict the quality of service of live streaming, whereas deploying dedicated servers immoderately will suffer from excessive costs. In this paper, we introduce economical-underloaded-emergent (EUE) principle to instruct resource scheduling for live streaming systems based on CDN-P2P hybrid architecture. Complying with this principle, we differentiate peers’ chunk requests according to their playback deadline and propose a set of mechanisms to provide distinct service for diverse requests. The results of simulation experiment demonstrate that EUE principle effectively optimize system performance, and achieve the remarkable reduction of startup delay and increase of chunk arrival ratio.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Multimedia Research Group Inc., http://www.mrgco.com/iptv/gf1210.html
Skevik KA, Goebel V, Plagemann T (2004) Design of a hybrid CDN, In: 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia Interactive Protocols and Systems, Grenoble, France, pp. 206–217
Liu Y, Hao Y, Zhu G et al (2008) Peer-assisted content delivery network for live streaming: Architecture and practice, In: International Conference on Networking, Architecture, and Storage, Chongqing, China, pp. 149–150
Li B, Xie S, Qu Y et al (2008) Inside the new coolstreaming: principles, measurements and performance implications, In: IEEE INFOCOM’08, Phoenix, AZ, USA, pp. 1031–1039
Huang Y, Fu TZJ, Chiu DM et al (2008) Challenges, design and analysis of a large-scale P2P-VoD system, In: ACM SIGCOMM’08, Seattle, Washington, USA, pp. 375–388
Zhang X, Liu J, Li B et al (2005) CoolStreaming/DONet: A data-driven overlay network for efficient live media streaming, In: IEEE INFOCOM’05, Miami, USA, pp. 2102–2111
Liao X, Jin H, Liu Y et al (2006) AnySee: Peer-to-peer live streaming, In: IEEE INFOCOM’06, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 1–10
Wang M, Li B (2007) R2: Random push with random network coding in live peer-to-peer streaming. IEEE J Sel Area Comm 25(9):1655–1666
Nguyen AT, Li B, Eliassen F (2010) Chameleon: Adaptive peer-to-peer streaming with network coding, In: IEEE INFOCOM’10, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 1–9
Zhou Y, Chiu DM, Lui JCS (2011) A simple model for chunk-scheduling strategies in P2P streaming. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 19(1):42–54
Yang Y, Chow ALH, Golubchik L et al (2010) Improving QoS in bitTorrent-like VoD systems, In: IEEE INFOCOM’10, San Diego, CA, USA, pp. 2061–2069
Peer-to-Peer streaming simulator, http://media.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~zhangm/download/
Magharei N, Rejaie R (2009) PRIME: Peer-to-peer receiver-driven mesh-based streaming. IEEE/ACM Transactions on networking 17(4):1052–1065
Wu D, Liang C, Liu Y et al (2009) View-upload decoupling: A redesign of multi-channel P2P video systems, In: IEEE INFOCOM’09, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, pp. 2726–2730
Bonald T, Massoulie L, Mathieu F et al (2008) Epidemic live streaming: Optimal performance trade-offs, In: Proceedings of ACM SIGMETRICS, Annapolis, USA, pp. 325–336
Massoulie L, Twigg A, Gkantsidis C et al (2007) Randomized decentralized broadcasting algorithms, In: IEEE INFOCOM’07, Anchorage, Alaska, USA, pp. 1073–1081
da Silva APC, Leonardi E, Mellia M et al (2008) A bandwidth-aware scheduling strategy for P2P-TV systems, In: Eighth International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing, pp. 279–288
Liu Y (2010) Delay bounds of chunk-based peer-to-peer video streaming. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 18(4):2726–2730
Abeni L, Kiraly C, Cigno RL (2009) On the optimal scheduling of streaming applications in unstructured meshes, In: Proceedings of Networking, pp. 117–130
Fortuna R, Leonardi E, Mellia M et al (2010) QoE in pull based P2P-TV systems: Overlay topology design tradeoffs, In: Tenth International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing, pp. 1–10
Liu S, Shen RZ, Jiang W et al (2008) Performance bounds for peer-assisted live streaming, In: Proceedings of ACM SIGMETRICS, Annapolis, USA, pp. 313–324
Kumar R, Liu Y, Ross K (2007) Stochastic fluid theory for P2P streaming systems, In: IEEE INFOCOM’07, Anchorage, Alaska, USA, pp. 919–927
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China under Grant No. 2012CB315806, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 90304016 and No.61103225, Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. BK2010133, and LMNT PLAUST. We are very thankful to Lihua Song, Han Wang and Yiting Duan-Mu, who gave helpful advice for our paper's revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, C., Chen, M., Xing, C. et al. EUE principle of resource scheduling for live streaming systems underlying CDN-P2P hybrid architecture. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 5, 312–322 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0140-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-012-0140-z