Abstract
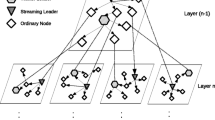
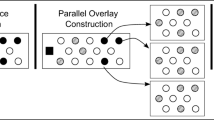
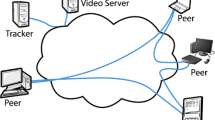
Multioverlay peer-to-peer live video streaming systems face the problem of finding a suitable peer upload bandwidth allocation among concurrent overlays. So far, no efficient solution has been proposed for the important case where the overall system is underprovisioned, that is, when peers do not have enough upload bandwidth to ensure video distribution at full quality. We design various objective functions for this upload bandwidth allocation problem and show how optimal solutions can be computed using a bipartite flow network. Simulation results show that our solutions improve on existing algorithms in terms of video quality.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Bouras C, Buyukkaya E, Hamzaoui R, Papazois A, Shani A, Simon G, Zhou F (2012) Peer-to-peer live streaming for massively multiplayer online games. In: Proc. of IEEE P2P. Tarragona. Spain
Ahmad S, Bouras C, Hamzaoui R, Liu J, Papazois A, Perelman E, Simon G, Tsichritzis G (2011) Community tools for massively multiplayer online games. Int J Adv Netw Serv 4(3–4):313–323
Ahuja RK, Orlin JB, Stein C, Tarjan RE (1994) Improved algorithms for bipartite network flow. SIAM J Comput 23(5):906–933
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, New York
Chen K, Huang P, Lei C (2006) Game traffic analysis: an mmorpg perspective. Comput Netw 50(16):3002–3023
Feng W, Brandt D, Saha D (2007) A long-term study of a popular mmorpg. In: Proc. of ACM Netgames. Melbourne, Australia
Ghosh S, Gupta A, Pemmaraju SV (1995) A self-stabilizing algorithm for the maximum flow problem. Distrib Comput 10:8–14
Goldberg AV (1997) An efficient implementation of a scaling minimum-cost flow algorithm. J Algoritm 22:1–29
Goldberg AV, Tarjan RE (1988) A new approach to the maximum flow problem. J ACM 35:921–940
Liang C, Zhao M, Liu Y (2011) Optimal bandwidth sharing in multiswarm multiparty p2p video-conferencing systems. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 19(6):1704–1716
Liu J, Ahmad S, Buyukkaya E, Hamzaoui R, Simon G (2012) Resource allocation in underprovisioned multioverlay live video sharing services. In: Proc. of ACM CoNEXT workshop on capacity sharing. Nice, France
Liu Z, Shen Y, Ross K, Panwar SS, Wang Y (2009) Layerp2p: using layered video chunks in p2p live streaming. IEEE Trans Multimedia 11(7):1340–1352
P2PTVSim. http://www.napa-wine.eu/cgi-bin/twiki/view/Public/P2PTVSim. Accessed April 2011
Prasad R, Dovrolis C, Murray M, Claffy K (2003) Bandwidth estimation: metrics, measurement techniques, and tools. IEEE Netw 17(6):27–35
Shen S, Iosup A (2011) The xfire online meta-gaming network: observation and high-level analysis. In: Proc. of IEEE MMVE. Qinhuangdao, Hebei, China
Sweha R, Ishakian V, Bestavros A (2012) Angelcast: cloud-based peer-assisted live streaming using optimized multi-tree construction. In: Proc. of ACM MMSys. Chapel Hill, North Carolina
Traud AL, Mucha PJ, Porter MA (2011) Social structure of facebook networks. CoRR, http://arxiv.org/abs/1102.2166
Wang M, Xu L, Ramamurthy B (2009) A flexible divide-and-conquer protocol for multi-view peer-to-peer live streaming. In: Proc. of IEEE P2P. Seattle, Washington
Wang M, Xu L, Ramamurthy B (2011) Improving multi-view peer-to-peer live streaming systems with the divide-and-conquer strategy. Comput Netw 55(18):4069–4085
Wu C, Li B, Li Z (2008) Dynamic bandwidth auctions in multioverlay p2p streaming with network coding. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 19(6):806–820
Wu C, Li B, Zhao S (2008) Multi-channel live p2p streaming: refocusing on servers. In: Proc. of IEEE INFOCOM. Phoenix, AZ, USA
Wu D, Liang C, Liu Y, Ross K (2010) Redesigning multi-channel p2p live video systems with view-upload decoupling. Comput Netw 54(12):2007–2018
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7, 2007–2013) under grant agreement no. ICT-248175 (“Community Network Game” project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Ahmad, S., Buyukkaya, E. et al. Resource allocation in underprovisioned multioverlay peer-to-peer live video sharing services. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 8, 399–413 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-014-0260-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-014-0260-8