Abstract
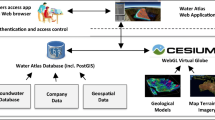
With the development of remote sensing and large-scale environmental modelling, large amount of environmental data are continuously becoming available. An intuitive and comprehensive visualization of these data could facilitate data exploration, communication and collaboration between the stakeholders for informed decisions making. In Poyang lake basin regions, we demonstrate how to develop a software platform that can visualize three-dimensionally environmental data layers including terrain, weather, river net, water level, land use changes and interrelations between these data layers for environmental system monitoring and decision supporting. The tool is built by combining several prevailing projects including Unity, Paraview, and hydrological models, etc. We develop an open standardized framework for the software tool to host environmental data layers permitting the application of the tool, which could be employed for the intuitive and comprehensive data visualization in other regions facing environmental challenges.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder JR, Hostetler SW (2015) Web based visualization of large climate data sets. Environ Modell Softw 68:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.02.016
Bearman N, Fisher PF (2012) Using sound to represent spatial data in ArcGIS. Comput Geosci 46:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.12.001
Bilke L et al (2014) TESSIN VISLab—laboratory for scientific visualization. Environ Earth Sci 72:3881–3899
Bing J, Deng P, Zhang X, Lv S, Marani M, Yi X (2018) Flood coincidence analysis of Poyang Lake and Yangtze River: risk and influencing factors. Stoch Env Res Risk A 32:879–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1514-4
Blackman S (2013) Beginning 3D Game Development with Unity 4: All-in-one, multi-platform game development. Apress, New York
Broderick J, Duggan J, Redfern S (2016a) Using game engines for marine visualisation and collaboration. In: IEEE International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC) IEEE, pp 96–101
Broderick J, Duggan J, Redfern S, Ieee (2016b) Using Game engines for marine visualisation and collaboration. 2016 International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing
Cao Y, Mo Z, Ai Z, Wang H, Xiao L (2016) An efficient and visually accurate multi-field visualization framework for high-resolution climate data. J Vis Jpn 19:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0335-5
Chen L, Michishita R, Xu B (2014) Abrupt spatiotemporal land and water changes and their potential drivers in Poyang Lake, 2000–2012. Isprs J Photogramm 98:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.09.014
Chen M, Lin H, Kolditz O, Chen C (2015) Developing dynamic virtual geographic environments (VGEs) for geographic research. Environ Earth Sci 74:6975–6980
Du Y, Peng W, Wang S, Liu X, Chen C, Liu C, Wang L (2018) Modeling of water quality evolution and response with the hydrological regime changes in Poyang Lake. Environ Earth Sci 77:265
Friese K-I, Herrlich M, Wolter F-E (2008) Using Game Engines for Visualization in Scientific Applications. In: New frontiers for entertainment computing. Springer US, Boston, pp 11–22
Gang S-M, Choi H-W, Kim D-R, Choung Y-J (2016) A Study on the Construction of the Unity 3D Engine Based on the WebGIS System for the Hydrological and Water Hazard Information Display. In: Kim JH, Kim HS, Yoo DG, Jung D, Song CG (eds) 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, vol 154. Procedia Engineering. pp 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.07.431
George RL, Robins PE, Davies AG, Ritsos PD, Roberts JC (2014) Interactive visual analytics of hydrodynamic flux for the coastal zone. Environ Earth Sci 72:3753–3766
Grainger S, Mao F, Buytaert W (2016) Environmental data visualisation for non-scientific contexts: Literature review and design framework. Environ Modell Softw 85:299–318
Guo H, Wang L, Chen F, Liang D (2014) Scientific big data and digital earth. Chinese Sci Bull 59:5066–5073
He Y, Su F, Du Y, Xiao R (2010) Web-based spatiotemporal visualization of marine environment data Chinese. Journal of Oceanology Limnology 28:1086–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-010-0029-8
Helbig C, Bauer H-S, Rink K, Wulfmeyer V, Frank M, Kolditz O (2014) Concept and workflow for 3D visualization of atmospheric data in a virtual reality environment for analytical approaches. Environ Earth Sci 72:3767–3780
Hocking J (2015) Unity in action: Multiplatform game development in C# with Unity 5. Manning Publications Shelter Island, New York
Hunter J, Brooking C, Reading L, Vink S (2016) A Web-based system enabling the integration, analysis, and 3D sub-surface visualization of groundwater monitoring data and geological models. Int J Digit Earth 9:197–214. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2014.1002866
Janicke H, Bottinger M, Mikolajewicz U, Scheuermann G (2009) Visual exploration of climate variability changes using wavelet analysis. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Gr 15:1375–1382. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvcg.2009.197
Klein B (2016) Managing the scalability of visual exploration using game engines to analyse UHI scenarios. In: Wong NH, Jusuf SK (eds) Fourth International Conference on Countermeasures to Urban Heat Island, vol 169. Procedia engineering. pp 272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.10.033
Kumpf A, Tost B, Baumgart M, Riemer M, Westermann R, Rautenhaus M (2018) Visualizing confidence in cluster-based ensemble weather forecast analyses. IEEE Ttans Vis Comput Gr 24:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvcg.2017.2745178
Kuntz S (2015) Middle VR a generic VR toolbox. In: 2015 IEEE Virtual Reality Conference Arles, France IEEE, pp 391–392
Li J, Xiao Z, Zhao H-Q, Meng Z-P, Zhang K (2016) Visual analytics of smogs in China. J Vis Jpn 19:461–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-015-0338-2
Liu D, Kenjeres S (2017) Google-earth based visualizations for environmental flows and pollutant dispersion in urban areas. Int J Env Res Pub He 14 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14030247
Lu W, Ai T, Zhang X, He Y (2017) An Interactive web mapping visualization of urban air quality monitoring data of China. Atmosphere 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080148
Manyoky M, Hayek UW, Heutschi K, Pieren R, Gret-Regamey A (2014) Developing a GIS-based visual-acoustic 3D simulation for wind farm assessment. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 3:29–48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi3010029
Rafiee A, Van der Male P, Dias E, Scholten H (2017) Developing a wind turbine planning platform: Integration of “sound propagation modele-GIS-game engine” triplet. Environ Modell Softw 95:326–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.06.019
Reyes MEP, Chen S-C, IEEE (2017) A 3D virtual environment for storm surge flooding animation. 2017 IEEE Third International Conference on Multimedia Big Data. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigMM.2017.54
Rink K, Fischer T, Selle B, Kolditz O (2013) A data exploration framework for validation and setup of hydrological models. Environ Earth Sci 69:469–477
Rink K, Bilke L, Kolditz O (2014a) Visualisation strategies for environmental modelling data. Environ Earth Sci 72:3857–3868
Rink K, Scheuermann G, Kolditz O (2014) Visualisation in environmental sciences. Environ Earth Sci 72:3749–3751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3759-7
Soldatova E, Sun Z, Maier S, Drebot V, Gao B (2018) Shallow groundwater quality and associated non-cancer health risk in agricultural areas (Poyang Lake basin, China). Environ Geochem Health 40:2223–2242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0094-z
Su T, Cao Z, Lv Z, Liu C, Li X (2016) Multi-dimensional visualization of large-scale marine hydrological environmental data. Adv Eng Softw 95:7–15
Wang S, Yuan H (2014) Spatial data mining: A perspective of big data. Int J Data Warehous 10:50–70. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijdwm.2014100103
Yue TX (2011) Surface modeling: High accuracy and high speed methods. CRC Press, New York
Wijk JJV (2005) The Value of Visualization. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Visualization pp 79–86
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Sino-German Cooperation Group "Modelling Platform Prototype for Environmental System Dynamics" (GZ1167), by National Statistics Research Project under Grant No. 2016LZ12, by the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System, and by Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program under Grant No. J18KA377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, C., Rink, K., Bilke, L. et al. A three-dimensional software framework for environmental system monitoring and decision support in Poyang lake basin. Earth Sci Inform 13, 901–913 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00480-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00480-7