Abstract
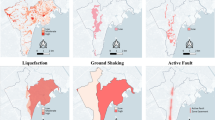
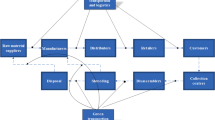
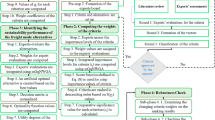
One of the most important issues in the crisis management is to supply and deliver the correct type and quantity of relief items in a dynamic environment of crisis situations. Current research presented a novel bi-objective bi-level optimization model in order to design an integrated framework for relief logistics operations. The Upper level objectives are to minimize total operational cost and total unsatisfied demand considering the effect of distribution locations of relief supplies. The lower level in the hierarchical decision process, proposes suppliers with lower supply risk. The proposed nonlinear model is reformulated as a single-level linear problem, and for the upper-level decision, the goal programming (GP) approach is employed for the exact solution of the model to minimize deviations from the goals of the bi-objective problem. Finally, a case study of emergency planning for earthquake disaster verifies the performance of the presented model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshar A, Haghani A (2012) Modeling integrated supply chain logistics in real-time large-scale disaster relief operations. Socioecon Plann Sci 46:327–338
Altay N, Green WG (2006) OR/MS research in disaster operations management. Eur J Oper Res 175:475–493
Aouni BD, Kettani O (2001) Goal programming model: a glorious history and a promising future. Eur J Oper Res 133:225–231
Arora SR, Gupta R (2009) Interactive fuzzy goal programming approach for bilevel programming problem. Eur J Oper Res 194:368–376
Bard JF (1984) Optimality conditions for the bilevel programming problem. Naval Res Logist Q 31:13–26
Ben-Tal A, Chung BD, Mandala SR, Yao T (2011) Robust optimization for emergency logistics planning: risk mitigation in humanitarian relief supply chains. Transp Res Part B Methodol 45:1177–1189
Berberian M (2014) Earthquakes and coseismic surface faulting on the Iranian Plateau. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bozorgi-Amiri A, Jabalameli MS, Mirzapour Al-e-Hashem SMJ (2013) A multi-objective robust stochastic programming model for disaster relief logistics under uncertainty. OR Spectr 35:905–933
Calvete HI, Gale C (2010) A multiobjective bilevel program for production-distribution planning in a supply chain. In: Ehrgott M, Naujoks B, Stewart TJ, Wallenius J (eds) Multiple criteria decision making for sustainable energy and transportation systems: proceedings of the 19th international conference on multiple criteria decision making, Auckland, New Zealand, 7–12 January 2008. Springer, Berlin
Calvete HI, Gale C, Iranzo JA (2014) Planning of a decentralized distribution network using bilevel optimization. Omega 49:30–41
Camacho-Vallejo J-F, González-Rodríguez E, Almaguer FJ, González-Ramírez RG (2015) A bi-level optimization model for aid distribution after the occurrence of a disaster. J Clean Prod 105:134–145
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Ferguson RO (1955) Optimal estimation of executive compensation by linear programming. Manage Sci 1:138–151
Cheng C-B (2011) Reverse auction with buyer–supplier negotiation using bi-level distributed programming. Eur J Oper Res 211:601–611
Dempe S, Dutta J, Lohse S (2006) Optimality conditions for bilevel programming problems. Optimization 55:505–524
Emam OE (2013) Interactive approach to bi-level integer multi-objective fractional programming problem. Appl Math Comput 223:17–24
Fazli S, Kiani Mavi R, Vosooghidizaji M (2015) Crude oil supply chain risk management with DEMATEL–ANP. Oper Res Int J 15:453–480
Feng C, Wen C (2005) A bi-level programming model for allocating private and emergency vehicle flows in seismic disaster areas. In: Proceedings of the Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, vol 5, 5, pp 1408–1423
Ghaedrahmati S, Bafghi RG, Bagheri A, Garizi IZ (2011) An analysis of Iran’s cities distributions in related to earthquake hazard. In: 1st International conference on urban construction in the vicinity of active faults
Gutjahr WJ, Dzubur N (2016) Bi-objective bilevel optimization of distribution center locations considering user equilibria. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 85:1–22
Haghani A, Afsharam (2009) Supply chain management in disaster response. Final Project report, Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, University of Maryland
Holguín-Veras J, Perez N, Jaller M, Van Wassenhove LN, Aros-Vera F (2013) On the appropriate objective function for post-disaster humanitarian logistics models. J Oper Manag 31:262–280
Hoyos MC, Morales RS, Akhavan-Tabatabaei R (2015) OR models with stochastic components in disaster operations management: a literature survey. Comput Ind Eng 82:183–197
Jensen L-M, Hertz S (2016) The coordination roles of relief organisations in humanitarian logistics. Int J Logist Res Appl 19(5):465–485. https://doi.org/10.1080/13675567.2015.1124845
Jeong K-Y, Hong J-D, Xie Y (2014) Design of emergency logistics networks, taking efficiency, risk and robustness into consideration. Intl J Logist Res Appl 17:1–22
Keyvanshokooh E, Ryan SM, Kabir E (2016) Hybrid robust and stochastic optimization for closed-loop supply chain network design using accelerated Benders decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 249:76–92
Mahdad M, Tajali M, Jafari M (2015) Red Crescent message, vol 342. The weekly internal Iranian Red Crescent Society, Tehran, Iran, pp 1–16
Mahdavi I, Aalaei A, Paydar MM, Solimanpur M (2010) Designing a mathematical model for dynamic cellular manufacturing systems considering production planning and worker assignment. Comput Math Appl 60:1014–1025
Naghavi M, Hosseini SK, Anbaran SM, Riahi MA (2008) Investigation of earthquake in Mazandaran province. In: 2nd Conference on natural disaster recovery College of Engineering, Tehran University
Nomura S, Parsons AJQ, Hirabayashi M, Kinoshita R, Liao Y, Hodgson S (2016) Social determinants of mid- to long-term disaster impacts on health: a systematic review. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 16:53–67
Nooraie SV, Mellat Parast M (2015) A multi-objective approach to supply chain risk management: integrating visibility with supply and demand risk. Int J Prod Econ 161:192–200
Paydar MM, Saidi-Mehrabad M, Teimoury E (2014) A robust optimisation model for generalised cell formation problem considering machine layout and supplier selection. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 27:772–786
Pieume CO, Marcotte P, Fotso LP, Siarry P (2013) Generating efficient solutions in bilevel multi-objective programming problems. Am J Oper Res 3:289–298
Pramanik S, Dey P (2011) Quadratic bi-level programming problem based on fuzzy goal programming approach. Int J Softw Eng Appl 2(4):41
Roghanian E, Aryanezhad MB, Sadjadi SJ (2008) Integrating goal programming, Kuhn–Tucker conditions, and penalty function approaches to solve linear bi-level programming problems. Appl Math Comput 195:585–590
Safaei AS, Moattar Husseini SM, Z.-Farahani R, Jolai F, Ghodsypour SH (2010) Integrated multi-site production-distribution planning in supply chain by hybrid modelling. Int J Prod Res 48:4043–4069
Talbi E-G (2013) Metaheuristics for bi-level optimization. Springer, Berlin
Tricoire F, Graf A, Gutjahr WJ (2012) The bi-objective stochastic covering tour problem. Comput Oper Res 39:1582–1592
Tzeng G-H, Cheng H-J, Huang TD (2007) Multi-objective optimal planning for designing relief delivery systems. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 43:673–686
Yu M-C, Goh M (2014) A multi-objective approach to supply chain visibility and risk. Eur J Oper Res 233:125–130
Zsidisin GA (2003) A grounded definition of supply risk. J Purch Supply Manag 9:217–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safaei, A.S., Farsad, S. & Paydar, M.M. Emergency logistics planning under supply risk and demand uncertainty. Oper Res Int J 20, 1437–1460 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0376-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0376-3