Abstract
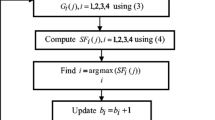
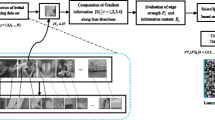
Joint sparse representation (JSR) based image fusion, as one of competitive sparse representation based fusion methods, has been widely studied recently. In this kind of methods, image features are represented as sparse coefficients. They are typically calculated with two decomposition algorithms, namely orthogonal matching pursuit and basis pursuit. In both of them, an error tolerance parameter is specified to control the fineness of a fused image. Intuitively, the more detailed an image fineness is, the more micro-information is presented; the more rough it is, the more macro-information is summarized. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that complementary information exists among the images generated by different error tolerance parameters. Motivated by this, in this paper, we have tried to combine the features in these images and verify the above assumption. Specifically, we have proposed a two-layer hierarchical framework based on JSR. Extensive experiments demonstrate that effectively combining features in images of different fineness does improve the quality of the fused image significantly. The proposed framework outperforms previous methods according to many objective evaluation criteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark A. Mindware: an introduction to the philosophy of cognitive science. New York: Oxford University Press; 2001.
Underwood G. Cognitive processes in eye guidance: algorithms for attention in image processing. Cognit Comput. 2009;1(1):64–76.
Cambria E, Hussain A. Sentic album: content-, concept-, and context-based online personal photo management system. Cognitive Computation. 2012;4(4):477–96.
He B, Xu D, Nian R, van Heeswijk M, Yu Q, Miche Y, Lendasse A. Fast face recognition via sparse coding and extreme learning machine. Cognitive Computation, 2013;1–14.
Yang B, Li S. Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2010;59(4):884–92.
Yang B, Li S. Pixel-level image fusion with simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. Inf Fus. 2012;13(1):10–9.
Yin H, Li S. Multimodal image fusion with joint sparsity model. Opt Eng. 2011;50(6):1–10.
Li H, Manjunath BS, Mitra SK. Multisensor image fusion using wavelet transform. Gr Models Image Process. 1995;57(3):235–45.
Goshtasby AA, Nikolov S. Image fusion: advances in the state of the art. Inf Fus. 2007;8(2):114–8.
Stathaki T. Image fusion: algorithms and applications. Oxford: Elsevier; 2008.
Olshausen BA, Field DJ. Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images. Nature. 1996;381(13):607–9.
Olshausen BA, Field DJ. Sparse coding with an over-complete basis set: a strategy employed by v1? Vision Res. 1997;37(23):3311–25.
Wang Z, Bovik AC. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2002;9(3):81–4.
Yu N, Qiu TS, Bi F, Wang AQ. Image features extraction and fusion based on joint sparse representation. IEEE J Sel Topics Signal Process. 2011;5(5):1074–82.
Yao Y, Xin X, Guo P. OMP or BP? a comparison study of image fusion based on joint sparse representation. Proc Int Conf Neural Inf Process. 2012;7667:75–82.
Pati YC, Rezaiifar R, Krishnaprasad PS. Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition. Proceedings of the 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals Systems and Computers. 1993; pp. 40–44.
Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev. 2001;43(1):129–59.
Akerman A. Pyramid techniques for multisensor fusion. Proceedings of SPIE. 1992;1828:124–31.
Li S, Kwok JT, Wang Y. Using the discrete wavelet frame transform to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic images. Inf Fus. 2002;3(1):17–23.
Lewis JJ, O’Callaghan RJ, Nikolov SG, Bull DR, Canagarajah CN. Region based image fusion using complex wavelets. In Seventh Int Conf Inf Fus. 2004;1:555–62.
Nencini F, Garzelli A, Baronti S, Alparone L. Remote sensing image fusion using curvelet transform. Inf Fus. 2007;8(2):143–56.
Chen T, Zhang J, Zhang Y. Remote sensing image fusion based on ridgelet transform. Proc Geosci Remote Sens Symp. 2005;2:1150–3.
Do MN, Vetterli M. The contourlet transform: an efficient directional multiresolution image representation. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2005;14(12):2091–106.
Cunha LD, Zhou JP. The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: theory, design and applications. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006;15(10):3089–101.
Yang B, Li ST, Sun FM. Image fusion using nonsubsampled contourlet transform. International Conference on Image and Graphics. 2007;719–724.
Elad M, Aharon M. Image Denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006;15(12):3736–45.
Yang J, Wright J, Huang T, Ma Y. Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2010;19(11):2861–73.
Zhao M, Li S, Kwok J. Text detection in images using sparse representation with discriminative dictionaries. Image Vis Comput. 2010;28(12):1590–9.
Bryt O, Elad M. Compression of facial images using the K-SVD algorithm. J Vis Commun Image Represent. 2008;19(4):270–83.
Shen B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Zhang YJ. Image inpainting via sparse representation. Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing. 2009; pp. 697–700.
Liu L, Li W, Tang S, Gong W. A novel separating strategy for face hallucination. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. 2012; pp. 1849–1852.
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein AM. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2006;54(11):4311–22.
Marial J, Ponce J, Sapiro G. Online dictionary learning for sparse coding. Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. 2009; pp. 689–696.
Bruckstein AM, Donoho DL, Elad M. From sparse solutions of systems of equations to sparse modeling of signals and images. SIAM Rev. 2009;51(1):34–81.
Elad M. Sparse and redundant representation: from theory to applications in signal and image processing. New York: Springer; 2010.
Mallat SG, Zhang Z. Matching pursuits and time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 1993;41(12):3397–415.
Gorodnistsky IF, Rao BD. Sparse signal reconstruction from limited data using FOCUSS: a re-weighted minimum norm algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 1997;45(3):600–16.
Duarte M, Sarvotham S, Baron D, Wakin M, Baraniuk R. Distributed compressed sensing of jointly sparse signals. Proceedings of Asilomar Conference on Signals Systems and Computers. 2005; pp. 1537–1541.
Donoho DL, Elad M, Temlyakov VN. Stable recovery of spare overcomplete representations in the presence of noise. IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 2006;52(1):6–18.
Efron B, Hastie T, Johnstone I, Tibshirani R. Least angle regression. The Annals of statistics. 2004;32(2):407–99.
Liu G, Yang W. A multi-resolution hierarchical image fusion scheme and its performance evaluation. In Proc SPIE. 2003;4898:200–6.
Qu G, Zhang D, Yan P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron Lett. 2002;38(7):313–5.
Piella G, Heijmans H. A new quality metric for image fusion. Int Conf Image Process. 2003;2:173–6.
Xydeas CS, Petrovic V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron Lett. 2000;36(4):308–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviews and editor for their insightful comments and suggestions. This work is supported by the Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 90820010, 60911130513 and 61375045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Guo, P., Xin, X. et al. Image Fusion by Hierarchical Joint Sparse Representation. Cogn Comput 6, 281–292 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-013-9235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-013-9235-y