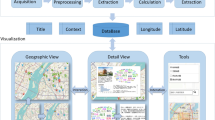
Abstract
Online review platforms offer customers the opportunities to express valuable feedback and personal views from various aspects on restaurants, products, works of art, or other items. A majority of previous studies on these user-generated reviews are devoted to controversy, bias, and opinion analysis. However, little work has been done to study urban characteristics via topic analysis from the city level in reviews. In this paper, we propose a visual analytics system, to visually explore spatiotemporal urban topics for cultural trend discovery, location mining, and decision making. Specifying a topic by users is supported due to the difference between review text and traditional text, such as news and books, and the diversity of topics and users. Sentiment analysis and statistical analysis are adopted to characterize the temporal trend and sentiment and topic geographical distributions of the user-specific topic. Our system allows the user to interactively explore the time-evolving frequency trend and characteristic geographical distributions of a topic in reviews. We evaluate the effectiveness and usefulness of our system using three case studies in different domains.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amendola L, Marra V, Quartin M (2015) The evolving perception of controversial movies. Palgrave Commun 1. http://doi.org/10.1057/palcomms.2015.38
Andrienko N, Andrienko G, Fuchs G, Jankowski P (2016) Scalable and privacy-respectful interactive discovery of place semantics from human mobility traces. Inf Vis 15(2):117–153
Bancken W, Alfarone D, Davis J (2014) Automatically detecting and rating product aspects from textual customer reviews. In: Proceedings of the 1st international workshop on interactions between data mining and natural language processing at ECML/PKDD, pp 1–16
Baroni M, Dinu G, Kruszewski G (2014) Don’t count, predict! a systematic comparison of context-counting vs. context-predicting semantic vectors. In: ACL, vol 1, pp 238–247
Bosch H, Thom D, Heimerl F, Püttmann E, Koch S, Krüger R, Wörner M, Ertl T (2013) Scatterblogs2: real-time monitoring of microblog messages through user-guided filtering. IEEE TVCG 19(12):2022–2031
Cao N, Cui W (2016) Introduction to text visualization. Atlantis briefs in artificial intelligence. Atlantis Press, Paris. http://cds.cern.ch/record/2230485
Chen L, Martineau J, Cheng D, Sheth A (2016) Clustering for simultaneous extraction of aspects and features from reviews. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp 789–799
Chen X, Liu Z, Sun M (2014) A unified model for word sense representation and disambiguation. In: EMNLP, Citeseer, pp 1025–1035
Cho I, Dou W, Wang DX, Sauda E, Ribarsky W (2016) Vairoma: a visual analytics system for making sense of places, times, and events in roman history. IEEE TVCG 22(1):210–219
Duan D, Qian W, Pan S, Shi L, Lin C (2012) Visa: a visual sentiment analysis system. In: Proceedings of the 5th international symposium on visual information communication and interaction. ACM, pp 22–28
Felix C, Pandey AV, Bertini E (2017) Texttile: an interactive visualization tool for seamless exploratory analysis of structured data and unstructured text. IEEE TVCG 23(1):161–170
Ferreira N, Klosowski JT, Scheidegger CE, Silva CT (2013) Vector field k-means: clustering trajectories by fitting multiple vector fields. In: Computer graphics forum, vol 32. Wiley Online Library, pp 201–210
Ferreira N, Poco J, Vo HT, Freire J, Silva CT (2013) Visual exploration of big spatio-temporal urban data: A study of new york city taxi trips. IEEE TVCG 19(12):2149–2158
Hao MC, Rohrdantz C, Janetzko H, Keim DA, Dayal U, Haug LE, Hsu M, Stoffel F (2013) Visual sentiment analysis of customer feedback streams using geo-temporal term associations. Inf Vis 12(3–4):273–290
Janetzko H, Jäckle D, Schreck T (2014) Geo-temporal visual analysis of customer feedback data based on self-organizing sentiment maps. International Journal on Advances in Intelligent Systems 7(1/2):237–246
Jiang X, Zhang J (2016) A text visualization method for cross-domain research topic mining. J Vis 19(3):561–576
Koh NS, Hu N, Clemons EK (2010) Do online reviews reflect a products true perceived quality? An investigation of online movie reviews across cultures. Electron Commer Res Appl 9(5):374–385
Li F, Huang M, Zhu X (2010) Sentiment analysis with global topics and local dependency. AAAI 10:1371–1376
Manning CD, Raghavan P, Schütze H et al (2008) Introduction to information retrieval, vol 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Miranda F, Doraiswamy H, Lage M, Zhao K, Gonçalves B, Wilson L, Hsieh M, Silva CT (2017) Urban pulse: capturing the rhythm of cities. IEEE TVCG 23(1):791–800
More S, Kale P (2016) Review paper on identifying features in opinion mining via intrinsic and extrinsic domain relevance. Int J Sci Res (IJSR) 5(1):651–654
Oelke D, Hao M, Rohrdantz C, Keim DA, Dayal U, Haug LE, Janetzko H (2009) Visual opinion analysis of customer feedback data. In: VAST 2009. IEEE Symposium. IEEE, pp 187–194
OpenStreetMap contributors (2017) Planet dump retrieved from https://planet.osm.org. https://www.openstreetmap.org
Palomo C, Guo Z, Silva CT, Freire J (2016) Visually exploring transportation schedules. IEEE TVCG 22(1):170–179
Pino C, Kavasidis I, Spampinato C (2016) Geosentiment: a tool for analyzing geographically distributed event-related sentiments. In: consumer communications & networking conference (CCNC), 2016 13th IEEE Annual. IEEE, pp 270–271
Ren D, Zhang X, Wang Z, Li J, Yuan X (2014) Weiboevents: a crowd sourcing weibo visual analytic system. In: Proceedings of IEEE PacificVis 2014. IEEE, pp 330–334
Rohrdantz C, Hao MC, Dayal U, Haug LE, Keim DA (2012) Feature-based visual sentiment analysis of text document streams. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol (TIST) 3(2):26
Ruder S, Ghaffari P, Breslin JG (2016) A hierarchical model of reviews for aspect-based sentiment analysis. arXiv:1609.02745
Scharl A, Hubmann-Haidvogel A, Jones A, Fischl D, Kamolov R, Weichselbraun A, Rafelsberger W (2016) Analyzing the public discourse on works of fiction-detection and visualization of emotion in online coverage about hbos game of thrones. Inf Process Manag 52(1):129–138
Socher R, Perelygin A, Wu JY, Chuang J, Manning CD, Ng AY, Potts C et al (2013) Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, vol 1631, p 1642
Trask A, Michalak P, Liu J (2015) sense2vec-a fast and accurate method for word sense disambiguation in neural word embeddings. arXiv:1511.06388
Wachsmuth H, Kiesel J, Stein B (2015) Sentiment flow-a general model of web review argumentation. In: EMNLP, pp 601–611
Wu F, Zhu M, Wang Q, Zhao X, Chen W, Maciejewski R (2017) Spatial-temporal visualization of city-wide crowd movement. J Vis 20(2):183–194
Wu HH, Tsai ACR, Tsai RTH, Hsu JYJ (2011) Sentiment value propagation for an integral sentiment dictionary based on commonsense knowledge. In: Technologies and applications of artificial intelligence (TAAI), 2011 international conference, IEEE, pp 75–81
Wu W, Xu J, Zeng H, Zheng Y, Qu H, Ni B, Yuan M, Ni LM (2016) Telcovis: visual exploration of co-occurrence in urban human mobility based on telco data. IEEE TVCG 22(1):935–944
Wu Y, Wei F, Liu S, Au N, Cui W, Zhou H, Qu H (2010) Opinionseer: interactive visualization of hotel customer feedback. IEEE TVCG 16(6):1109–1118
Xu J, Tao Y, Lin H (2016) Semantic word cloud generation based on word embeddings. In: Proceedings of IEEE PacificVis 2016. IEEE, pp 239–243
Xu J, Tao Y, Lin H, Zhu R, Yan Y (2017) Exploring controversy via sentiment divergences of aspects in reviews. In: Proceedings of IEEE PacificVis 2017. IEEE, pp 240–249
Yin Z, Cao L, Han J, Zhai C, Huang T (2011) Geographical topic discovery and comparison. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on World wide web. ACM, pp 247–256
Zeng W, Fu CW, Arisona SM, Qu H (2013) Visualizing interchange patterns in massive movement data. In: Computer graphics forum, vol 32. Wiley Online Library, pp 271–280
Zhang C, Zhang K, Yuan Q, Zhang L, Hanratty T, Han J (2016) Gmove: group-level mobility modeling using geo-tagged social media. In: KDD: proceedings. International conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, vol 2016. NIH Public Access, p 1305
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China no. 61472354 and 61672452, NSFC-Guangdong Joint Fund no. U1611263, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Tao, Y., Yan, Y. et al. VAUT: a visual analytics system of spatiotemporal urban topics in reviews. J Vis 21, 471–484 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-017-0464-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12650-017-0464-0