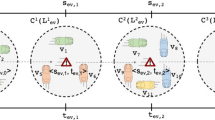
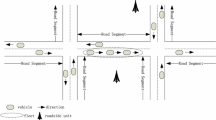
Abstract
Vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication systems enable vehicles to share information captured by their local sensors with other interested vehicles. To ensure that this information is delivered at the right time and location, context-aware routing is vital for intelligent inter-vehicular communication. Traditional network addressing and routing schemes do not scale well for large vehicular networks. The conventional network multicasting and broadcasting cause significant overhead due to a large amount of irrelevant and redundant transmissions. To address these challenges, we first take into account contextual properties such as location, direction, and information interest to reduce the network traffic overhead. Second, to improve the relevancy of the received information we leverage the mobility patterns of vehicles and the road layouts to further optimize the peer-to-peer routing of the information. Third, to ensure our approach is scalable, we propose a context-based grouping mechanism in which relevant information is shared in an intelligent way within and between the groups. We evaluate our approach based on groups with common spatio-temporal characteristics. Our simulation experiments show that our context-based routing scheme and grouping mechanism significantly reduces the propagation of irrelevant and redundant information.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldauf M, Dustdar S, Rosenberg F (2007) A survey on context-aware systems. Int J Ad Hoc Ubiquitous Comput 2:263–277. ISSN 1743-8225
Behera PK, Meher PK (2002) Prospects of group-based communication in mobile ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Distributed Computing, Mobile and Wireless Computing, IWDC ’02. Springer, London, pp 174–183. ISBN 3-540-00355-X
Cutting D, Quigley A, Landfeldt B (2007) Special interest messaging: a comparison of igm approaches. doi:10.1093/comjnl/bxm076
Delmastro F, Passarella A, Conti M (2008) P2p multicast for pervasive ad hoc networks. Pervasive Mob Comput 4:62–91. ISSN 1574–1192
Delot T, Ilarri S, Thilliez M, Vargas-Solar G, Lecomte S (2011) Multi-scale query processing in vehicular networks. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 2:1–14
EU (2009) eCall—saving lives through in-vehicle communication technology. European Commission: Information Society and Media Report, pp 1–2
Harjula E, Ala-Kurikka J, Howie D, Ylianttila M (2006) Analysis of peer-to-peer sip in a distributed mobile middleware system. In: IEEE GLOBECOM
Henricksen K, Indulska J, McFadden T, Balasubramaniam S (2005) Middleware for distributed context-aware systems. In: International Symposium on Distributed Objects and Applications (DOA). Springer, pp 846–863
Hu X, Ding Y, Paspallis N, Papadopoulos GA, Bratskas P, Barone P, Mamelli A, Vanrompay Y, Berbers Y (2007) A peer-to-peer based infrastructure for context distribution in mobile and ubiquitous environments. In: Proceedings of the 2007 OTM confederated international conference on On the move to meaningful internet systems, vol. Part I, OTM’07. Springer, Berlin, pp 236–239. ISBN: 3-540-76887-4, 978-3-540-76887-6
Indulska J, McFadden T, Kind M, Henricksen K (2003) Scalable location management for context-aware systems. In: Proceedings of 4th IFIP International Conference on Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems (DAIS 2003). pp 224–235
Iwan LH, Safar M (2010) Pattern mining from movement of mobile users. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 1(4):295–308
Johansson P, Larsson T, Hedman N, Mielczarek B, Degermark M (1999) Scenario-based performance analysis of routing protocols for mobile ad-hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking. ACM, pp 195–206
Khambatti M, Ryu KD, Dasgupta P (2003) Structuring peer-to-peer networks using interest-based communities. In: DBISP2P, pp 48–63
Khan MA, Boloni L (2005) Convoy driving through ad-hoc coalition formation. In: Real Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium, 2005. RTAS 2005. 11th IEEE. IEEE, ISBN 0769523021, pp 98–105
Kirsch-Pinheiro M, Vanrompay Y, Victor K, Berbers Y, Valla M, Frà C, Mamelli A, Barone P, Hu X, Devlic A, Panagiotou G (2008) Context grouping mechanism for context distribution in ubiquitous environments. In: Proceedings of the OTM 2008 Confederated International Conferences, CoopIS, DOA, GADA, IS, and ODBASE 2008. Part I on On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems, OTM ’08. Springer, Berlin, pp 571–588. ISBN 978-3-540-88870-3
Leontiadis I, Costa P, Mascolo C (2009) Persistent content-based information dissemination in hybrid vehicular networks. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications. IEEE Computer Society, Washington. ISBN temp-isbn
Mahajan R, Zahorjan J, Zill B (2007) Understanding wifi-based connectivity from moving vehicles. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM conference on Internet measurement, IMC ’07. ACM, New York, pp 321–326. ISBN 978-1-59593-908-1
Mantadelis T, Paridel K, Janssens G, Vanrompay Y, Berbers Y (2011) Analysing a publish/subscribe system for mobile ad hoc networks with problog. Practical Aspects of Declarative Languages, pp 34–37
Nadeem T, Shankar P, Iftode L (2006) A comparative study of data dissemination models for vanets. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems
Naumov V, Baumann R, Gross T (2006) An evaluation of inter-vehicle ad hoc networks based on realistic vehicular traces. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM international symposium on Mobile ad hoc networking and computing. ACM, pp 108–119
Ni SY, Tseng YC, Chen YS, Sheu JP (1999) The broadcast storm problem in a mobile ad hoc network. In Proceedings of the 5th annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking. ACM, pp 151–162
Nose Y, Kanzaki A, Hara T, Nishio S (2010) A route construction based on measured characteristics of radio propagation in wireless sensor networks. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 1(4):259–270
Paganelli F, Bianchi G, Giuli D (2007) A context model for context-aware system design towards the ambient intelligence vision: experiences in the etourism domain. In: Proceedings of the 9th conference on User interfaces for all, ERCIM’06. Springer, Berlin. ISBN 978-3-540-71024-0
Paridel K, Vanrompay Y, Berbers Y (2010) Fadip: Lightweight publish/subscribe for mobile ad hoc networks. On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems, OTM 2010, pp 798–810
Preuveneers D, Berbers Y (2007) Architectural backpropagation support for managing ambiguous context in smart environments. In Proceedings of the 4th international conference on Universal access in human-computer interaction: ambient interaction, UAHCI’07. Springer, Berlin, pp 178–187. ISBN 978-3-540-73280-8
Qin H, Li Z, Wang Y, Lu X, Zhang W, Wang G (2010) An integrated network of roadside sensors and vehicles for driving safety: Concept, design and experiments. In: Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), 2010 IEEE International Conference on. pp 79–87
Rao P, Sagonas K, Swift T, Warren D, Freire J (1997) Xsb: A system for efficiently computing well-founded semantics. In Logic Programming And Nonmonotonic Reasoning, vol 1265 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Berlin, pp 178–187. ISBN 978-3-540-63255-9
Royer EM, Melliar-Smith PM, Moser LE (2001) An analysis of the optimum node density for ad hoc mobile networks. In: Communications, 2001. ICC 2001. IEEE International Conference on, vol 3. IEEE, pp 857–861
Singh A, Ramakrishnan C, Smolka S (2008) A process calculus for mobile ad hoc networks. In: Coordination Models and Languages. Springer, pp 296–314
Yasar A, Preuveneers D, Berbers Y (2010a) Evaluation framework for adaptive context-aware routing in large scale mobile peer-to-peer systems. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, pp 1–13. ISSN 1936-6442. 10.1007/s12083-010-0090-2
Yasar A, Vanrompay Y, Preuveneers D, Berbers Y (2010b) Optimizing information dissemination in large scale mobile peer-to-peer networks using context-based grouping. In: 13th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, number 13. IEEE. ISBN 978-1-4244-7658-9
Ye J, Li J, Zhu Z, Gu X, Shi H (2007) Pcsm: A context sharing model in peer-to-peer ubiquitous computing environment. In: Convergence Information Technology, 2007. International Conference on. pp 1868 –1873
Zhang Y, Liao J, Zhu X, Wu W, Ma J (2007) Inter-working between simple and imps. Comput Stand Interfaces 29:584–600. ISSN 0920-5489
Acknowledgments
This research is partially funded by the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Programme Belgian State, Belgian Science Policy, and by the Research Fund K. U. Leuven. We want to thank the reviewers for their constructive comments that helped us to improve our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paridel, K., Mantadelis, T., Yasar, AUH. et al. Analyzing the efficiency of context-based grouping on collaboration in VANETs with large-scale simulation. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 5, 475–490 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-012-0115-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-012-0115-1