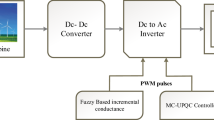
Abstract
This paper proposes a fuzzy controller for improving fault ride-through (FRT) capability of doubly fed induction generator based wind turbines (WTs). The controller is designed in order to compensate the voltage at the point of common coupling by regulating the reactive and active power generated by WTs simultaneously. The performances of the controller are assessed in different case studies. Simulation results reveal that the proposed controller can improve the FRT capability.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegría IM, Andreu J, Martín JL, Ibañez P, Villate JL, Camblong H (2007) Connection requirements for wind farms: a survey on technical requirements and regulation. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11(8):1858–1872
Calderaro V, Galdi V, Piccolo A, Siano P (2008) A fuzzy controller for maximum energy extraction from variable speed wind power generation systems. Electr Power Syst Res 78(6):1109–1118
Carrasco JM, Franquelo LG, Bialasiewicz JT, Galvan E, Guisado RCP (2006) Power-electronic systems for the grid integration of renewable energy sources: a survey. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 53(4):1002–1016
E.ON Netz GmbH (2008) Requirements for offshore grid connections in the E.ON Netz Network, Bayreuth
European Commission (2006) European smart grids technology platform: vision and strategy for Europe’s electricity networks of the future, pp 1–44. ISBN 92-79-01414-5. http://www.smartgrids.eu/documents/vision.pdf
Feltes C, Wrede H, Koch FW, Erlich I (2009) Enhanced fault ride-through method for wind farms connected to the grid through VSC-based HVDC transmission. IEEE Trans Power Syst 24(3):1537–1546
Galdi V, Piccolo A, Siano P (2008) Designing an adaptive fuzzy controller for maximum wind energy extraction. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 23(2):559–569
Galdi V, Piccolo A, Siano P (2009) Exploiting maximum energy from variable speed wind power generation systems by using an adaptive Takagi–Sugeno-Kang fuzzy model. Energy Convers Manage 50(2):413–421
Gao W, Wang G, Ning J (2009) Development of low voltage ride through control strategy for wind power generation using real time digital simulator. In: IEEE Power system conference and exposition, 15–18 March, p 1–6
Grid code for TNO (2004) (Arreˆte′ du Gouvernement wallon relatif a` la re′ vision du re`glement technique pour la gestion du re′seau de transport local d’e′ lectricite′ en Re′gion wallonne et l’acce`s a` celui-ci)’
Hatta H, Kobayashi H (2007) A study of centralized voltage control method for distribution system with distributed generation. In: CIRED 19th International Conference on Electricity Distribution, Vienna, pp1–4. http://www.winddata.com
Hu J, He Y, Xu L, Williams BW (2009) Improved control of DFIG systems during network unbalance using PI-R current regulators. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(2):439–451
Karimi-Davijani H, Sheikholeslami A, Livani H, Karimi-Davijani M (2009) Fuzzy logic control of doubly fed induction generator wind turbine. World Appl Sci J 6(4):499–508
Mathwork (2009) SimPower system Toolbox of MATLAB. http://www.mathworks.com
Nordic grid code (2007) Nordel (Nordic Connections of rules), pp.1–189
Regulation TF 3.2.6 (2004) Grid connection of wind turbines to networks with voltages below 100 kV, Energinet, Denmark
Tande JOG (2000) Exploitation of wind-energy resources in proximity to weak electric grids. Appl Energy 65(1):395–401
Tapia A, Tapia G, Ostolaza JX, Saenz JR (2003) Modeling and control of a wind driven doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 18(2):194–200
Walloon Energy Commission (2007) Commission Wallone pour l’ Energie-CWaPE. Wallonia, Belgium
Yao J, Li H, Liao Y, Chen Z (2008) An improved control strategy of limiting the DC-link voltage fluctuation for a Doubly fed induction wind generator. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(8):1205–1213
Zhan C, Barker C (2006) Fault ride-through capability investigation of a doubly-fed induction generator with an additional series-connected voltage source converter. In: Proceedings 8th IEE Int. Conf. AC and DC power transmission, AC/DC, pp 79–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokryani, G., Siano, P. & Piccolo, A. Fault ride-through enhancement of wind turbines in distribution networks. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 4, 605–611 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-012-0162-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-012-0162-7